[ad_1]
At 11:58 am on Saturday, 1 September 1923, the Kanto area of Japan began to shake. The earthquake started with a violent horizontal back-and-forth movement, adopted by two vertical jolts, after which one other horizontal shock even stronger than the primary. The depth of the tremor broken the seismometer that took the studying under, interrupting the waveform within the north–south path. The earthquake went on for someplace between 4 and 10 minutes.
What made the Great Kanto Earthquake so harmful?
For the following a number of hours, seismological stations world wide recorded violent aftershocks, and over the following 10 days, they continued to document greater than 1,000 aftershocks sturdy sufficient to be felt by people. The preliminary destruction within the inhabitants facilities of Tokyo, Yokohama, and Kawasaki included buckled roads and collapsed partitions, chimneys, and smokestacks. But it paled compared to the destruction about to be unleashed.
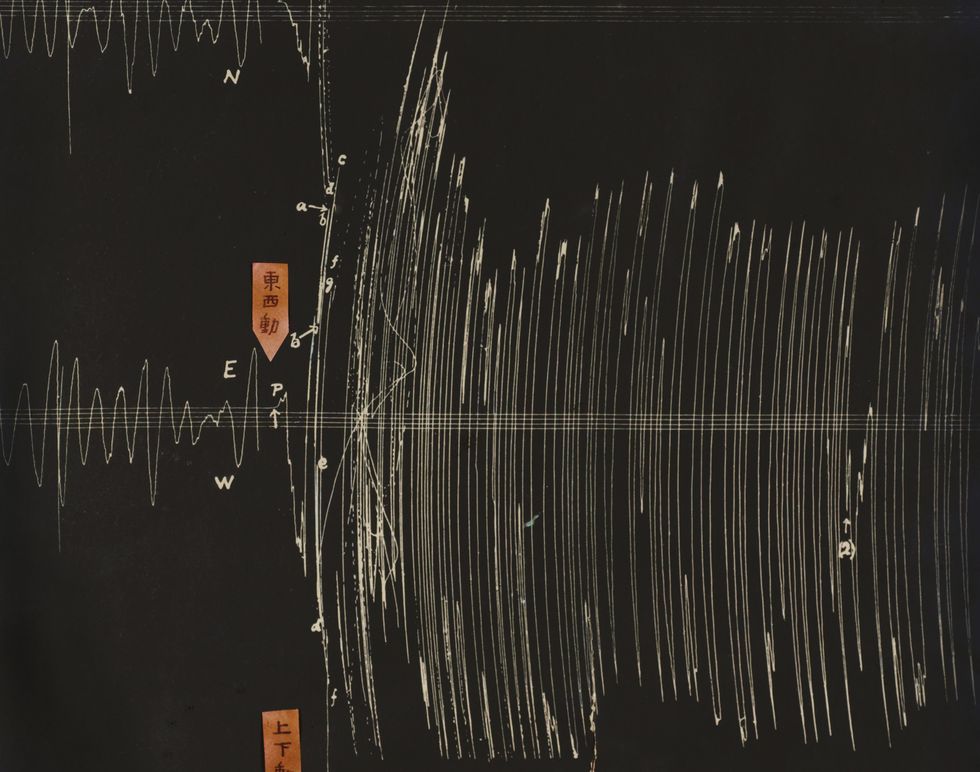 The Great Kanto Earthquake was so giant that the seismometer taking this studying stopped recording. Great Kanto Earthquake Memorial Museum
The Great Kanto Earthquake was so giant that the seismometer taking this studying stopped recording. Great Kanto Earthquake Memorial Museum
The estimated 7.9-magnitude earthquake struck simply as households have been making ready their noon meals, many over charcoal fires and open flames. The violent vertical thrusts of the quake ruptured fuel traces and water mains. More than 130 main fires broke out, with little capability to suppress them. In Tokyo, the fires merged right into a firestorm so intense that it created its personal wind system and set alight town’s many wood buildings. Survivors rushed to hunt security. Bridges turned choke factors, and as these made from wooden caught fireplace, individuals have been trapped.
In some of the horrific incidents, about 38,000 individuals sought refuge at a former clothes depot of the Japanese Imperial Army. Around 4:00 pm, the construction was engulfed by a 90-meter-tall fireplace whirl, an intense vortex of superheated air and flame. Only 300 individuals survived. In the aftermath of the destruction, the 6.7-hectare website turned a makeshift assortment level for the identification and cremation of town’s useless.
Tokyo burned for 2 days. In the top, greater than 140,000 individuals perished.
