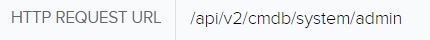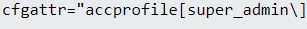[ad_1]
Executive abstract:
Fortinet’s latest vulnerability, CVE-2022-40684, permitting for authentication bypass to control admin SSH keys, unauthorized downloading of configuration information, and creating of tremendous admin accounts, is put an enormous goal on the again’s of unpatched and uncovered Fortinet gadgets.
An AT&T Managed Extended Detection and Response (MXDR) buyer was concerned in a real optimistic compromise that was found by means of a risk hunt initiated off an Intrusion Protection System (IPS) alert from Fortinet. With coordination between buyer and MXDR and the client’s community and safety groups, the risk was remediated and contained, and the susceptible gadgets have been patched.
Investigation
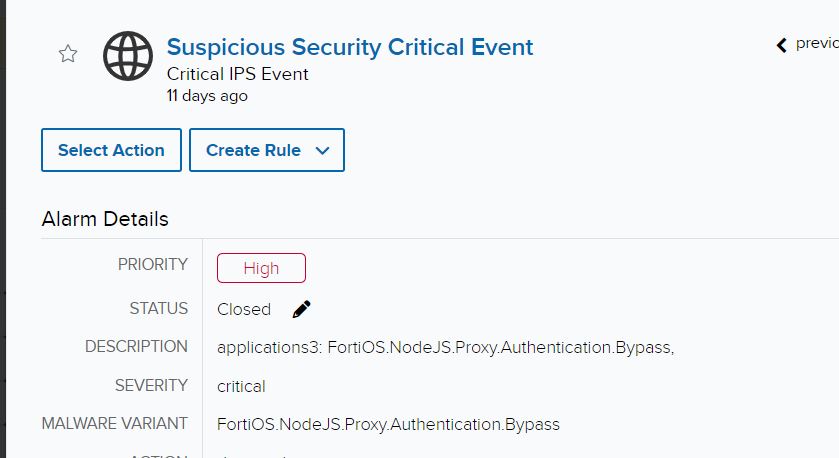
The preliminary investigation started throughout a tactical check-in with the client, who talked about an investigation relating to an IPS detection for 2 IP addresses that have been making an attempt the authentication bypass exploit.
If we pivot to the occasion, we are able to see Fortinet created detections for probably unauthorized API requests to the cmdb filepath.
Through Fortinet’s advisory on the vulnerability, we discovered that potential malicious exercise would originate from a consumer Local_Process_Access and would make the most of the Node.js or Report Runner interface. Reports point out that a number of the handlers for API connections test sure circumstances, together with IP deal with being a loopback deal with and User-Agent being both Report Runner or Node.js. Off that data, we’re in a position to flip our consideration to potential true positives that weren’t picked up by the IPS. Doing a fast filter on the Local_Process_Access consumer produced some fascinating occasions:
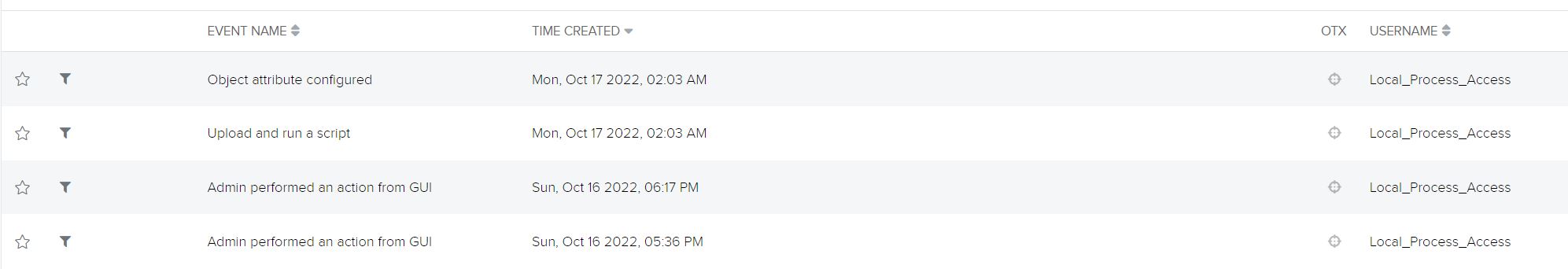
This doesn’t look good. The first occasion we are able to see the attacker handle to efficiently obtain the Local Certificate:
This permits the attacker to see certificates data similar to e-mail deal with for the certificates proprietor, IP deal with of the Fortigate, firm title, location the place the Fortigate was put in, and different delicate particulars. These native certificates a generated and offered to the Certificate Authority (CA) for atmosphere belief.
Shortly after, the attacker managed to obtain the system config of the Fortigate:
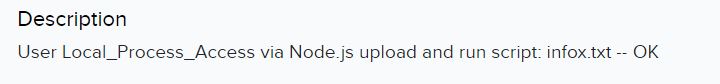
Finally, just a few hours later they managed to add a script and run it to create a super_admin consumer:
This is the place the observable exercise ended from the Local_Process_User and newly created admin account. Remediation started at this level.
Response
After discovery of the administrator account, a community administrator was urgently contacted and was in a position to take away the account. During the remediation course of, the community administrator noticed that the administration port’s exterior interface had HTTPS open, which is probably going how the attacker gained the preliminary foothold. It’s believed the super_admin account that was created was for use as a backdoor in case the machine was patched, as no exercise was seen from the account after creation. The script utilized by the attacker was not recovered, however following its add and execution it was doubtless simply used to create the admin account.
Importance of patching:
Fortinet did launch a patch the day this vulnerability was introduced, in addition to mitigation steps if patching was not instantly possible. One of the mitigation steps was to disable HTTPS/HTTP on the exterior going through administration interface if not wanted. The Fortinet Fortigate in query was the one machine that had the administration interface open, and thus allowed the attacker a simple path to take advantage of the vulnerability.
As a results of the detection of this exercise by means of risk searching by means of buyer logs, extra correlation logic was created for the USM Anywhere platform to detect future compromises.
[ad_2]