[ad_1]
Diffusion fashions have lately emerged because the de facto normal for producing complicated, high-dimensional outputs. You might know them for his or her potential to provide beautiful AI artwork and hyper-realistic artificial pictures, however they’ve additionally discovered success in different functions akin to drug design and continuous management. The key thought behind diffusion fashions is to iteratively remodel random noise right into a pattern, akin to a picture or protein construction. This is usually motivated as a most probability estimation downside, the place the mannequin is skilled to generate samples that match the coaching knowledge as intently as potential.
However, most use circumstances of diffusion fashions will not be straight involved with matching the coaching knowledge, however as a substitute with a downstream goal. We don’t simply need a picture that appears like current pictures, however one which has a particular kind of look; we don’t simply need a drug molecule that’s bodily believable, however one that’s as efficient as potential. In this put up, we present how diffusion fashions may be skilled on these downstream targets straight utilizing reinforcement studying (RL). To do that, we finetune Stable Diffusion on a wide range of targets, together with picture compressibility, human-perceived aesthetic high quality, and prompt-image alignment. The final of those targets makes use of suggestions from a big vision-language mannequin to enhance the mannequin’s efficiency on uncommon prompts, demonstrating how highly effective AI fashions can be utilized to enhance one another with none people within the loop.
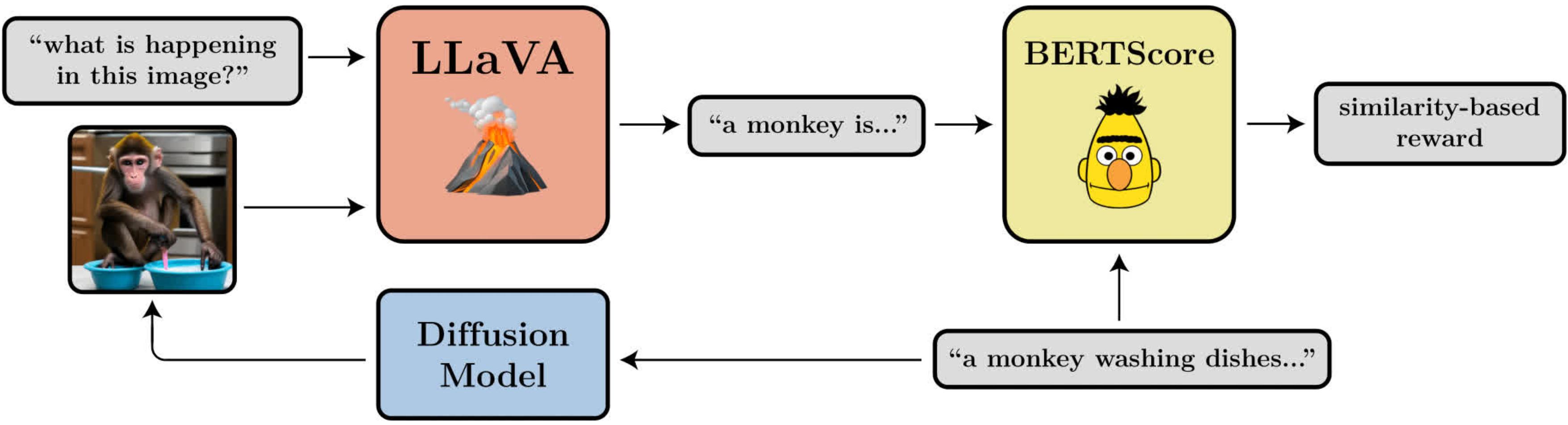
A diagram illustrating the prompt-image alignment goal. It makes use of LLaVA, a big vision-language mannequin, to judge generated pictures.
Denoising Diffusion Policy Optimization
When turning diffusion into an RL downside, we make solely essentially the most primary assumption: given a pattern (e.g. a picture), we now have entry to a reward perform that we will consider to inform us how “good” that pattern is. Our objective is for the diffusion mannequin to generate samples that maximize this reward perform.
Diffusion fashions are sometimes skilled utilizing a loss perform derived from most probability estimation (MLE), which means they’re inspired to generate samples that make the coaching knowledge look extra doubtless. In the RL setting, we now not have coaching knowledge, solely samples from the diffusion mannequin and their related rewards. One manner we will nonetheless use the identical MLE-motivated loss perform is by treating the samples as coaching knowledge and incorporating the rewards by weighting the loss for every pattern by its reward. This offers us an algorithm that we name reward-weighted regression (RWR), after current algorithms from RL literature.
