[ad_1]
The Zerobot DDoS botnet has acquired substantial updates that increase on its capability to focus on extra internet-connected gadgets and scale its community.
Microsoft Threat Intelligence Center (MSTIC) is monitoring the continuing menace beneath the moniker DEV-1061, its designation for unknown, rising, or growing exercise clusters.
Zerobot, first documented by Fortinet FortiGuard Labs earlier this month, is a Go-based malware that propagates via vulnerabilities in net functions and IoT gadgets like firewalls, routers, and cameras.
“The most up-to-date distribution of Zerobot contains further capabilities, reminiscent of exploiting vulnerabilities in Apache and Apache Spark (CVE-2021-42013 and CVE-2022-33891 respectively), and new DDoS assault capabilities,” Microsoft researchers stated.
Also referred to as ZeroStresser by its operators, the malware is obtainable as a DDoS-for-hire service to different prison actors, with the botnet marketed on the market on varied social media networks.
Microsoft stated that one area with connections to Zerobot – zerostresser[.]com – was among the many 48 domains that had been seized by the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) this month for providing DDoS assault options to paying clients.
The newest model of Zerobot noticed by Microsoft not solely targets unpatched and improperly secured gadgets, but in addition makes an attempt to brute-force over SSH and Telnet on ports 23 and 2323 for spreading to different hosts.
The checklist of newly added recognized flaws exploited by Zerobot 1.1 is as follows –
- CVE-2017-17105 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – A command injection vulnerability in Zivif PR115-204-P-RS
- CVE-2019-10655 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – An unauthenticated distant code execution vulnerability in Grandstream GAC2500, GXP2200, GVC3202, GXV3275, and GXV3240
- CVE-2020-25223 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – A distant code execution vulnerability within the WebAdmin of Sophos SG UTM
- CVE-2021-42013 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – A distant code execution vulnerability in Apache HTTP Server
- CVE-2022-31137 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – A distant code execution vulnerability in Roxy-WI
- CVE-2022-33891 (CVSS rating: 8.8) – An unauthenticated command injection vulnerability in Apache Spark
- ZSL-2022-5717 (CVSS rating: N/A) – A distant root command injection vulnerability in MiniDVBLinux
Upon profitable an infection, the assault chain proceeds to obtain a binary named “zero” for a particular CPU structure that permits it to self-propagate to extra prone programs uncovered on-line.
Additionally, Zerobot is claimed to proliferate by scanning and compromising gadgets with recognized vulnerabilities that aren’t included within the malware executable, reminiscent of CVE-2022-30023, a command injection vulnerability in Tenda GPON AC1200 routers.
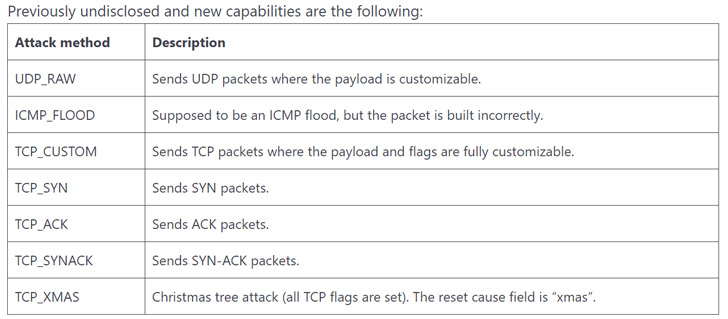
Zerobot 1.1 additional incorporates seven new DDoS assault strategies by making use of protocols reminiscent of UDP, ICMP, and TCP, indicating “steady evolution and fast addition of latest capabilities.”
“The shift towards malware as a service within the cyber economic system has industrialized assaults and has made it simpler for attackers to buy and use malware, set up and keep entry to compromised networks, and make the most of ready-made instruments to carry out their assaults,” the tech large stated.
[ad_2]