[ad_1]
The risk actor behind a distant entry trojan referred to as RomCom RAT has been noticed concentrating on Ukrainian army establishments as a part of a brand new spear-phishing marketing campaign that commenced on October 21, 2022.
The improvement marks a shift within the attacker’s modus operandi, which has been beforehand attributed to spoofing reliable apps like Advanced IP Scanner and pdfFiller to drop backdoors on compromised methods.
“The preliminary ‘Advanced IP Scanner’ marketing campaign occurred on July 23, 2022,” the BlackBerry analysis and intelligence group mentioned. “Once the sufferer installs a Trojanized bundle, it drops RomCom RAT to the system.”
While earlier iterations of the marketing campaign concerned using trojanized Advanced IP Scanner, the unidentified adversarial collective has since switched to pdfFiller as of October 20, indicating an lively try on a part of the adversary to refine ways and thwart detection.
These lookalike web sites host a rogue installer package deal that leads to the deployment of the RomCom RAT, which is able to harvesting data and capturing screenshots, all of which is exported to a distant server.
The adversary’s newest exercise directed in opposition to the Ukrainian army is a departure in that it employs a phishing e-mail with an embedded hyperlink as an preliminary an infection vector, resulting in a faux web site dropping the subsequent stage downloader.
This downloader, signed utilizing a legitimate digital certificates from “Blythe Consulting sp. z o.o.” for an additional layer of evasion, is then used to extract and run the RomCom RAT malware. BlackBerry mentioned the identical signer is utilized by the reliable model of pdfFiller.
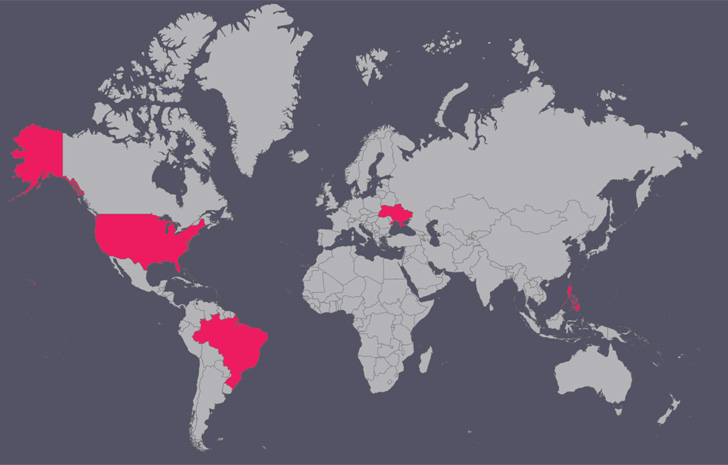
Besides the Ukrainian army, different targets of the marketing campaign embrace IT corporations, meals brokers, and meals manufacturing entities within the U.S., Brazil, and the Philippines.
“This marketing campaign is an effective instance of the blurred line between cybercrime-motivated risk actors and focused assault risk actors,” Dmitry Bestuzhev, risk researcher at BlackBerry, instructed The Hacker News.
“In the previous, each teams acted independently, counting on totally different tooling. Today, focused assault risk actors rely extra on conventional tooling, making attribution more durable.”