However, there are a couple of issues with this strategy. One is that RWR shouldn’t be a very precise algorithm — it maximizes the reward solely roughly (see Nair et. al., Appendix A). The MLE-inspired loss for diffusion can be not precise and is as a substitute derived utilizing a variational certain on the true probability of every pattern. This signifies that RWR maximizes the reward by means of two ranges of approximation, which we discover considerably hurts its efficiency.
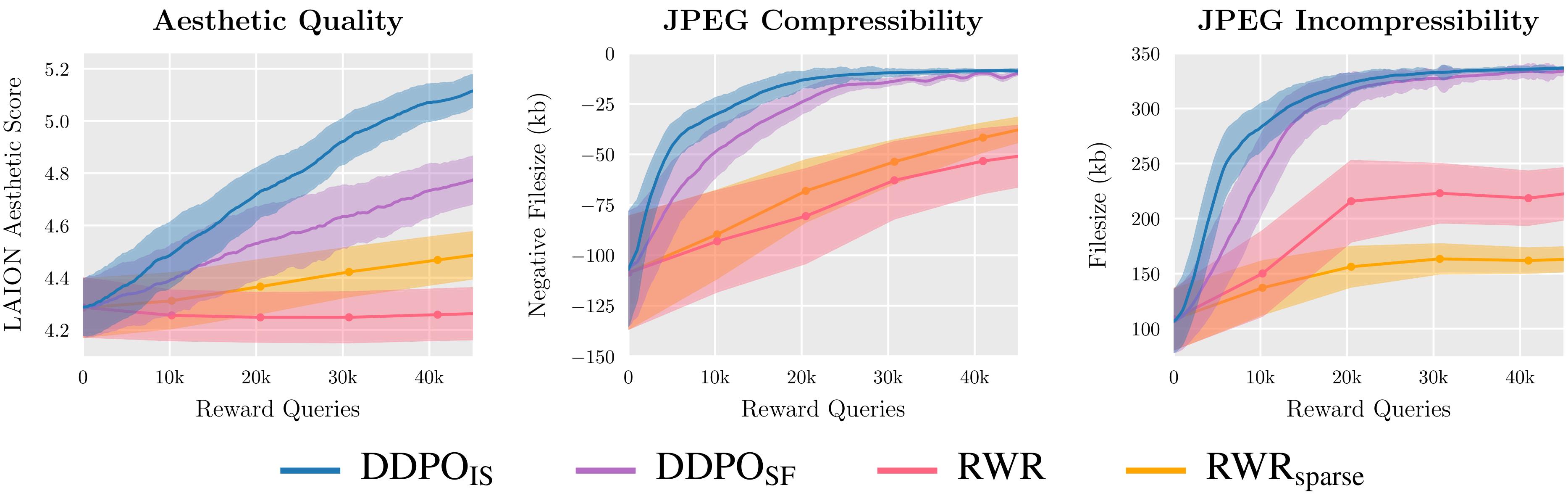
We consider two variants of DDPO and two variants of RWR on three reward capabilities and discover that DDPO constantly achieves the very best efficiency.
The key perception of our algorithm, which we name denoising diffusion coverage optimization (DDPO), is that we will higher maximize the reward of the ultimate pattern if we take note of your entire sequence of denoising steps that received us there. To do that, we reframe the diffusion course of as a multi-step Markov resolution course of (MDP). In MDP terminology: every denoising step is an motion, and the agent solely will get a reward on the ultimate step of every denoising trajectory when the ultimate pattern is produced. This framework permits us to use many highly effective algorithms from RL literature which are designed particularly for multi-step MDPs. Instead of utilizing the approximate probability of the ultimate pattern, these algorithms use the precise probability of every denoising step, which is extraordinarily simple to compute.
We selected to use coverage gradient algorithms as a consequence of their ease of implementation and previous success in language mannequin finetuning. This led to 2 variants of DDPO: DDPOSF, which makes use of the straightforward rating perform estimator of the coverage gradient often known as REINFORCE; and DDPOIS, which makes use of a extra highly effective significance sampled estimator. DDPOIS is our best-performing algorithm and its implementation intently follows that of proximal coverage optimization (PPO).
Finetuning Stable Diffusion Using DDPO
For our foremost outcomes, we finetune Stable Diffusion v1-4 utilizing DDPOIS. We have 4 duties, every outlined by a unique reward perform:
- Compressibility: How simple is the picture to compress utilizing the JPEG algorithm? The reward is the unfavourable file measurement of the picture (in kB) when saved as a JPEG.
