[ad_1]
The Sophos Active Adversary Report celebrates its fifth anniversary this 12 months. The report grew out of a easy query: What occurs after attackers breach an organization? Knowing the adversary’s playbook, in spite of everything, helps defenders higher battle an lively assault. (There’s a purpose we began life as “The Active Adversary Playbook.”) At the identical time we have been discussing methods to instrument a testing surroundings to reply that what-happens query, Sophos was getting ready to launch an incident response (IR) service. A cross-team mission was born.
 For 5 years, we’ve offered our information – first solely from the IR service, however finally increasing to incorporate information from IR’s sister staff supporting present MDR prospects — and supplied evaluation on what we expect it means. As we proceed to refine our course of for gathering and analyzing the info, this report will deal with some key observations and evaluation – and, to have a good time a half-decade of this work, we’re giving the world entry to our 2024 dataset, in hope of beginning broader conversations. More info on that, and the hyperlink to the Active Adversary repository on GitHub, may be discovered on the finish of this report.
For 5 years, we’ve offered our information – first solely from the IR service, however finally increasing to incorporate information from IR’s sister staff supporting present MDR prospects — and supplied evaluation on what we expect it means. As we proceed to refine our course of for gathering and analyzing the info, this report will deal with some key observations and evaluation – and, to have a good time a half-decade of this work, we’re giving the world entry to our 2024 dataset, in hope of beginning broader conversations. More info on that, and the hyperlink to the Active Adversary repository on GitHub, may be discovered on the finish of this report.
Key takeaways
- Differences between MDR and IR findings present, quantitatively, the statistical worth of lively monitoring
- Compromised credentials proceed to result in preliminary entry; MFA is important
- Dwell time drops (once more!)
- Attacker abuse of living-off-the-land binaries (LOLBins) explodes
- Remote ransomware poses a novel problem / alternative for actively managed methods
- Attack impacts comprise classes about potential detections
Where the info comes from
As with our earlier Active Adversary Report, information for this version is drawn from chosen circumstances dealt with in 2024 by two Sophos groups: a) the Sophos Incident Response (IR) staff, and b) the response staff that handles important circumstances occurring amongst our Managed Detection and Response (MDR) prospects. (For comfort, we seek advice from the 2 on this report as IR and MDR.) Where applicable, we examine findings from the 413 circumstances chosen for this report with information from earlier Sophos X-Ops casework, stretching again to the launch of our IR service in 2020.
For this report, 84% of the dataset was derived from organizations with fewer than 1000 workers. This is decrease than the 88% in our earlier report; the distinction is primarily (however not completely) because of the addition of MDR’s circumstances to the combination. Just over half (53%) of organizations requiring our help have 250 workers or fewer.
And what do these organizations do? As has been the case in our Active Adversary Reports since we started, the manufacturing sector was the more than likely to request Sophos X-Ops response companies, although the proportion of consumers hailing from Manufacturing decreased from 25% in 2023 to 16% in 2024. Education (10%), Construction (8%), Information Technology (7%), and Healthcare (6%) spherical out the highest 5. In complete, 32 business sectors are represented on this dataset.
Further notes on the info and methodology used to pick circumstances for this report may be discovered within the Appendix. SecureWorks incident response information just isn’t included on this report.
The major occasion: MDR vs IR
 As we compiled and normalized the IR and MDR datasets, the Active Adversary staff hypothesized that we’d seemingly observe higher safety outcomes in organizations the place expert lively monitoring and logging have been already in place – in different phrases, the MDR circumstances. While that will appear apparent, it’s the magnitude of a number of the variations that shocked us, and it’s these variations we’ll spotlight on this report.
As we compiled and normalized the IR and MDR datasets, the Active Adversary staff hypothesized that we’d seemingly observe higher safety outcomes in organizations the place expert lively monitoring and logging have been already in place – in different phrases, the MDR circumstances. While that will appear apparent, it’s the magnitude of a number of the variations that shocked us, and it’s these variations we’ll spotlight on this report.
We’re one (however we’re not the identical): Ransomware and dwell time
In the earlier report cycle, we noticed, however didn’t report on, distinct variations between the assault sorts prevalent for MDR prospects and people prevalent for IR prospects. This was the primary sturdy indication of the hole between the 2 datasets, and it was that distinction which set the tone and focus for this report.
In all earlier stories, ransomware has dominated the charts, as one may anticipate from IR-derived information. A ransomware assault is just too damaging for a lot of organizations to remediate on their very own, particularly smaller organizations that will lack the sources essential to mount a full response.
The earlier 4 years of IR-only information noticed ransomware incidence range between 68% and 81% of circumstances. For 2024 it’s all the way down to 40% of circumstances, dropping its high spot to community breaches at 47%. When we break it down by information origin, the proportion for IR circumstances appears to be like very very similar to all earlier information. Ransomware (65%) is the dominant assault kind, adopted by community breaches (27%). The MDR information paints a distinct image, by which community breaches (56%) outpace ransomware (29%) nearly two to 1.
