[ad_1]

By now, everyone ought to be utilizing a password that appears like, properly, gibberish — one thing like s;3HiMom!&%ok#$l. Actually, given the rising sophistication of attackers, that one may quickly be a couple of characters wanting offering actual safety.
SEE: Password breach: Why popular culture and passwords don’t combine (free PDF) (TechRepublic)
With instruments like password sprayers simply obtainable to malefactors, it’s time to take a look at what you and your organization ought to completely not be utilizing as the important thing to your accounts and your group’s knowledge trove.
Jump to:
The world’s commonest passwords
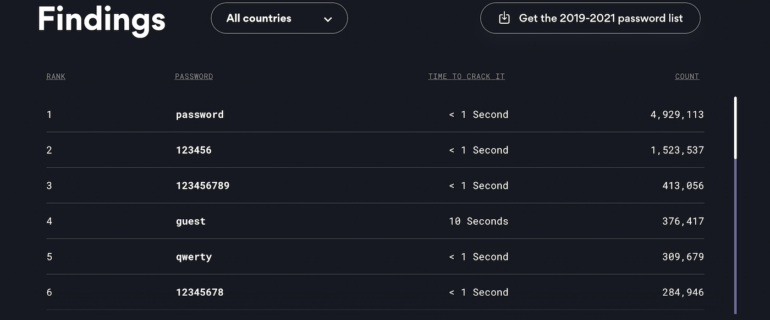
Thankfully, password supervisor NordPass is out with its annual rating of the world’s 200 commonest passwords. Heading up this yr’s invidious class is, you guessed it, “password.” Beating out 2021 and 2020’s winner is “123456.” This might look unhealthy, however there may be some enchancment: In 2019, it was “12345.”
SEE: Improper use of password managers leaves folks weak to id theft (TechRepublic)
The NordPass record parses passwords by nation, gender and issues like the common time it takes to crack them. In the U.S., the most typical password of 2022 was “guest” with “password” coming in fourth place. “12345” and “123456” are additionally on the record.
Additionally, the rating contains an estimate of the time it could take to crack most of those codes, which was beneath one second. Number 9 on the worldwide record, “col123456,” would take a whopping 11 seconds to hack. Worldwide, the opposite most used passwords included “qwerty,” “guest,” and “111111” (Figure A).
Figure A
How NordPass performed the research
Karolis Arbaciauskas, head of enterprise improvement at NordPass, defined that the corporate partnered with impartial researchers, who discovered a 3TB dimension database filled with leaked passwords, which he described as “a solid basis to evaluate which passwords are, year after year, putting people in danger online.”
He mentioned “password” was discovered over 4.9 million instances within the database and that in comparison with the info from 2021, 73% of the 200 commonest passwords in 2022 stay the identical.
“Since we know these passwords appeared among leaked ones, we would avoid many cybersecurity incidents if people stopped using them,” Arbaciauskas mentioned.
Poor password hygiene is a widespread drawback
Carl Kriebel, shareholder of cybersecurity consulting providers at international accounting agency Schneider Downs, mentioned poor passwords are certainly a ubiquitous drawback.
“In the 75 or so penetration tests we do per year, passwords are consistently the weak link in the chain more often than not,” he mentioned, including that though protocols like fry/fail lockouts might solely lengthen the time attackers have to infiltrate, that makes a distinction.
“Like everyone else, attackers are measuring ROI, including time,” Kriebel added.
Ready entry to issues like password spraying know-how reduces that point to just about zero for accounts with frequent codes and simply guessable passwords, so remediating that problem throughout an establishment is the primary order of effort, he famous.
SEE: Best penetration testing instruments: 2022 purchaser’s information (TechRepublic)
“If we can quickly password spray our way in, then obviously there’s a policy problem,” Kriebel mentioned. “Every organization should have try/fails and then lock the password — even for an hour.”
This May, NordPass introduced a research on the passwords enterprise executives use to safe their accounts, and final yr, its researchers investigated passwords leaked from Fortune 500 firms.
Secure your knowledge in accordance with these tips
At this level few firms ought to be utilizing single-factor authentication.
“We highly encourage remote access multi-factor capability,” Kriebel mentioned. “If not, or if an organization has a broad-based network where applications are multifaceted with numerous entry points, our recommendation is instituting a standardized policy for password setting with a far higher threshold.”
Additional safety suggestions to your group
- Change passwords, rotate them and reset them on a daily cadence.
- Use passphrases — not passwords.
- Companies ought to do danger dialogue about how the group ought to embrace insurance policies round passwords; don’t simply put the onus on the CIO.
- Implement password blacklists.
- Every firm ought to have some type of attempt/fail password locking.
Eight characters is seven too few
Kriebel mentioned establishments have to advocate for advanced passwords — not simply by rising the combination of characters, symbols and numbers, however by rising the character rely too. Many folks nonetheless use simply eight characters, however that’s nowhere close to sufficient, he mentioned.
While advocating for implementation of 15 character passwords, Kriebel concedes that formalizing stronger insurance policies requires a specific amount of organizational fortitude, as a result of firms don’t need to be burdensome to the purpose at which individuals push again.
“Even simply adding characters makes it exponentially more difficult to hack passwords,” Kriebel added.
Passphrases are higher than alphabet soup
Even higher: Passphrases, even apparently apparent ones, are extraordinarily tough to hack. Kriebel mentioned that even with the instruments hackers at present have at their disposal even one thing so simple as “Mary had a little lamb” is tough to crack.
“If you make a very simple alteration to that phrase, removing the space between ‘a’ and ‘little,’ for example, the passphrase becomes almost impossible to crack,” Kriebel mentioned.
Kriebel recommends firms transfer to acquire password blacklists and make prohibition of their use a part of their safety coverage, which is a more moderen improvement in defensive techniques. Further, organizations ought to be sure these lists don’t include merely generic, frequent passwords, but in addition these with cognitive connections round apparent issues like an organization’s location.
Arbaciauskas mentioned a multiple-step method is the important thing to organizational safety. Businesses have to set cybersecurity insurance policies of their group, have specialists answerable for their implementation and hold the staff educated concerning the cybersecurity dangers confronted. Companies additionally want fashionable technological instruments to assist safe accounts.
“Password managers allow not only secure password storing but also sharing among employees,” Arbaciauskas mentioned.
Password era instruments supplied by many password managers robotically create sturdy and distinctive passwords consisting of random mixtures of letters, numbers and symbols.
“By using password managers, companies prevent themselves from human mistakes — the creation of easy passwords and their reuse,” Arbaciauskas added.
To study greatest practices to strengthen your password safety protocols, obtain Password administration coverage (TechRepublic Premium).
[ad_2]