- Incompressibility: How laborious is the picture to compress utilizing the JPEG algorithm? The reward is the optimistic file measurement of the picture (in kB) when saved as a JPEG.
- Aesthetic Quality: How aesthetically interesting is the picture to the human eye? The reward is the output of the LAION aesthetic predictor, which is a neural community skilled on human preferences.
- Prompt-Image Alignment: How nicely does the picture signify what was requested for within the immediate? This one is a little more difficult: we feed the picture into LLaVA, ask it to explain the picture, after which compute the similarity between that description and the unique immediate utilizing BERTScore.
Since Stable Diffusion is a text-to-image mannequin, we additionally want to select a set of prompts to present it throughout finetuning. For the primary three duties, we use easy prompts of the shape “a(n) [animal]”. For prompt-image alignment, we use prompts of the shape “a(n) [animal] [activity]”, the place the actions are “washing dishes”, “playing chess”, and “riding a bike”. We discovered that Stable Diffusion usually struggled to provide pictures that matched the immediate for these uncommon situations, leaving loads of room for enchancment with RL finetuning.
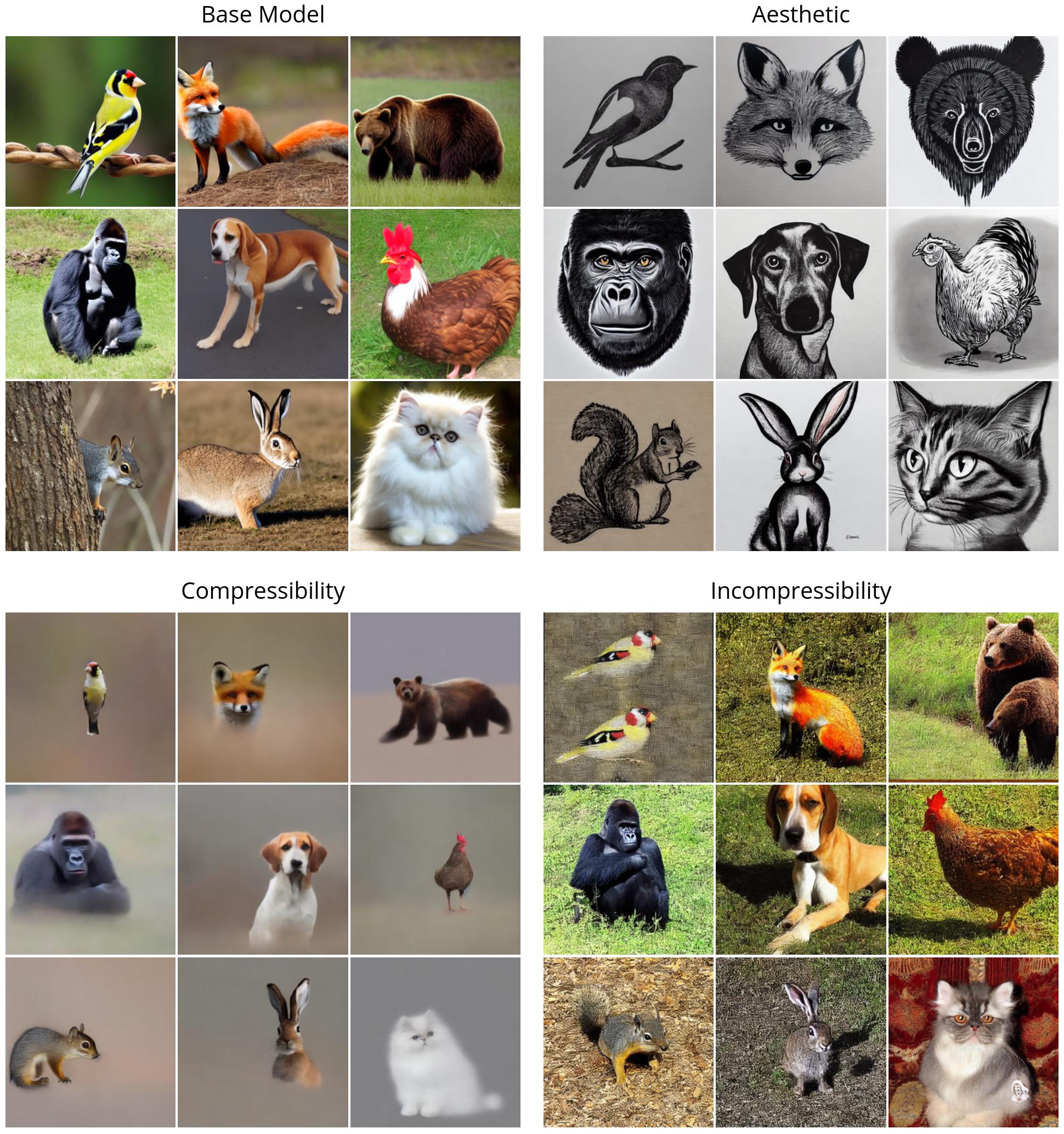
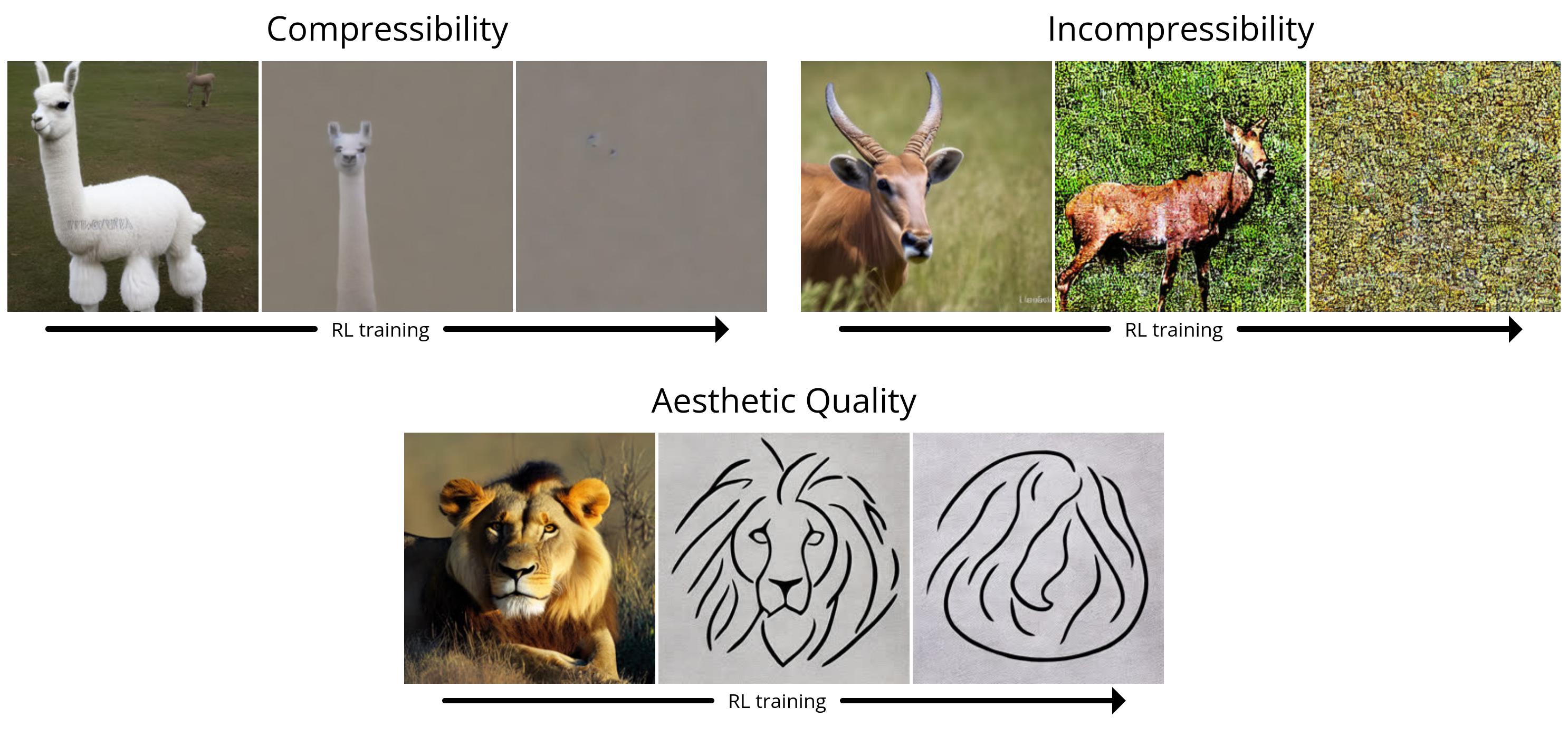
First, we illustrate the efficiency of DDPO on the straightforward rewards (compressibility, incompressibility, and aesthetic high quality). All of the photographs are generated with the identical random seed. In the highest left quadrant, we illustrate what “vanilla” Stable Diffusion generates for 9 completely different animals; the entire RL-finetuned fashions present a transparent qualitative distinction. Interestingly, the aesthetic high quality mannequin (high proper) tends in direction of minimalist black-and-white line drawings, revealing the sorts of pictures that the LAION aesthetic predictor considers “more aesthetic”.