Figure 1: The change in attack-type findings in our dataset is hanging – in 2024, community breaches overtook ransomware because the assault kind we mostly noticed. At the underside of the chart, nevertheless, there’s one other outstanding story – regardless of the dataset, every time the 12 months, no assault kind rises above 10 % of all circumstances seen; whether or not ransomware or community breaches are the primary occasion in a given 12 months, every little thing else is frankly secondary
The second set of information supporting our speculation issues dwell time. Previous years have seen dwell time reducing however stabilizing in the previous couple of stories. (We handled dwell time to a deep evaluation in our 1H 2024 report.) As far as we have been involved, dwell time was useless — till we noticed the statistics for this 12 months.
We gained’t bury the lede: Median dwell time for all circumstances in 2024 was a swift two days. We see a well-recognized sample emerge in IR circumstances: Overall median dwell time is 7 days, with ransomware circumstances at 4 days and non-ransomware circumstances at 11.5 days. MDR dwell occasions, then again, have been decrease throughout the board, and the order of dwell occasions for ransomware (3 days) and non-ransomware (1 day) assaults have been inverted.
We imagine it is because sure actions (for example, exfiltrating the info) can not go any sooner, since they depend on human exercise, information throughput, or different pretty inflexible time frames. That’s to not say the assaults can’t be achieved sooner, as a result of they’ll, however the information reveals that ransomware assaults have historically required longer timeframes than different assault sorts. The undeniable fact that dwell occasions for ransomware circumstances dealt with by every service have been roughly equal is subsequently not shocking.
Non-ransomware circumstances, then again, have fewer velocity bumps, and right here’s the place the info highlights the variations between the companies. For instance, with IR circumstances, an attackers might reside within the sufferer’s community undetected for for much longer, till an occasion happens that causes adequate noise or impression. An attacker utilizing legitimate credentials, who silently exfiltrates information from a community over anticipated channels, may not be detected till they contact the sufferer, in the event that they ever do. (It also needs to be famous that the ransomware sector has attracted an amazing most of the extra amateurish kind of attacker, which is normally much less adept at retaining quiet and overlaying its tracks. Ransomware continues to be a numbers recreation, so getting knocked off a excessive share of methods is simply a part of the enterprise mannequin.)
MDR circumstances for non-ransomware (or pre-ransomware) incidents, then again, are generated extra rapidly attributable to a mix of detection engineering and fixed vigilance. Suspicious occasions are investigated sooner, and people who warrant extra investigation are escalated. In brief, sooner detection usually results in aborted ransomware, which implies the next proportion of assaults categorised as community breaches — and higher outcomes for the victims.
Come collectively: Root trigger
In distinction, we didn’t see a lot distinction between IR and MDR circumstances when it got here to root causes. Here we see the acquainted mixture of compromised credentials (41%) and exploiting vulnerabilities (22%) main the best way as soon as once more, and brute drive assaults (21%) muscling their technique to third place, as proven in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Root trigger in 2024 different between MDR and IR circumstances, however compromised credentials are nonetheless the main explanation for ache in each datasets
Brute drive assaults have been perennially relegated to the also-ran class within the IR information, however noticed a dramatic enhance within the MDR information, which vaulted the assault kind up the rankings for 2024. This could also be all the way down to a distinction within the out there root-cause information. In IR investigations, logs are sometimes unavailable, which reduces the investigative staff’s capacity to find out the foundation causes of the assault. In distinction, MDR investigations have extra constant information sources out there, which permits for extra exact analyses.
A take a look at the year-to-year information, as proven in Figure 3, reveals the change in percentages between earlier years and 2024.
Figure 3: Compromised credentials in 2024 retreated from earlier excessive ranges as the commonest root explanation for issues, nevertheless it’s nonetheless a nasty state of affairs. (Data from 2020 circumstances just isn’t represented on this chart attributable to a change in our information labeling for this class)
In 2024, logs have been lacking in 47% of circumstances – 66% for IR, 39% for MDR. The main purpose for lacking logs in all circumstances was that they have been merely unavailable (20%) to analysts throughout the investigation, adopted by 17% of logs being cleared by the attackers and seven% lacking attributable to inadequate retention durations.
(One instrument that usually will get used to clear logs is the Microsoft binary wevtutil.exe [the Windows Event Utility]. This will generate Windows occasion log IDs 1102 [for security logs] and 104 [for system logs]. Organizations ought to take into account configuring their safety instruments and menace hunts to detect this exercise.)
The rise in brute drive as a root trigger aligns nicely with preliminary entry (TA0001) statistics. External Remote Services (T1133) was the favored preliminary entry methodology, noticed in 71% of circumstances. As we’ve acknowledged beforehand, that is usually tightly coupled with Valid Accounts (T1078); this 12 months the duo teamed up in 78% of circumstances. Exploiting a Public-Facing Application (T1190) was the second-most single contributor to preliminary entry. The high vulnerability immediately exploited for preliminary entry was CVE-2023-4966 (Citrix Bleed; 5%). Other elements included uncovered Remote Desktop infrastructure (18%), susceptible VPNs (12%), and uncovered inside companies (11%).
You down with TTP?
We demonstrated in a earlier report that there have been few variations in TTPs between assaults with brief (5 days or fewer) versus lengthy (greater than 5 days) dwell occasions. Those information have been completely IR circumstances. Looking on the TTPs from this 12 months’s report, we see the sample maintain when evaluating IR and MDR circumstances.
