[ad_1]

Imagine you’re proven two similar objects after which requested to shut your eyes. When you open your eyes, you see the identical two objects in the identical place. How can you establish if they’ve been swapped backwards and forwards? Intuition and the legal guidelines of quantum mechanics agree: If the objects are really similar, there isn’t any solution to inform.
While this seems like frequent sense, it solely applies to our acquainted three-dimensional world. Researchers have predicted that for a particular kind of particle, referred to as an anyon, that’s restricted to maneuver solely in a two-dimensional (2D) airplane, quantum mechanics permits for one thing fairly totally different. Anyons are indistinguishable from each other and a few, non-Abelian anyons, have a particular property that causes observable variations within the shared quantum state beneath alternate, making it potential to inform once they have been exchanged, regardless of being totally indistinguishable from each other. While researchers have managed to detect their kinfolk, Abelian anyons, whose change beneath alternate is extra delicate and unattainable to instantly detect, realizing “non-Abelian exchange behavior” has confirmed tougher as a result of challenges with each management and detection.
In “Non-Abelian braiding of graph vertices in a superconducting processor”, revealed in Nature, we report the commentary of this non-Abelian alternate habits for the primary time. Non-Abelian anyons may open a brand new avenue for quantum computation, by which quantum operations are achieved by swapping particles round each other like strings are swapped round each other to create braids. Realizing this new alternate habits on our superconducting quantum processor might be an alternate path to so-called topological quantum computation, which advantages from being sturdy towards environmental noise.
Exchange statistics and non-Abelian anyons
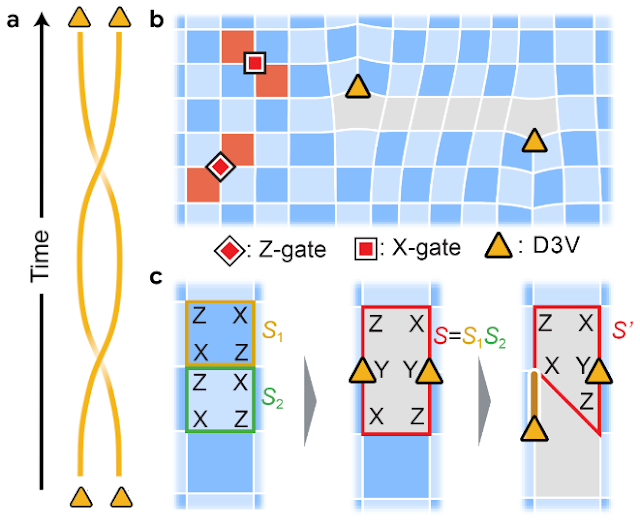
In order to grasp how this unusual non-Abelian habits can happen, it’s useful to think about an analogy with the braiding of two strings. Take two similar strings and lay them parallel subsequent to 1 one other. Swap their ends to kind a double-helix form. The strings are similar, however as a result of they wrap round each other when the ends are exchanged, it is rather clear when the 2 ends are swapped.
The alternate of non-Abelian anyons might be visualized in an identical approach, the place the strings are comprised of extending the particles’ positions into the time dimension to kind “world-lines.” Imagine plotting two particles’ areas vs. time. If the particles keep put, the plot would merely be two parallel strains, representing their fixed areas. But if we alternate the areas of the particles, the world strains wrap round each other. Exchange them a second time, and also you’ve made a knot.
While a bit tough to visualise, knots in 4 dimensions (three spatial plus one time dimension) can at all times simply be undone. They are trivial — like a shoelace, merely pull one finish and it unravels. But when the particles are restricted to 2 spatial dimensions, the knots are in three complete dimensions and — as we all know from our on a regular basis 3D lives — can not at all times be simply untied. The braiding of the non-Abelian anyons’ world strains can be utilized as quantum computing operations to rework the state of the particles.
A key side of non-Abelian anyons is “degeneracy”: the complete state of a number of separated anyons shouldn’t be fully specified by native data, permitting the identical anyon configuration to symbolize superpositions of a number of quantum states. Winding non-Abelian anyons about one another can change the encoded state.
How to make a non-Abelian anyon
So how can we understand non-Abelian braiding with considered one of Google’s quantum processors? We begin with the acquainted floor code, which we not too long ago used to realize a milestone in quantum error correction, the place qubits are organized on the vertices of a checkerboard sample. Each coloration sq. of the checkerboard represents considered one of two potential joint measurements that may be fabricated from the qubits on the 4 corners of the sq.. These so-called “stabilizer measurements” can return a price of both + or – 1. The latter is known as a plaquette violation, and might be created and moved diagonally — similar to bishops in chess — by making use of single-qubit X- and Z-gates. Recently, we confirmed that these bishop-like plaquette violations are Abelian anyons. In distinction to non-Abelian anyons, the state of Abelian anyons modifications solely subtly when they’re swapped — so subtly that it’s unattainable to instantly detect. While Abelian anyons are attention-grabbing, they don’t maintain the identical promise for topological quantum computing that non-Abelian anyons do.
To produce non-Abelian anyons, we have to management the degeneracy (i.e., the variety of wavefunctions that causes all stabilizer measurements to be +1). Since a stabilizer measurement returns two potential values, every stabilizer cuts the degeneracy of the system in half, and with sufficiently many stabilizers, just one wave operate satisfies the criterion. Hence, a easy solution to enhance the degeneracy is to merge two stabilizers collectively. In the method of doing so, we take away one edge within the stabilizer grid, giving rise to 2 factors the place solely three edges intersect. These factors, known as “degree-3 vertices” (D3Vs), are predicted to be non-Abelian anyons.
