[ad_1]
A malicious extension for Chromium-based internet browsers has been noticed to be distributed by way of a long-standing Windows info stealer referred to as ViperSoftX.
Czech-based cybersecurity firm dubbed the rogue browser add-on VenomSoftX owing to its standalone options that allow it to entry web site visits, steal credentials and clipboard knowledge, and even swap cryptocurrency addresses by way of an adversary-in-the-middle (AiTM) assault.
ViperSoftX, which first got here to gentle in February 2020, was characterised by Fortinet as a JavaScript-based distant entry trojan and cryptocurrency stealer. The malware’s use of a browser extension to advance its information-gathering targets was documented by Sophos risk analyst Colin Cowie earlier this 12 months.
“This multi-stage stealer displays fascinating hiding capabilities, hid as small PowerShell scripts on a single line in the course of in any other case innocent-looking massive log information, amongst others,” Avast researcher Jan Rubín stated in a technical write-up.
“ViperSoftX focuses on stealing cryptocurrencies, clipboard swapping, fingerprinting the contaminated machine, in addition to downloading and executing arbitrary further payloads, or executing instructions.”
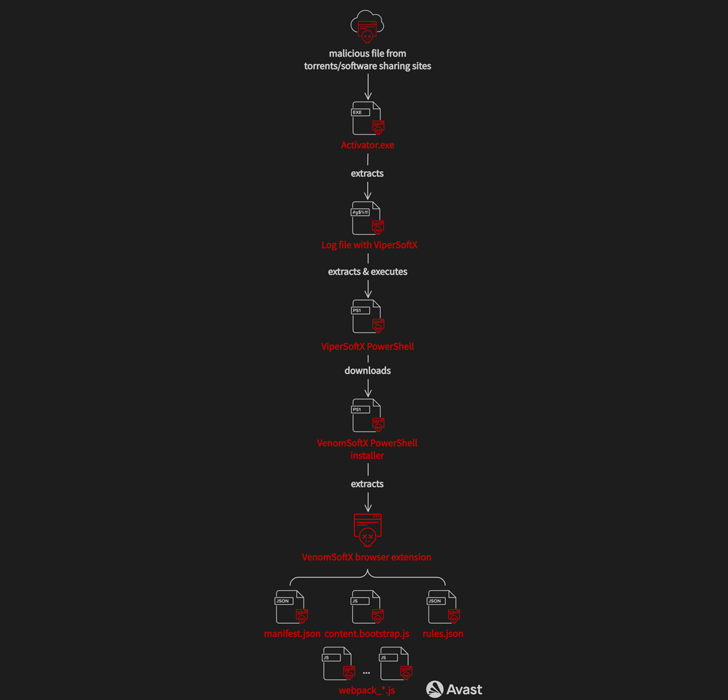
The distribution vector used to propagate ViperSoftX is often achieved by cracked software program for Adobe Illustrator and Microsoft Office which are hosted on file-sharing websites.
The downloaded executable file comes with a clear model of cracked software program together with further information that arrange persistence on the host and harbor the ViperSoftX PowerShell script.
Newer variants of the malware are additionally able to loading the VenomSoftX add-on, which is retrieved from a distant server, to Chromium-based browsers comparable to Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Opera, Brave, and Vivaldi.
This is achieved by trying to find LNK information for the browser purposes and modifying the shortcuts with a “–load-extension” command line swap that factors to the trail the place the unpacked extension is saved.
“The extension tries to disguise itself as well-known and customary browser extensions comparable to Google Sheets,” Rubín defined. “In actuality, the VenomSoftX is yet one more info stealer deployed onto the unsuspecting sufferer with full entry permissions to each web site the consumer visits from the contaminated browser.”
It’s price noting that the –load-extension tactic has additionally been put to make use of by one other browser-based info stealer known as ChromeLoader (aka Choziosi Loader or ChromeAgain).
VenomSoftX, like ViperSoftX, can also be orchestrated to steal cryptocurrencies from its victims. But not like the latter, which features as a clipper to reroute fund transfers to an attacker-controlled pockets, VenomSoftX tampers with API requests to crypto exchanges to empty the digital property.
Services focused by the extension embrace Blockchain.com, Binance, Coinbase, Gate.io, and Kucoin.
The improvement marks a brand new degree of escalation to conventional clipboard swapping, whereas additionally not elevating any quick suspicion because the pockets handle is changed at a way more basic degree.
Avast stated it has detected and blocked over 93,000 infections because the begin of 2022, with a majority of the impacted customers situated in India, the U.S., Italy, Brazil, the U.Ok., Canada, France, Pakistan, and South Africa.
An evaluation of the hard-coded pockets addresses within the samples reveals that the operation has netted its authors a sum whole of about $130,421 as of November 8, 2022, in varied cryptocurrencies. The collective financial achieve has since dropped to $104,500.
“Since the transactions on blockchains/ledgers are inherently irreversible, when the consumer checks the transaction historical past of funds afterward, it’s already too late,” Rubín stated.
[ad_2]