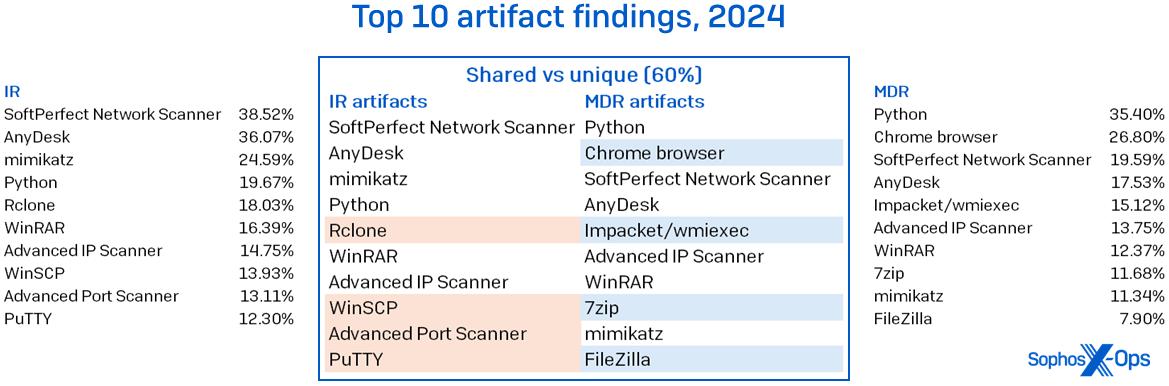
There have been barely extra artifacts seen in MDR circumstances (+24%), although the MDR dataset was round 240% bigger than that taken from IR. There was a 60% overlap within the 10 instruments most utilized by attackers. Among the highest legit instruments being abused have been some acquainted names: SoftPerfect Network Scanner, AnyDesk, WinRAR, and Advanced IP Scanner, as proven in Figure 4.
Figure 4: The instruments seen abused in IR and MDR circumstances didn’t range a lot on the high of the charts, however sure variations and absences are hanging
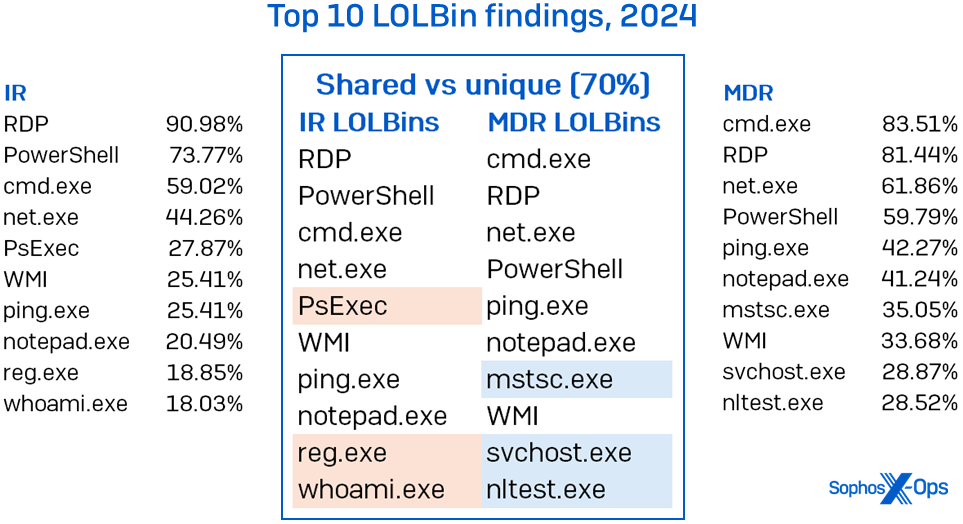
Microsoft binaries exhibited a tighter correlation between the datasets. The high 10 abused LOLBins had a 70% overlap, as proven in Figure 5. There was a slight shuffle within the high spot, with cmd.exe beating out RDP as probably the most abused LOLBin within the MDR case load. This isn’t completely shocking, since many MDR circumstances have a restricted blast radius: When approved to take action, analysts will robotically isolate affected hosts, thereby limiting attackers’ lateral-movement capabilities.
Figure 5: LOLBin abuse presents itself a lot the identical regardless of which staff is trying; particularly, the distinction between MDR and IR on the subject of RDP abuse exists however just isn’t substantial
The remaining comparability appears to be like on the “other” class, by which we group methods and traces that don’t fall into the opposite two classes. The high 10 had an 80% overlap in IR and MDR circumstances; creating accounts, deleting recordsdata, putting in companies, malicious scripts, and modifying the registry have been the dominant methods, as proven in Figure 6. Others, akin to SAM (Security Account Manager) dumping, have been extra frequent in a single staff’s dataset.
Figure 6: As we see, in additional than half of all circumstances, the attackers used acquainted and related TTPs. (Note that percentages add as much as over 100%, since most circumstances have a number of findings on this class)
The chew from inside (reprise)
As has grow to be the norm at Active Adversary HQ, we prefer to verify in on a few of our findings from earlier stories, particularly these for which the info interval is lower than 12 months. The subsequent part appears to be like on the key takeaways from our earlier report (overlaying the primary six months of 2024) and compares them to the total 12 months’s dataset.