Next, we exhibit DDPO on the extra complicated prompt-image alignment process. Here, we present a number of snapshots from the coaching course of: every sequence of three pictures exhibits samples for a similar immediate and random seed over time, with the primary pattern coming from vanilla Stable Diffusion. Interestingly, the mannequin shifts in direction of a extra cartoon-like type, which was not intentional. We hypothesize that it is because animals doing human-like actions usually tend to seem in a cartoon-like type within the pretraining knowledge, so the mannequin shifts in direction of this type to extra simply align with the immediate by leveraging what it already is aware of.

Unexpected Generalization
Surprising generalization has been discovered to come up when finetuning massive language fashions with RL: for instance, fashions finetuned on instruction-following solely in English usually enhance in different languages. We discover that the identical phenomenon happens with text-to-image diffusion fashions. For instance, our aesthetic high quality mannequin was finetuned utilizing prompts that have been chosen from an inventory of 45 frequent animals. We discover that it generalizes not solely to unseen animals but in addition to on a regular basis objects.

Our prompt-image alignment mannequin used the identical record of 45 frequent animals throughout coaching, and solely three actions. We discover that it generalizes not solely to unseen animals but in addition to unseen actions, and even novel combos of the 2.

Overoptimization
It is well-known that finetuning on a reward perform, particularly a discovered one, can result in reward overoptimization the place the mannequin exploits the reward perform to realize a excessive reward in a non-useful manner. Our setting is not any exception: in all of the duties, the mannequin ultimately destroys any significant picture content material to maximise reward.
We additionally found that LLaVA is inclined to typographic assaults: when optimizing for alignment with respect to prompts of the shape “[n] animals”, DDPO was in a position to efficiently idiot LLaVA by as a substitute producing textual content loosely resembling the right quantity.

There is presently no general-purpose technique for stopping overoptimization, and we spotlight this downside as an necessary space for future work.
Conclusion
Diffusion fashions are laborious to beat in the case of producing complicated, high-dimensional outputs. However, up to now they’ve largely been profitable in functions the place the objective is to study patterns from heaps and many knowledge (for instance, image-caption pairs). What we’ve discovered is a solution to successfully practice diffusion fashions in a manner that goes past pattern-matching — and with out essentially requiring any coaching knowledge. The potentialities are restricted solely by the standard and creativity of your reward perform.
The manner we used DDPO on this work is impressed by the latest successes of language mannequin finetuning. OpenAI’s GPT fashions, like Stable Diffusion, are first skilled on big quantities of Internet knowledge; they’re then finetuned with RL to provide helpful instruments like ChatGPT. Typically, their reward perform is discovered from human preferences, however others have extra lately discovered the right way to produce highly effective chatbots utilizing reward capabilities based mostly on AI suggestions as a substitute. Compared to the chatbot regime, our experiments are small-scale and restricted in scope. But contemplating the big success of this “pretrain + finetune” paradigm in language modeling, it definitely looks like it’s value pursuing additional on the planet of diffusion fashions. We hope that others can construct on our work to enhance massive diffusion fashions, not only for text-to-image technology, however for a lot of thrilling functions akin to video technology, music technology, picture modifying, protein synthesis, robotics, and extra.
Furthermore, the “pretrain + finetune” paradigm shouldn’t be the one manner to make use of DDPO. As lengthy as you may have a very good reward perform, there’s nothing stopping you from coaching with RL from the beginning. While this setting is as-yet unexplored, this can be a place the place the strengths of DDPO may actually shine. Pure RL has lengthy been utilized to all kinds of domains starting from enjoying video games to robotic manipulation to nuclear fusion to chip design. Adding the highly effective expressivity of diffusion fashions to the combo has the potential to take current functions of RL to the subsequent degree — and even to find new ones.
This put up is predicated on the next paper:
If you need to study extra about DDPO, you possibly can try the paper, web site, unique code, or get the mannequin weights on Hugging Face. If you need to use DDPO in your personal undertaking, try my PyTorch + LoRA implementation the place you possibly can finetune Stable Diffusion with lower than 10GB of GPU reminiscence!
If DDPO evokes your work, please cite it with:
@misc{black2023ddpo,
title={Training Diffusion Models with Reinforcement Learning},
creator={Kevin Black and Michael Janner and Yilun Du and Ilya Kostrikov and Sergey Levine},
12 months={2023},
eprint={2305.13301},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG}
}