In order to braid the D3Vs, we now have to maneuver them, which means that we now have to stretch and squash the stabilizers into new shapes. We accomplish this by implementing two-qubit gates between the anyons and their neighbors (center and proper panels proven under).
Now that we now have a solution to create and transfer the non-Abelian anyons, we have to confirm their anyonic habits. For this we look at three traits that might be anticipated of non-Abelian anyons:
- The “fusion rules” — What occurs when non-Abelian anyons collide with one another?
- Exchange statistics — What occurs when they’re braided round each other?
- Topological quantum computing primitives — Can we encode qubits within the non-Abelian anyons and use braiding to carry out two-qubit entangling operations?
The fusion guidelines of non-Abelian anyons
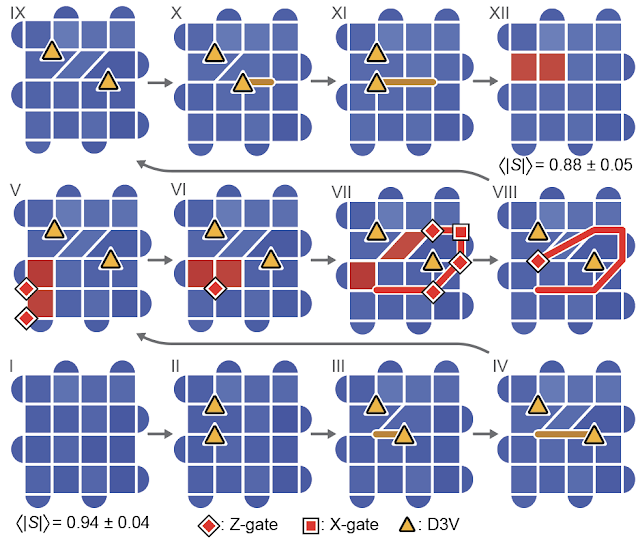
We examine fusion guidelines by learning how a pair of D3Vs work together with the bishop-like plaquette violations launched above. In explicit, we create a pair of those and convey considered one of them round a D3V by making use of single-qubit gates.
While the foundations of bishops in chess dictate that the plaquette violations can by no means meet, the dislocation within the checkerboard lattice permits them to interrupt this rule, meet its accomplice and annihilate with it. The plaquette violations have now disappeared! But deliver the non-Abelian anyons again involved with each other, and the anyons abruptly morph into the lacking plaquette violations. As bizarre as this habits appears, it’s a manifestation of precisely the fusion guidelines that we count on these entities to obey. This establishes confidence that the D3Vs are, certainly, non-Abelian anyons.
Observation of non-Abelian alternate statistics
After establishing the fusion guidelines, we need to see the true smoking gun of non-Abelian anyons: non-Abelian alternate statistics. We create two pairs of non-Abelian anyons, then braid them by wrapping one from every pair round one another (proven under). When we fuse the 2 pairs again collectively, two pairs of plaquette violations seem. The easy act of braiding the anyons round each other modified the observables of our system. In different phrases, for those who closed your eyes whereas the non-Abelian anyons have been being exchanged, you’d nonetheless have the ability to inform that they’d been exchanged when you opened your eyes. This is the hallmark of non-Abelian statistics.
Topological quantum computing
Finally, after establishing their fusion guidelines and alternate statistics, we exhibit how we are able to use these particles in quantum computations. The non-Abelian anyons can be utilized to encode data, represented by logical qubits, which needs to be distinguished from the precise bodily qubits used within the experiment. The variety of logical qubits encoded in N D3Vs might be proven to be N/2–1, so we use N=8 D3Vs to encode three logical qubits, and carry out braiding to entangle them. By learning the ensuing state, we discover that the braiding has certainly led to the formation of the specified, well-known quantum entangled state referred to as the Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger (GHZ) state.
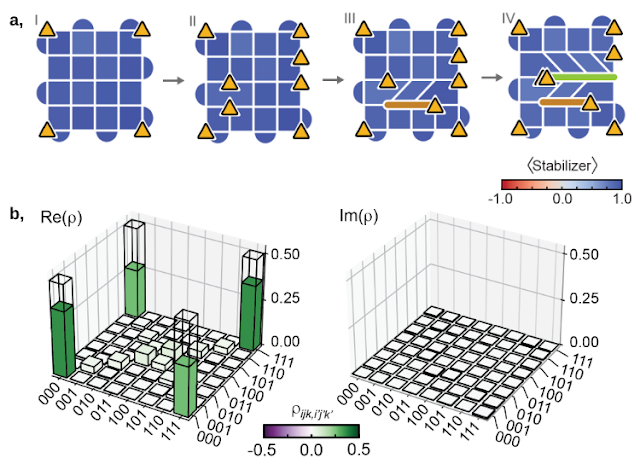 |
| Using non-Abelian anyons as logical qubits. a, We braid the non-Abelian anyons to entangle three qubits encoded in eight D3Vs. b, Quantum state tomography permits for reconstructing the density matrix, which might be represented in a 3D bar plot and is discovered to be in keeping with the specified extremely entangled GHZ-state. |
Conclusion
Our experiments present the primary commentary of non-Abelian alternate statistics, and that braiding of the D3Vs can be utilized to carry out quantum computations. With future additions, together with error correction throughout the braiding process, this might be a serious step in direction of topological quantum computation, a long-sought technique to endow qubits with intrinsic resilience towards fluctuations and noise that might in any other case trigger errors in computations.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Katie McCormick, our Quantum Science Communicator, for serving to to write down this weblog publish.
[ad_2]