LOLBins
The abuse of Microsoft binaries continued unabated within the second half of 2024, and the ratio of distinctive LOLBins to earlier years additionally continued to rise. In the primary half of 2024 we noticed a 51% rise within the depend of distinctive LOLBins, which completed the 12 months at 126% over 2023 counts. There was a 17% case rise in 2H 2024 and a 24% rise in distinctive binaries used. There have been no significant variations within the particular person binaries used all year long. Between the primary half and second half of the 12 months, there was a 95% overlap within the 20 most-abused instruments in IR and MDR circumstances. Tools that can be utilized for enumeration – along with legit and malicious makes use of — continued to be extremely represented in each datasets, making up 50% of the 20 most-abused binaries.
Notepad.exe was a brand new entry on this 12 months’s high 10. This instrument was predominantly used for looking recordsdata on the community, together with recordsdata containing passwords saved in plaintext (5%). Tools like Notepad present an attention-grabbing detection alternative. We would argue that the majority customers usually are not utilizing Notepad in favor of different Office applications. But there’s additionally an enormous distinction between clicking on the Notepad icon, typing notepad in Windows search, or typing notepad.exe on the command line. Being capable of discriminate between these three completely different launch strategies can inform the intent of its use.
The identical is true of instruments like PowerShell. We’re not going to recommend that IT groups cease utilizing it, however there are some fast heuristics that may be utilized utilizing detection engineering. Was that PowerShell script closely obfuscated, and did it attain out to the web? If it did, it ought to in all probability be investigated.
The major difficulty with LOLBins is they have a tendency to generate quite a lot of noise. The problem for IT groups is knowing the place the sign exists.
RDP
RDP detections proceed to high the chart of abused Microsoft instruments. In 2024, it was utilized by attackers in 84% of circumstances, with 67% getting used just for inside lateral motion and three% getting used solely externally. That’s earlier than we add the circumstances the place it was used each internally and externally. The addition of these circumstances brings the totals to 83% and 19% respectively.
Despite RDP’s continued abuse – and our pleas for it to be banished past the wall – we perceive why it persists in networks. To that finish, it supplies us with a possibility to discover how we would each constrain its use and instrument some detections for its abuse.
Ideally, all RDP use is constrained by each community choke factors and person identities. Where potential we want so as to add MFA to the authentication movement and apply the precept of least privilege. By constraining its use, and understanding what regular appears to be like like, it turns into simpler to detect anomalies.
There are a number of methods to detect authentication occasions, however broadly talking, you possibly can search for Windows logging occasion IDs 4624 and 4625. The former is a profitable authentication occasion, whereas the latter signifies a failed try. Successful login occasions may help you catch an attacker utilizing legitimate credentials exterior of regular use, whereas a number of failed makes an attempt may give you an early warning to any brute drive exercise towards your accounts.
If you employ a company normal for naming your units, as many firms do, you need to use that as one other indicator. Any profitable authentication that doesn’t conform to the usual ought to be investigated. If your group doesn’t have a normal, this may very well be a possibility to implement one and create passive journey wires for attackers. Then once more, if the hostname “kali” reveals up in your community, because it did in 6% of circumstances, you must examine.
Finally, you possibly can reap the benefits of time-zone bias in RDP logging. This is the distant consumer’s time offset from UTC. If most of your customers are in UTC-6, however an otherwise-unremarkable distant consumer logs in utilizing legitimate credentials and a traditional trying hostname, however has a time-zone bias of +3, run like hell to seek out out why. (And then there are the occasions we’ve seen innocuous-looking machines related, however sharing a Russian-named printer for some purpose…)
The thought behind these detection alternatives is to take impartial, however generally noisy or weak alerts, and sew them collectively to realize a stronger, extra dependable sign. Or, because the cool children name it, protection in depth.
Those eager to know extra about RDP and tips on how to detect its abuse can discover extra particulars in our RDP collection.
Attribution
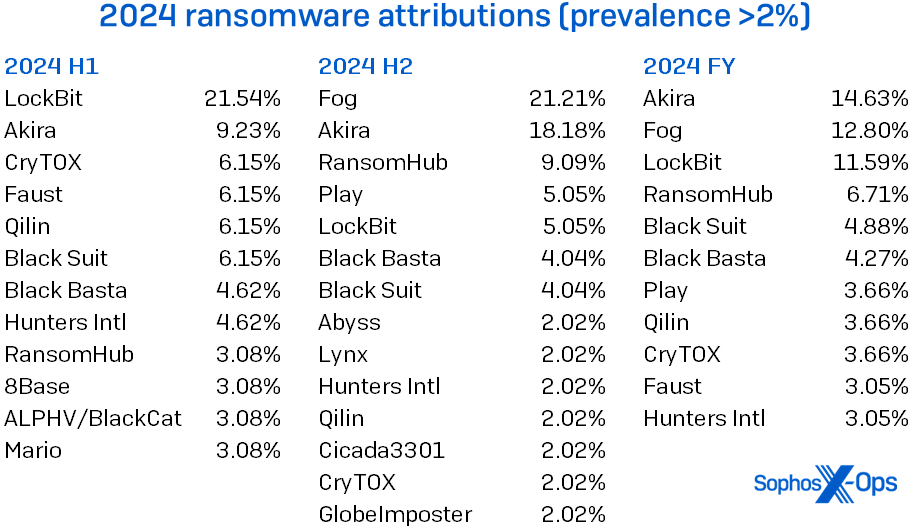
In the final report, we predicted that in 2024 there would in the end be no overwhelmingly dominant ransomware adversary; with a legislation enforcement takedown early within the 12 months kneecapping LockBit, 2023’s main miscreant, the sphere opened up for the Next Big (Bad) Thing. As the desk in Figure 7 reveals, this was appropriate – Akira rose to the highest of the pack, however solely simply. (LockBit was, then again, so dominant firstly of final 12 months that it nonetheless got here in third within the rankings regardless of the takedown.) During the second half of the 12 months, Fog seeped onto the charts, edging out Akira for the highest spot. (The MDR staff did see a few trailing-edge LockBit infections early within the second half, however even these traces evaporated by 12 months’s finish.) The sample might but break down in 2025 due to seemingly modifications in (amongst different issues) law-enforcement effort coordination – and LockBit nonetheless swears they’re making a comeback. We’ll be watching with curiosity.
