[ad_1]

Last yr we offered outcomes demonstrating {that a} deep studying system (DLS) may be educated to investigate exterior eye pictures and predict an individual’s diabetic retinal illness standing and elevated glycated hemoglobin (or HbA1c, a biomarker that signifies the three-month common stage of blood glucose). It was beforehand unknown that exterior eye pictures contained indicators for these circumstances. This thrilling discovering recommended the potential to scale back the necessity for specialised tools since such pictures may be captured utilizing smartphones and different shopper gadgets. Encouraged by these findings, we got down to uncover what different biomarkers may be discovered on this imaging modality.
In “A deep learning model for novel systemic biomarkers in photos of the external eye: a retrospective study”, printed in Lancet Digital Health, we present that quite a few systemic biomarkers spanning a number of organ programs (e.g., kidney, blood, liver) may be predicted from exterior eye pictures with an accuracy surpassing that of a baseline logistic regression mannequin that makes use of solely clinicodemographic variables, corresponding to age and years with diabetes. The comparability with a clinicodemographic baseline is beneficial as a result of danger for some ailments is also assessed utilizing a easy questionnaire, and we search to grasp if the mannequin decoding photos is doing higher. This work is within the early phases, however it has the potential to extend entry to illness detection and monitoring by new non-invasive care pathways.
 |
| A mannequin producing predictions for an exterior eye photograph. |
Model improvement and analysis
To develop our mannequin, we labored with companions at EyePACS and the Los Angeles County Department of Health Services to create a retrospective de-identified dataset of exterior eye pictures and measurements within the type of laboratory assessments and very important indicators (e.g., blood strain). We filtered all the way down to 31 lab assessments and vitals that have been extra generally out there on this dataset after which educated a multi-task DLS with a classification “head” for every lab and very important to foretell abnormalities in these measurements.
Importantly, evaluating the efficiency of many abnormalities in parallel may be problematic due to a better likelihood of discovering a spurious and inaccurate outcome (i.e., because of the a number of comparisons downside). To mitigate this, we first evaluated the mannequin on a portion of our improvement dataset. Then, we narrowed the checklist all the way down to the 9 most promising prediction duties and evaluated the mannequin on our check datasets whereas correcting for a number of comparisons. Specifically, these 9 duties, their related anatomy, and their significance for related ailments are listed within the desk beneath.
| Prediction activity | Organ system | Significance for related ailments | ||||||
| Albumin < 3.5 g/dL | Liver/Kidney | Indication of hypoalbuminemia, which may be because of decreased manufacturing of albumin from liver illness or elevated lack of albumin from kidney illness. | ||||||
| AST > 36.0 U/L | Liver |
Indication of liver illness (i.e., harm to the liver or biliary obstruction), generally attributable to viral infections, alcohol use, and weight problems. |
||||||
| Calcium < 8.6 mg/dL | Bone / Mineral | Indication of hypocalcemia, which is mostly attributable to vitamin D deficiency or parathyroid problems. | ||||||
| eGFR < 60.0 mL/min/1.73 m2 | Kidney |
Indication of continual kidney illness, mostly because of diabetes and hypertension. |
||||||
| Hgb < 11.0 g/dL | Blood rely | Indication of anemia which can be because of blood loss, continual medical circumstances, or poor eating regimen. | ||||||
| Platelet < 150.0 103/µL | Blood rely |
Indication of thrombocytopenia, which may be because of decreased manufacturing of platelets from bone marrow problems, corresponding to leukemia or lymphoma, or elevated destruction of platelets because of autoimmune illness or medicine unwanted effects. |
||||||
| TSH > 4.0 mU/L | Thyroid | Indication of hypothyroidism, which impacts metabolism and may be attributable to many various circumstances. | ||||||
| Urine albumin/creatinine ratio (ACR) ≥ 300.0 mg/g | Kidney |
Indication of continual kidney illness, mostly because of diabetes and hypertension. |
||||||
| WBC < 4.0 103/µL | Blood rely | Indication of leukopenia which may have an effect on the physique’s capability to combat an infection. |
Key outcomes
As in our earlier work, we in contrast our exterior eye mannequin to a baseline mannequin (a logistic regression mannequin taking clinicodemographic variables as enter) by computing the space beneath the receiver operator curve (AUC). The AUC ranges from 0 to 100%, with 50% indicating random efficiency and better values indicating higher efficiency. For all however one of many 9 prediction duties, our mannequin statistically outperformed the baseline mannequin. In phrases of absolute efficiency, the mannequin’s AUCs ranged from 62% to 88%. While these ranges of accuracy are seemingly inadequate for diagnostic purposes, it’s consistent with different preliminary screening instruments, like mammography and pre-screening for diabetes, used to assist determine people who could profit from extra testing. And as a non-invasive accessible modality, taking pictures of the exterior eye could provide the potential to assist display screen and triage sufferers for confirmatory blood assessments or different scientific follow-up.
