[ad_1]

Hackers have been exploiting a now-patched vulnerability in VMware Workspace ONE Access in campaigns to put in varied ransomware and cryptocurrency miners, a researcher at safety agency Fortinet mentioned on Thursday.
CVE-2022-22954 is a distant code execution vulnerability in VMware Workspace ONE Access that carries a severity score of 9.8 out of a attainable 10. VMware disclosed and patched the vulnerability on April 6. Within 48 hours, hackers reverse-engineered the replace and developed a working exploit that they then used to compromise servers that had but to put in the repair. VMware Workspace ONE entry helps directors configure a collection of apps staff want of their work environments.
In August, researchers at Fortiguard Labs noticed a sudden spike in exploit makes an attempt and a serious shift in techniques. Whereas earlier than the hackers put in payloads that harvested passwords and picked up different information, the brand new surge introduced one thing else—particularly, ransomware generally known as RAR1ransom, a cryptocurrency miner generally known as GuardMiner, and Mirai, software program that corrals Linux gadgets into a large botnet to be used in distributed denial-of-service assaults.
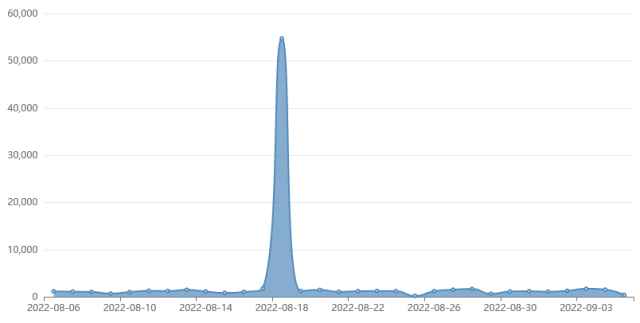
FortiGuard
“Although the critical vulnerability CVE-2022-22954 is already patched in April, there are still multiple malware campaigns trying to exploit it,” Fortiguard Labs researcher Cara Lin wrote. Attackers, she added, had been utilizing it to inject a payload and obtain distant code execution on servers working the product.
The Mirai pattern Lin noticed getting put in was downloaded from http[:]//107[.]189[.]8[.]21/pedalcheta/cutie[.]x86_64 and relied on a command and management server at “cnc[.]goodpackets[.]cc. Besides delivering junk site visitors utilized in DDoSes, the pattern additionally tried to contaminate different gadgets by guessing the executive password they used. After decoding strings within the code, Lin discovered the next listing of credentials the malware used:
|
hikvision |
1234 |
win1dows |
S2fGqNFs |
|
root |
tsgoingon |
newsheen |
12345 |
|
default |
solokey |
neworange88888888 |
visitor |
|
bin |
consumer |
neworang |
system |
|
059AnkJ |
telnetadmin |
tlJwpbo6 |
iwkb |
|
141388 |
123456 |
20150602 |
00000000 |
|
adaptec |
20080826 |
vstarcam2015 |
v2mprt |
|
Administrator |
1001chin |
vhd1206 |
assist |
|
NULL |
xc3511 |
QwestM0dem |
7ujMko0admin |
|
bbsd-client |
vizxv |
fidel123 |
dvr2580222 |
|
par0t |
hg2x0 |
samsung |
t0talc0ntr0l4! |
|
cablecom |
hunt5759 |
epicrouter |
zlxx |
|
pointofsale |
nflection |
admin@mimifi |
xmhdipc |
|
icatch99 |
password |
daemon |
netopia |
|
3com |
DOCSIS_APP |
hagpolm1 |
klv123 |
|
OxhlwSG8 |
In what seems to be a separate marketing campaign, attackers additionally exploited CVE-2022-22954 to obtain a payload from 67[.]205[.]145[.]142. The payload included seven information:
- phpupdate.exe: Xmrig Monero mining software program
- config.json: Configuration file for mining swimming pools
- networkmanager.exe: Executable used to scan and unfold an infection
- phpguard.exe: Executable used for guardian Xmrig miner to maintain working
- init.ps1: Script file itself to maintain persistence through creating scheduled process
- clear.bat: Script file to take away different cryptominers on the compromised host
- encrypt.exe: RAR1 ransomware
In the occasion RAR1ransom has by no means been put in earlier than, the payload would first run the encrypt.exe executable file. The file drops the reputable WinRAR information compression executable in a short lived Windows folder. The ransomware then makes use of WinRAR to compress consumer information into password-protected information.
The payload would then begin the GuardMiner assault. GuardMiner is a cross-platform mining Trojan for the Monero foreign money. It has been lively since 2020.
The assaults underscore the significance of putting in safety updates in a well timed method. Anyone who has but to put in VMware’s April 6 patch ought to accomplish that without delay.
[ad_2]