A quick historical past of seismography
Japan isn’t any stranger to seismic catastrophe. The island nation sits alongside the Pacific Ring of Fire, a geologically unstable belt the place a number of of the Earth’s tectonic plates converge. The ring is understood for volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and tsunamis. The Japan Trench, which runs north to south alongside the coast of the nation, was created over millennia by the Pacific tectonic plate subducting (or bending) beneath the North American-Okhotsk plate on the fee of two to 12 centimeters per yr. Subduction alongside this plate triggered the 9.0-magnitude Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami of 11 March 2011, setting off the meltdown on the Fukushima nuclear energy plant. It was essentially the most highly effective earthquake to hit Japan since fashionable seismography started.
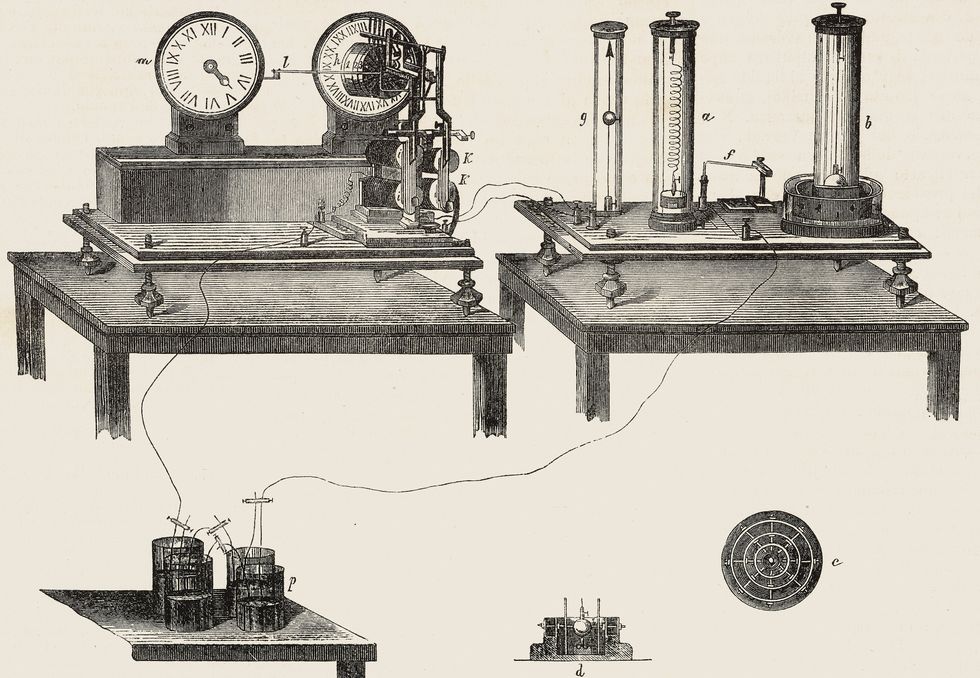 Italian physicist Luigi Palmieri invented the primary electromagnetic system that recorded the time of an earthquake and its motion.De Agostini Picture Library/Getty Images
Italian physicist Luigi Palmieri invented the primary electromagnetic system that recorded the time of an earthquake and its motion.De Agostini Picture Library/Getty Images
The detection of earthquakes has a protracted historical past. In China, information of earthquakes have been stored since at the least 780 BCE. During the Han Dynasty, it turned the responsibility of the Astronomical Bureau to document them.
In the second century CE, the Chinese scientist Zhang Heng developed an “earthquake weathercock.” This early seismoscope detected the motion of the bottom however captured no document of time, period, or power. No bodily instance or illustration of the system survives, however in response to descriptions, it was bronze and cylindrical in form, much like an urn. Eight dragon heads have been mounted on the surface, every holding a ball in its tooth, and eight corresponding toads ringed the bottom. When an earthquake struck, the dragon would launch its ball, which dropped into the gaping mouth of the toad, indicating the compass path of the quake. Most individuals consider a pendulum triggered the mechanism that launched the ball.
It took a millennium and a half earlier than a scientist on the opposite facet of the world, in one other earthquake-prone area, made a big advance in seismography. In 1855, Italian physicist Luigi Palmieri created the primary electromagnetic system that recorded the time of an earthquake and its motion. Palmieri’s seismograph consisted of U-shaped tubes full of mercury. When the bottom shook, the mercury would shut {an electrical} circuit and cease an hooked up clock. His system is on show on the Museum of the Royal Vesuvius Observatory, in Naples.
 The seismological station at Oxford, England, was certainly one of many who confirmed the timing and severity of the Great Kanto earthquake. SSPL/Getty Images
The seismological station at Oxford, England, was certainly one of many who confirmed the timing and severity of the Great Kanto earthquake. SSPL/Getty Images
Over the following few a long time, many scientists labored on earthquake detectors, and it’s laborious to type out who really invented the primary fashionable seismograph, one that might reliably document the bottom’s motion over time. Italian physicist Filippo Cecchi has one declare. In 1875 he invented a tool that recorded the relative movement of pendulums with respect to the bottom as a perform of time. A recording floor tracked the bottom movement in increments of 1 cm per second. His system was not notably delicate.