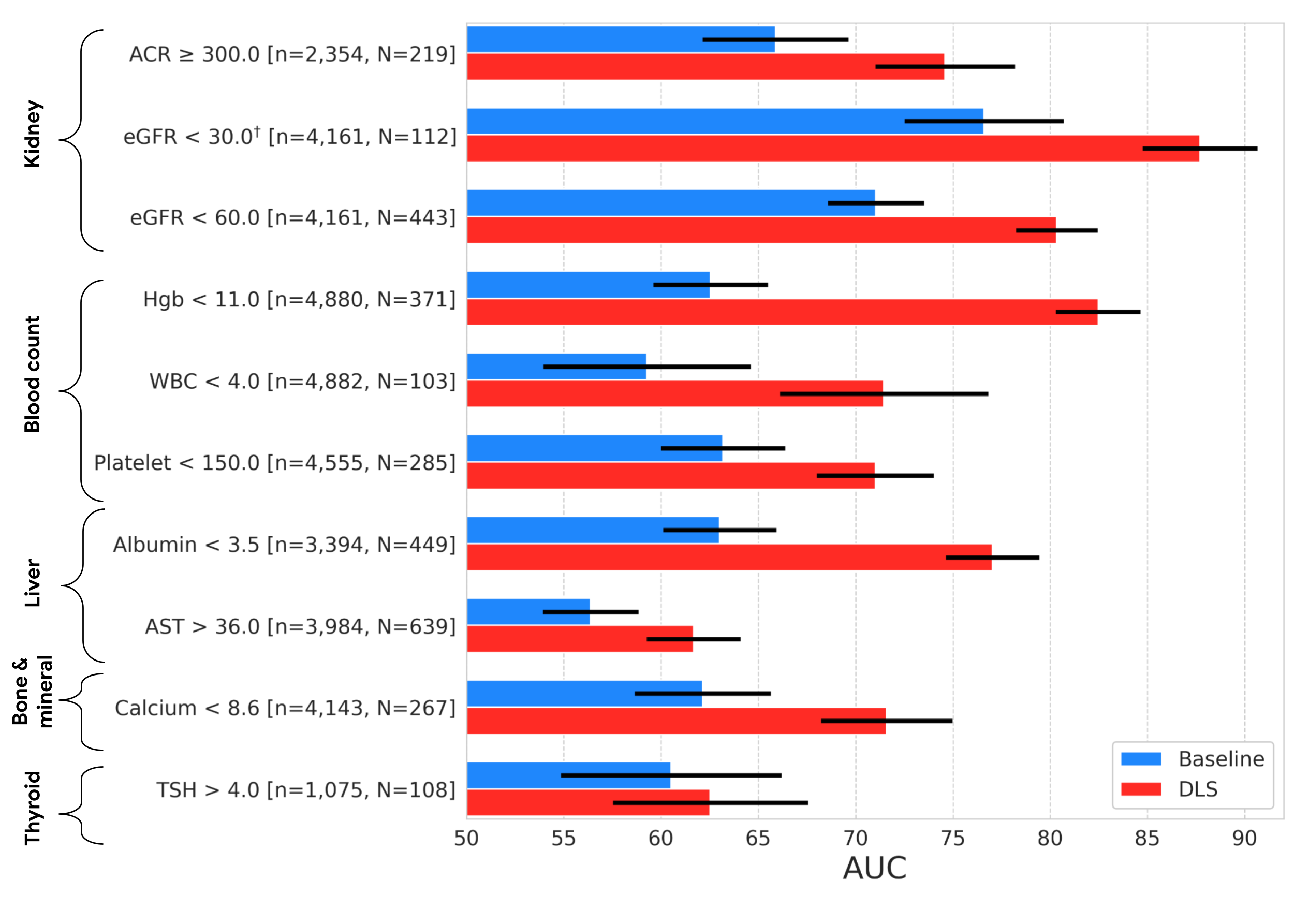 |
| Results on the EyePACS check set, displaying AUC efficiency of our DLS in comparison with a baseline mannequin. The variable “n” refers back to the complete variety of datapoints, and “N” refers back to the variety of positives. Error bars present 95% confidence intervals computed utilizing the DeLong methodology. †Indicates that the goal was pre-specified as secondary evaluation; all others have been pre-specified as major evaluation. |
The exterior eye pictures utilized in each this and the prior examine have been collected utilizing desk prime cameras that embrace a head relaxation for affected person stabilization and produce top quality photos with good lighting. Since picture high quality could also be worse in different settings, we needed to discover to what extent the DLS mannequin is powerful to high quality adjustments, beginning with picture decision. Specifically, we scaled the photographs within the dataset all the way down to a spread of sizes, and measured efficiency of the DLS when retrained to deal with the downsampled photos.
Below we present a collection of the outcomes of this experiment (see the paper for extra full outcomes). These outcomes display that the DLS is pretty sturdy and, most often, outperforms the baseline mannequin even when the photographs are scaled all the way down to 150×150 pixels. This pixel rely is beneath 0.1 megapixels, a lot smaller than the everyday smartphone digital camera.
 |
| Effect of enter picture decision. Top: Sample photos scaled to completely different sizes for this experiment. Bottom: Comparison of the efficiency of the DLS (pink) educated and evaluated on completely different picture sizes and the baseline mannequin (blue). Shaded areas present 95% confidence intervals computed utilizing the DeLong methodology. |
Conclusion and future instructions