Figure 7: Fame is fleeting, as LockBit’s perpetrators discovered within the latter half of 2024; in the meantime, a heavy Fog rolled in
Being capable of attribute hassle to a particular adversary is soothing, in some way. But practitioners are sometimes combating forces which can be nominally on their facet, whereas coping with decisions made by the bigger enterprise that really feel like yet another battle to be dealt with. Our case research on this report describes how that went for one “unlucky” MDR buyer.
Case research: Two towards one
While we proceed to reiterate basic safety tenets (shut uncovered RDP posts, use MFA, and patch susceptible methods), within the face of enterprise change processes past practitioners’ management, it’s not all the time that simple. Security practitioners usually are not solely combating the battle towards the threats posed by exterior adversaries, however an inside wrestle with enterprise processes and alter administration. This tug-of-war got here again to chew one MDR buyer. Following a community breach by which the menace actor gained preliminary entry by way of a susceptible VPN, the shopper confronted a two-month estimated timeframe to patch the VPN equipment. With a ransomware gang ready within the wings, the battle between safety priorities and people of the bigger enterprise resolved in simply concerning the worst approach potential.
You and me towards me
The Sophos MDR staff lately responded to this buyer’s important incident, with preliminary entry recognized as one in all our common suspects – an unpatched VPN equipment. In this case, a FortiGate firewall was working on firmware model 5.6.11, which was launched in July 2010; the firewall itself reached end-of-life in October 2021. In addition, MDR recognized a misconfiguration in VPN user-access controls, which considerably elevated the danger of unauthorized entry.
After gaining preliminary entry, the menace actor moved laterally to the area controller, leveraged AV-killer instruments, carried out enumeration, and gained persistence on quite a lot of units throughout the property. At this stage, MDR’s response staff disrupted the attacker exercise, and calm resumed.
The MDR staff really helpful the shopper (at minimal) patch the 14-year-old VPN firmware with urgency, and disable the SSL VPN within the meantime. However, the shopper’s enterprise processes weren’t cooperative; disabling the VPN altogether would trigger unacceptable enterprise impression, and the patches couldn’t be utilized for 2 months (!). The misconfiguration, the shopper estimated, would take one week to treatment.
Already combating
It’s an unlucky reality of incident-response life that we can not compel; we are able to solely advocate – and, generally, we are able to solely stand by watching historical past repeat itself. And it was repeating: The identical buyer had already skilled a related breach, involving the identical susceptible VPN, 14 months earlier. In that case, the shopper didn’t but have MFA enabled for VPN logins; a brute drive assault was profitable, and the attacker was capable of disable protections and dump credentials. In the method, the attacker managed to compromise a key service account, leaving the shopper unable to carry out a vital credential reset attributable to – once more – enterprise necessities. (Remember that service account; we’re about to see it once more.)
The hole between the primary breach and the second was, as talked about, 14 months. The hole between the second and the third was far shorter.
So what’s one other one?
The second incident concluded. The VPN and that service account – one factor out of help for almost 4 years, one factor known-compromised for over a 12 months – waited in business-process limbo, as did the VPN misconfiguration. The safety practitioners have been affected person. The attacker wasn’t. Nine days after the shut of the second breach, CryTOX roared in. Using the compromised service account and taking full benefit of the unpatched and (nonetheless) misconfigured VPN, the ransomware ran rampant by way of the system, shifting laterally, killing endpoint-security processes, and in the end encrypting your entire property.
It could also be stated on this case that ransomware gained the tug of struggle between safety practices and enterprise change processes. (Silver lining: After the third incident, the VPN was lastly disabled, although affected accounts have been nonetheless re-enabled with out credential resets.) While not all organizations are so unfortunate, on this case the look ahead to enterprise change approval was a risk-assessment gamble that failed terribly.
Best of the remaining
As we wrap up our 2024 findings, let’s verify in on different statistics that drew our consideration.