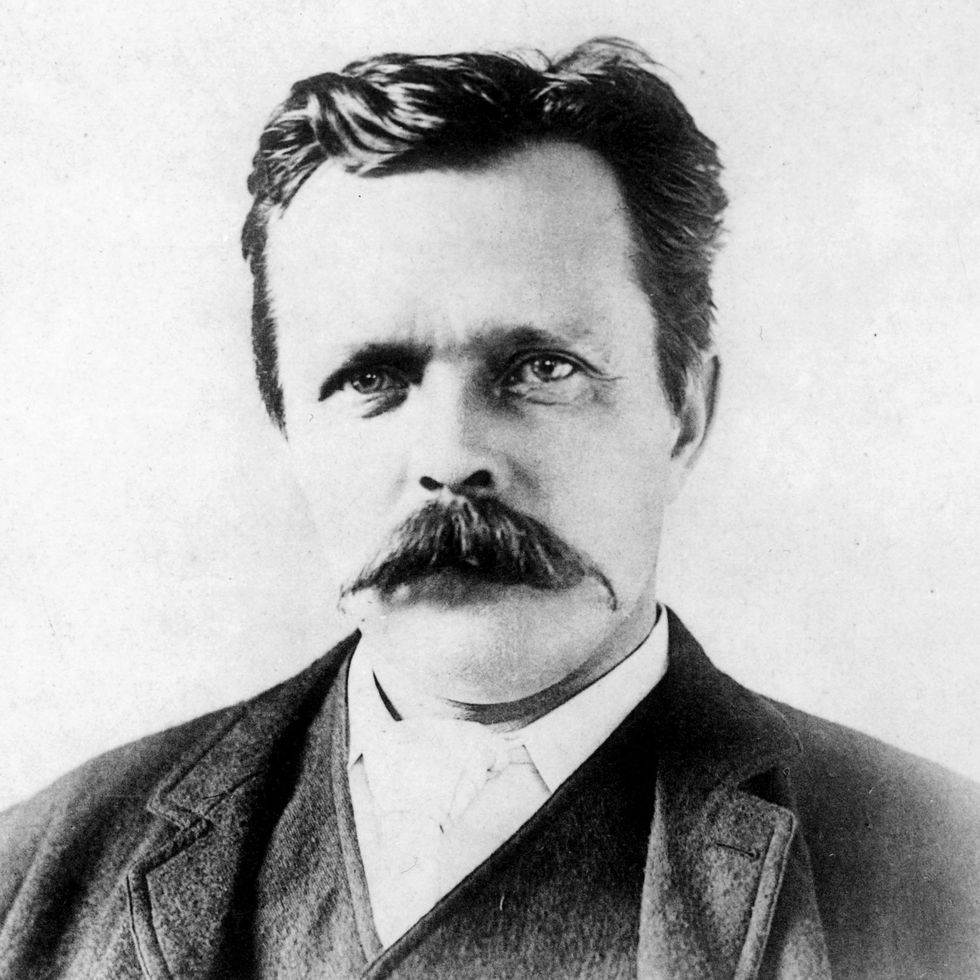

The British geologist John Milne studied earthquakes in Japan beginning within the 1870s and later advocated for the institution of a worldwide community of seismological stations.
SSPL/Getty Images
Meanwhile, the consideration of recording the primary seismogram went to a gaggle of British and Scottish engineers working in Japan. On 22 February 1880, John Milne, James Ewing, and Thomas Gray, recorded a minor earthquake in Yokohama. Their detector traced the earthquake’s movement on a soot-covered rotating glass pane. After the earthquake, they arrange the Seismological Society of Japan. Members of the society labored to develop extra exact devices.
Seismology moved from a regional examine to world science when on 17 April 1889, the German scientist Ernst von Rebeur-Paschwitz recorded an earthquake utilizing two separate units, one in Potsdam and the opposite 400 kilometers away, in Wilhelmshaven, close to the North Sea. It wasn’t till Rebeur-Paschwitz learn a report within the 13 June 1889 problem of Nature about an earthquake hitting Tokyo on 18 April that he acknowledged the hyperlink to his twin readings. Based on the timing of the earthquake in Tokyo and the distinction in longitude, Rebeur-Paschwitz calculated that his devices recorded the shock wave by means of the Earth simply over an hour after it struck Tokyo. His outcomes, together with photos of his seismograms, have been printed as a letter to the editor within the 25 July 1889 problem of Nature.
At the 1895 International Geographical Congress, Rebeur-Paschwitz proposed establishing a worldwide community of seismological stations. Although he died later that yr, John Milne took up the trigger when he returned to England from Japan. That community registered the large Kanto earthquake in 1923 and first alerted the worldwide neighborhood of the necessity to ship help.