Our earlier analysis demonstrated the promise of the exterior eye modality. In this work, we carried out a extra exhaustive search to determine the doable systemic biomarkers that may be predicted from these pictures. Though these outcomes are promising, many steps stay to find out whether or not expertise like this can assist sufferers in the actual world. In specific, as we point out above, the imagery in our research have been collected utilizing giant tabletop cameras in a setting that managed elements corresponding to lighting and head positioning. Furthermore, the datasets used on this work consist primarily of sufferers with diabetes and didn’t have enough illustration of quite a few vital subgroups – extra targeted information assortment for DLS refinement and analysis on a extra basic inhabitants and throughout subgroups might be wanted earlier than contemplating scientific use.
We are excited to discover how these fashions generalize to smartphone imagery given the potential attain and scale that this permits for the expertise. To this finish, we’re persevering with to work with our co-authors at accomplice establishments like Chang Gung Memorial Hospital in Taiwan, Aravind Eye Hospital in India, and EyePACS within the United States to gather datasets of images captured on smartphones. Our early outcomes are promising and we stay up for sharing extra sooner or later.
Acknowledgements
This work concerned the efforts of a multidisciplinary workforce of software program engineers, researchers, clinicians and cross useful contributors. Key contributors to this mission embrace: Boris Babenko, Ilana Traynis, Christina Chen, Preeti Singh, Akib Uddin, Jorge Cuadros, Lauren P. Daskivich, April Y. Maa, Ramasamy Kim, Eugene Yu-Chuan Kang, Yossi Matias, Greg S. Corrado, Lily Peng, Dale R. Webster, Christopher Semturs, Jonathan Krause, Avinash V Varadarajan, Naama Hammel and Yun Liu. We additionally thank Dave Steiner, Yuan Liu, and Michael Howell for his or her suggestions on the manuscript; Amit Talreja for reviewing code for the paper; Elvia Figueroa and the Los Angeles County Department of Health Services Teleretinal Diabetic Retinopathy Screening program employees for information assortment and program help; Andrea Limon and Nikhil Kookkiri for EyePACS information assortment and help; Dr. Charles Demosthenes for extracting the info and Peter Kuzmak for getting photos for the VA information. Last however not least, a particular due to Tom Small for the animation used on this weblog publish.