In addition to an elevated variety of circumstances, this 12 months’s dataset included the most important year-to-year enhance in all noticed TTPs. In comparability with 2023, the variety of abused instruments was up 80%, LOLBins have been up 126%, and every little thing else (“other”) was up 28%. What’s attention-grabbing about these numbers is the lengthy tail for every class – that’s, the variety of instruments or LOLBins or “other” that appeared ten occasions or fewer within the dataset. When we tally each single discovering in each single case, these rarities account for 35% of all instrument use (689 findings of 1945 complete; 334 distinctive objects), 12% of all LOLBin use (508 findings of 4357; 184 distinctive objects), and 12% of all “other” (476 findings of 4036; 189 distinctive objects). A biologist may name these vestigial tails; we name them a decrease investigation precedence than the dominant beasts on the tops of the TTP charts.
No time to waste
When it involves sure targets, attackers don’t fritter and waste the hours in an offhand approach. We first reported on the race to Active Directory compromise in 2023. This statistic has continued to pattern downward, and the median now stands at 0.46 days. In different phrases, as soon as an attacker enters the surroundings, it’s solely 11 hours earlier than they go after the AD server. Most (62%) of the compromised servers have been working working methods that have been out of mainstream help.
Games with out frontiers
Another time-related statistic that we first reported on in 2023 was the time of day that attackers selected to deploy ransomware payloads. While extra information softens the values considerably, the outcomes are nonetheless compelling. In 2024, 83% of ransomware binaries have been deployed exterior the goal’s native enterprise hours; the all-time statistic stands at 88%. While it seems that ransomware deployments solely come out at evening, there doesn’t nevertheless appear to be any lingering desire in days of the week.
Tools to stroll by way of life
The proportion and varieties of instruments – each legit and malicious – that make up this class have remained comparatively steady for a few years. Here are some highlights from this 12 months’s information, along with the problems lined above.
We’ve seen an enormous drop within the proportion of assaults that use Cobalt Strike. This instrument occupied the highest spot in abused instruments from 2020-2022, dropping to second place in 2023. This 12 months noticed it slip all the best way all the way down to thirteenth on our listing, showing in simply 7.51% of circumstances. Due to its historic reputation with attackers, it nonetheless occupies the highest spot within the all-time rankings, the place it has been concerned in 25% of assaults up to now 5 years. We imagine the lower is because of elevated prevention and detection capabilities. Cobalt Strike was widespread as a result of it was efficient. Now that its effectiveness has declined, so has its use. While that is welcome information, it additionally means that one thing else has or will take its place.
A instrument that has seen an order of magnitude enhance in abuse is Impacket. Impacket instruments have been round for at the very least a decade and may carry out a wide range of actions, together with manipulating community protocols, dumping credentials, and reconnaissance. Its use has steadily grown in recent times, from 0.69% in 2021 to 21.43% in 2023; attackers actually ramped up their use of Impacket in 2024, when it overtook all different instruments and landed within the high spot. The most used Impacket instrument was wmiexec.py, which featured in 35% of assaults. (In our statistics, we establish the particular Impacket subclass every time potential; if there may be doubt, we merely classify it as Impacket, no subclass.)
A venerable instrument seeing a slight year-on-year decline is mimikatz. The credential-harvesting instrument was reliably noticed in round 1 / 4 of assaults in earlier years however slipped to fifteen% in 2024. While we are able to’t decisively attribute its decline to anybody factor, it’s potential that it’s associated to the elevated use of Impacket instruments; particularly, the secretsdump.py script that can be utilized to dump hashes from distant machines. This correlates with a year-on-year enhance in distant registry dumping and a halving of LSASS dumps (mostly attributed to mimikatz in our information). Secretsdump.py was seen in at the very least 6% of assaults and was the second most used Impacket instrument after wmiexec.py.
Of the highest 15 instruments being abused, 47% are sometimes used for exfiltration of information. These instruments embrace well-known archiving software program and file switch instruments.
Other findings
Since we began monitoring the provision of multifactor authentication (MFA) in breached organizations, the information has gotten worse. In 2022, we noticed 22% of victims didn’t have MFA configured. That proportion almost tripled to 63% in 2024. This is one space the place there was no significant distinction between IR and MDR circumstances. MFA was unavailable in 66% of IR circumstances and 62% of MDR circumstances. This highlights a method by which even probably the most succesful detection and response program can nonetheless depart organizations susceptible to assault.
Another regarding metric was the proportion of unprotected methods present in breached organizations. In 40% of the circumstances we investigated, there have been unprotected methods. When we take into account there have been additionally susceptible VPNs (12%), susceptible methods (11%), and end-of-life methods (5%) in a few of these environments (this report’s case research, for example, had all three), attackers may really feel like a crafty fox within the rooster’s lair.
Some might ask why we’re nonetheless seeing ransomware circumstances in any respect in an MDR service. One massive purpose has to do with unprotected methods and their relationship with distant ransomware. All that malicious exercise – ingress, payload execution, and encryption – happens on unmanaged machines, subsequently bypassing the group’s safety instruments. The solely indication of compromise is the transmission of paperwork to and from different machines. Our telemetry signifies that there was a 141% year-on-year enhance in intentional distant encryption assaults since 2022, as proven in Figure 8. (We’ve talked beforehand about distant ransomware and tips on how to parry it, together with a deep dive into our CryptoGuard expertise; because the numbers rise, distant ransomware could also be a significant matter in a later Active Adversary Report.)