What is the legacy of the Great Kanto Earthquake?
And so, during the last century and a half, seismographs have moved from pendulum-driven units to optical mirror units to the trendy commonplace of an electromagnetic system. Earthquake-prone areas have invested closely in making their buildings and infrastructure as earthquake-resilient as attainable. A couple of locations, akin to Japan, have additionally deployed automated early-warning techniques, to offer at the least a couple of minutes’ discover of impending quakes, as IEEE Spectrum’s Jean Kumagai has reported.
One of the easier technological responses to the Great Kanto Earthquake was the invention of the seismic fuel shutoff valve, or SGSV. This mechanical system mechanically closes pure fuel traces when a big earthquake strikes. It must be manually reset after water mains and fuel traces have been checked and, if vital, repaired. Modern constructing codes in earthquake-prone areas in Japan, the United States, Italy, and elsewhere typically require SGSVs, though varied constituents have fought towards the mandate. The twin earthquakes that struck Turkey and Syria on 6 February this yr present the bodily devastation and accompanying demise toll that may happen when constructing codes are ignored and never enforced.
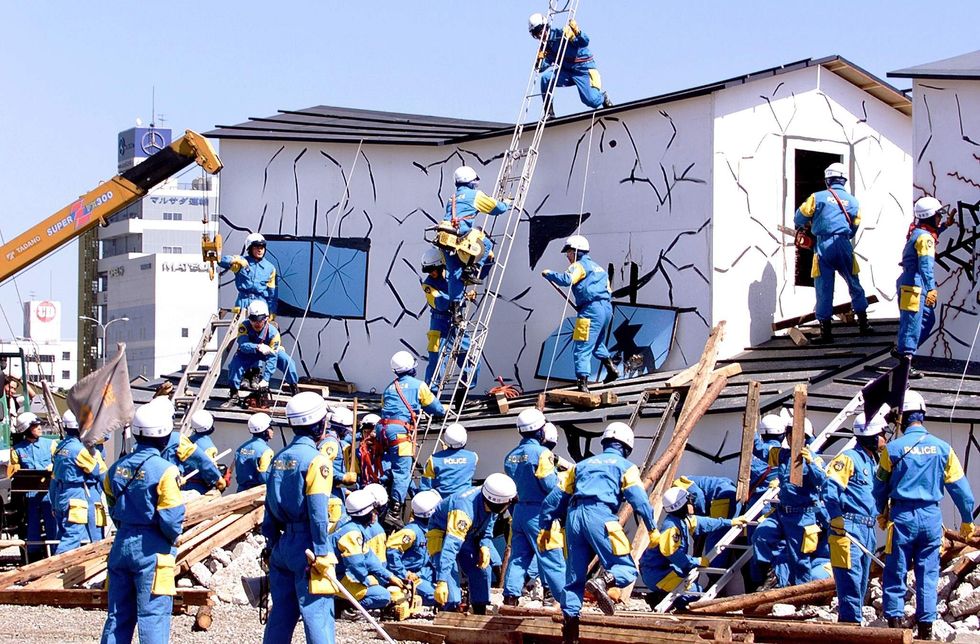

On 1 September, the Japanese authorities conducts earthquake preparedness drills, like this one in Tokyo, as a part of its commemoration of the Great Kanto earthquake.
Kazuhiro Nogi/AFP/ Getty Images
Cultural memorials are one other means society responds to earthquake disasters. In 1931, the federal government of Tokyo opened the Earthquake Memorial Hall and Earthquake Reconstruction Memorial Museum in Yokoamicho Park. The memorial corridor holds the cremated stays of greater than 58,000 individuals who died within the Great Kanto earthquake. The museum, in the meantime, homes tons of of artifacts marking the second of destruction, akin to mangled workplace gear melted within the fires, in addition to pictures and art work documenting the occasion, together with the seismograph at prime.
In 1951, the memorial corridor and the museum have been renamed the Tokyo Metropolitan Reconstruction Memorial Hall and the Tokyo Reconstruction Memorial Museum, and their missions expanded to memorialize the victims of World War II bombing raids. This distinctive museum focuses on the harmful fires that twice destroyed Japan’s capital and the city redevelopment that resulted.
Since 1960, the Japanese authorities has designated 1 September as Disaster Prevention Day to mourn these misplaced in pure disasters, rejoice first responders, and conduct drills for earthquakes, tsunamis, and typhoons.
Part of a persevering with collectiontaking a look at historic artifacts that embrace the boundless potential of expertise.
An abridged model of this text seems within the September 2023 print problem as “The Earthquake That Was Too Big to Measure.”
From Your Site Articles
Related Articles Around the Web
[ad_2]
