[ad_1]
A brand new Comcast examine hints at a serious threat to companies, governments and public methods on account of poor cybersecurity within the booming Internet of Things business.

With the speedy growth of Internet-connected units, each shopper and industrial, the cyber-threat panorama is rising quicker than people’ capacity to maintain up. Consumer prowess at noticing threats, a lot much less defending towards them, is lagging. With shoppers detached about securing their internet touchpoints comes dangers to commerce in addition to private and non-private infrastructure and methods.
Comcast’s biennial tackle shopper cyber well being, the 2022 Xfinity Cyber Health Report, discovered that there are a mean of 15 linked units per family, up 25% from 2020 — with “power users” having as many as 34.
Home IoT: Backdoor to infrastructure assaults
The implications will not be simply dire for people: Vulnerabilities at any node — whether or not a house local weather management system, automotive, or main equipment — can function entry factors for menace actors, in keeping with Yury Dvorkin of Johns Hopkins University’s Ralph O’Connor Sustainable Energy Institute, an professional on energy infrastructure and cyber-physical resiliency.
SEE: Internet of Things (IoT) cheat sheet: Complete information for 2022 (TechRepublic)
“The hypothesis that such IoT devices can be hacked at scale is something that underpins our work on EV security,” Dvorkin mentioned.
Dvorkin co-authored analysis on how EVs and different excessive wattage home equipment will be topic to demand-side cyberattacks with implications for the grid. This is as a result of they’ve IoT communication and management interfaces, together with integration with smartphone apps.
The poster-child for IoT vulnerabilities would possibly nicely be the notorious Mirai botnet DDoS assault that in 2016 contaminated over a half-million IoT units with factory-set default authentication credentials. The assault on the Dyn DNS supplier briefly took down Airbnb, PayPal and Twitter, and it price Dyn roughly 8% of its clients.
“An attacker can potentially modify the power consumption of compromised IoT-controlled loads to maliciously cause load shedding, reduce security margins or even trigger a cascading failure,” Dvorkin mentioned.
Why you’re underestimating the cybersecurity threat
Noopur Davis, chief data safety and product privateness officer at Comcast, wrote within the examine that the speedy cultural shift to distant and hybrid work and the evolution and progress of IoT has “continued to blur the lines between our professional and private lives, which — unknowingly to many — create new vulnerabilities and openings for cybercriminals” (Figure A).
Figure A
In the paper, which mixes knowledge from a brand new shopper survey with menace knowledge collected by Comcast’s Xfinity’s xFi Advanced Security platform:
- 58% of survey respondents reported that they plan to purchase not less than one linked system throughout the upcoming vacation purchasing season.
- 61% both considerably, strongly or fully imagine (erroneously) that new good house units are shielded from most cyber threats by default.
- 78% of respondents admitted to dangerous on-line behaviors that open them as much as cyber threats, similar to reusing or sharing passwords and skipping software program updates — a 14% p.c improve from simply two years in the past
- When requested how quickly they might know whether or not they had been a sufferer of a cyberattack, solely 20% mentioned instantly, whereas roughly one-third (32%) of shoppers mentioned they aren’t positive they’d ever know in the event that they had been a sufferer of a cyberattack and 51% of respondents famous they aren’t actually assured that they might know if a non-screen system was hacked.
- Three-quarters of Americans wrongly imagine that fewer than 10 assaults hit their house community each month — Comcast reported that safety protocols block a mean of 23 distinctive threats per family every month, with the overall variety of assaults truly touchdown at three-to-four instances that quantity, as many assaults are repeated.
SEE: Top 5 methods industrial IoT differs from IoT (TechRepublic)
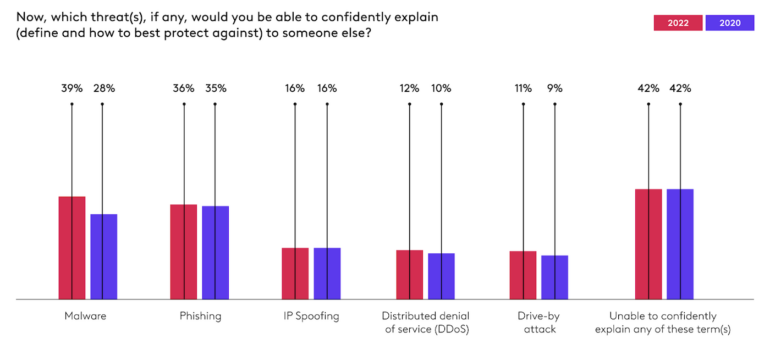
On the plus aspect, the examine discovered an enchancment in folks’s common consciousness of threats: In the 2020 examine, 53% of respondents had heard of phishing, however solely 28% believed they might confidently describe what it’s. In the brand new survey, 71% of respondents mentioned they’ve heard of phishing, with 39% noting they’d be capable to confidently clarify it (Figure B).
Figure B

Generational variations in private cybersecurity
Nearly three-quarters of child boomers mentioned they take such dangers as reusing passwords and declining multifactor authentication, however 80% of Generation X, 82% of millennials and 87% of Generation Z mentioned the identical.
A bit over three quarters of millennials surveyed mentioned they’re most probably to buy a sensible system this vacation season, together with new smartphones, laptops and gaming consoles. Only 56% of Gen Z respondents reported that that they had heard of malware, and solely 38% had heard of phishing. By distinction, 72% of millennials have heard of malware and 65% of phishing.
Defending your enterprise towards dangers
You can’t management who’s attacking you and from which route they’re approaching, however there are a number of methods to cut back your group’s publicity by taking such actions as conducting safety threat assessments, figuring out which dangers are distinctive to your operation and conducting an asset stock. To discover ways to scale back safety dangers in your group, obtain these greatest practices.
[ad_2]