Figure 8: According to Sophos X-Ops information, 2024’s distant ransomware tally was 141% of that of 2022; observe the startling rise in circumstances over the past 18 months of the info
The lack of visibility for recordsdata shifting across the community – and of lacking logs – additionally contributes to exfiltration statistics. In 2024, analysts have been capable of affirm that exfiltration occurred in 27% of circumstances. When we embrace proof of information staging and potential exfiltration, this rises to 36%. Ransomware victims had their information exfiltrated in 43% of the incidents we investigated. An extra 14% had potential exfiltration or proof of information staging. Unlike time-to-AD, exfiltration findings happen in the direction of the tip of an assault. There was a median time of 72.98 hours (3.04 days) between the beginning of an assault and exfiltration, however solely 2.7 hours (0.11 days) from exfiltration to assault detected for ransomware, information exfiltration, and information extortion circumstances.
Bring the noise
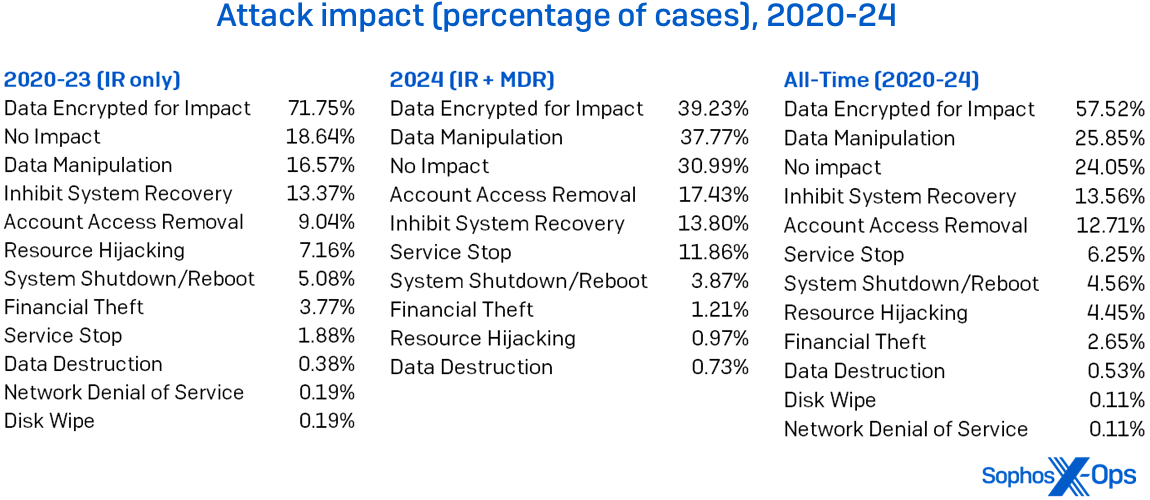
Finally, this report has historically checked out MITRE impacts (TA0040). Given ransomware’s prevalence within the information, it’s not shocking that as proven in Figure 9, Data Encrypted for Impact (T1486) tops the chart, because it has yearly. But the remainder of the impacts, we see a possibility for defenders: The causes of most of the different impacts are occasions that may be detected.
Figure 9: MITRE’s Impact classes change over time, however Data Encrypted for Impact’s reign on the high of the Active Adversary charts is unbroken all through our five-year historical past, together with each IR’s and MDR’s circumstances this 12 months. (Note that percentages add as much as over 100%, since some circumstances have a number of impacts)
For occasion, Inhibit System Recovery (T1490) is usually invoked as a result of the menace actor deleted quantity shadow copies. Tools like vssadmin.exe, the shadow-copy administration instrument (seen abused in 10% of all circumstances), or the WMI command line (seen abused in 24%) are used to do the deed. You may also detect when vssadmin is used to create shadow copies, which precedes its exfiltration. Likewise, we noticed attackers delete recordsdata in 26% of all circumstances. In that circumstance, anticipating sudden use of del.exe could also be an indication of adversary motion. Detection engineering can pay attention for suspicious occasions of this ilk, to listen to the noise attackers make once they’re making an attempt to trigger you hurt.
Conclusion
To the practitioners on the market, we see you. You’re doing the work and you recognize the enterprise. You additionally know the restrictions of what you possibly can accomplish. The excellent news is that you simply don’t must be helplessly hoping issues will get higher, particularly when assist is obtainable.
To the enterprise and tech leaders, give your groups an opportunity. We know cash and sources are tight. That usually means loading up your IT employees with extra work and accountability than they’ll deal with. Though it might sound self-serving coming from a analysis staff connected to a safety vendor, we imagine IT groups have to deal with how they allow the enterprise and let specialists do the soiled work of combating the attackers. Because one factor is evident from the info: When there’s somebody being attentive to the surroundings and they’re able to act rapidly and decisively, outcomes dramatically enhance. The various is repeating errors from the previous. The selection is yours: You can get with this, or you may get with that. We suppose you’ll get with this, for that is the place it′s at.
Acknowledgements
The authors want to thank the Sophos IR and MDR groups, Mark Loman, Chester Wisniewski, and Matt Wixey for his or her contributions to the AAR course of.
