[ad_1]
A current paper by Ben et al. (2023) offers an R tutorial for implementing financial evaluations–usually value effectiveness analyses–utilizing information from medical trials and analyzed utilizing R. The article begins by offering a summaries of key points researchers face when conducting these financial evaluations:
- Missing values. Missing information are widespread in medical trials both attributable to disenrollment, restricted follow-up, or non-response. What are some strategies to deal with this? The authors write: “Naïve methods, such as mean imputation of missing values and last observation carried forward, are discouraged because they do not account for the uncertainty in the imputed observations. More robust methods for handling missing and/or censored data are multiple imputation (MI), inverse probability weighting (IPW), likelihood-based models and Bayesian models. Of them, MI is most frequently used and is a valid method when missing data are related to observed data (e.g. missing at random, MAR) in economic evaluations.” The related R package deal for MI is mice.
- Skewed information. Cost information is usually right-skewed with most observations across the median however a non-trivial quantity of very excessive value outliers. The authors cite a scoping assessment (El Alili et al. 2022) and state that acceptable strategies to deal with skewed value information embrace: “non-parametric bootstrapping, generalized linear models (GLM), hurdle models and Bayesian models with a gamma distribution.”
- Correlated prices and results. Sometimes, remedy results could also be correlated (positively or negatively) with prices. Approaches to deal with correlated prices and results, embrace “seemingly unrelated regressions (SUR), bootstrapping costs and effects in pairs, and Bayesian bivariate models.”
- Baseline imbalances in trial traits. Even when people are randomized in a trial, randomization could also be imperfect and trial traits could also be imbalanced. Some approaches to deal with these variations embrace: embrace regression-based adjustment, propensity rating adjustment and matching.
Here is a few pattern code for implementing every of the 4 approaches.
Missing values. The related R package deal for MI is mice.
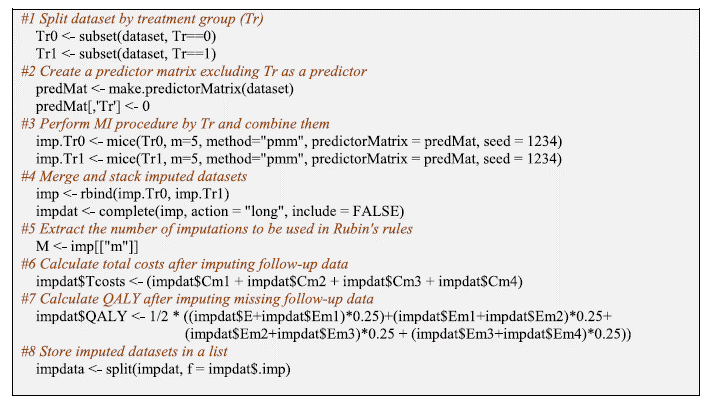
Addressing skewed information and correlated prices with bootstrapping and seemingly unrelated regressions (SUR) methodology. The authors use the boot operate offered by the boot R Package. The boot operate is used to resample the information and for every bootstrap pattern a SUR mannequin is match utilizing the systemfit operate. [The authors note that rather than using SUR, a linear mixed model (LMM) could be fit instead using the lme4 or nlme R packages].
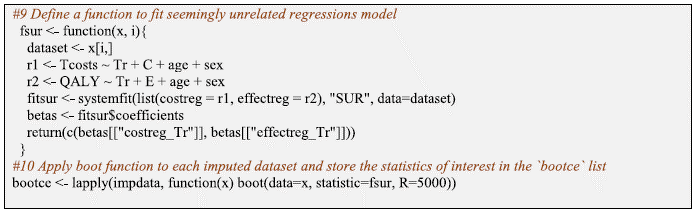
Then one can extract related statistics of curiosity as follows:

Additional directions are given on how one can create a cost-effectiveness aircraft and cost-effectiveness acceptability curve. You can learn the complete article right here.
[ad_2]