Appendix: Demographics and methodology
For this report, we targeted on 413 circumstances that may very well be meaningfully parsed for info on the state of the adversary panorama all through 2024. Protecting the confidential relationship between Sophos and our prospects is after all our first precedence, and the info herein has been vetted at a number of phases throughout this course of to make sure that no single buyer is identifiable by way of this information – and that no single buyer’s information skews the combination inappropriately. When unsure a few particular case, we excluded that buyer’s information from the dataset.
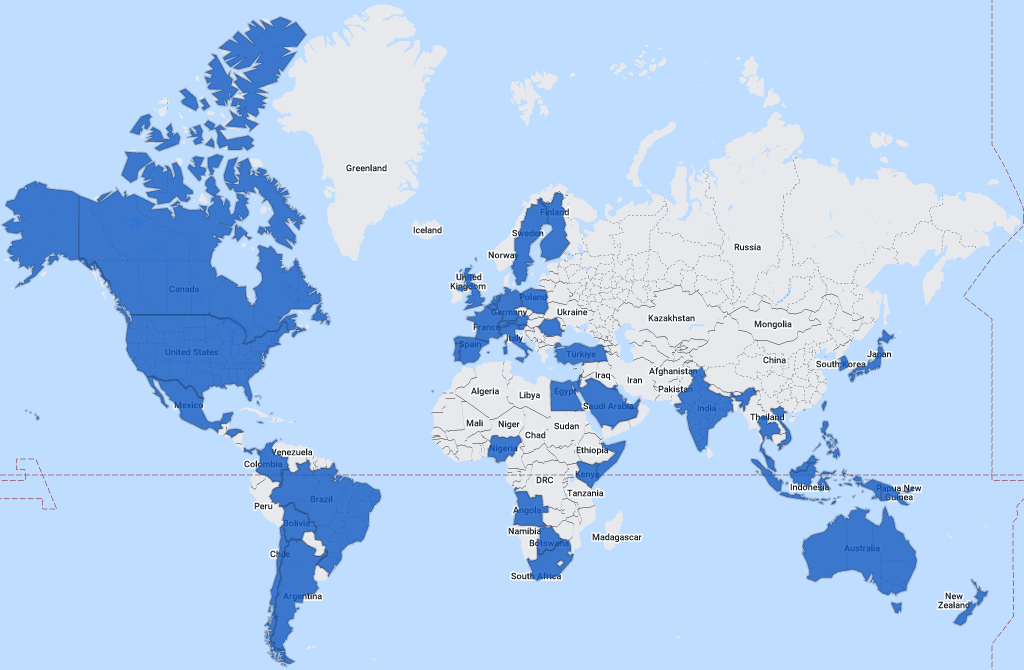
Figure A1: We get round: It’s Sophos Incident Response and MDR at work world wide (map generated courtesy of 29travels.com)
The following 57 nations and different areas are represented within the full dataset:
| Angola | Hong Kong | Qatar |
| Argentina | India | Romania |
| Aruba | Indonesia | Saudi Arabia |
| Australia | Israel | Singapore |
| Austria | Italy | Slovenia |
| Bahamas | Jamaica | Somalia |
| Bahrain | Japan | South Africa |
| Belgium | Kenya | South Korea |
| Bolivia | Kuwait | Spain |
| Botswana | Malaysia | Sweden |
| Brazil | Mexico | Switzerland |
| Canada | Netherlands | Taiwan |
| Chile | New Zealand | Thailand |
| Colombia | Nigeria | Turkey |
| Egypt | Panama | Turks and Caicos Islands |
| Finland | Papua New Guinea | United Arab Emirates |
| France | Philippines | United Kingdom |
| Germany | Poland | United States of America |
| Honduras | Portugal | Vietnam |
Industries
The following 32 industries are represented within the full dataset:
| Advertising | Financial | News Media |
| Agriculture | Food | Non-profit |
| Architecture | Government | Pharmaceutical |
| Communication | Healthcare | Real property |
| Construction | Hospitality | Retail |
| Education | Information Technology | Services |
| Electronics | Legal | Transportation |
| Energy | Logistics | Travel and tourism |
| Engineering | Manufacturing | Utilities |
| Entertainment | Mining | Wholesale |
| Finance Services | MSP/Hosting |
Methodology
The information on this report was captured over the course of particular person investigations undertaken by Sophos’ X-Ops Incident Response and MDR groups. For this primary report of 2025, we gathered case info on all investigations undertaken by the groups all through 2024 and normalized it throughout 52 fields, inspecting every case to make sure that the info out there was applicable intimately and scope for combination reporting as outlined by the main focus of the proposed report. We additional labored to normalize the info between our MDR and IR reporting processes.
When information was unclear or unavailable, the authors labored with particular person IR and MDR case results in clear up questions or confusion. Incidents that might not be clarified sufficiently for the aim of the report, or about which we concluded that inclusion risked publicity or different potential hurt to the Sophos-client relationship, have been put aside. We then dissected every remaining case’s timeline to realize additional readability on such issues as preliminary ingress, dwell time, exfiltration, and so forth. We retained 413 circumstances, and people are the muse of the report. The information supplied within the downloadable dataset has been additional redacted to make sure buyer confidentiality.
[ad_2]