[ad_1]
Within our lifetimes, we are going to see robotic applied sciences that may assist with on a regular basis actions, enhancing human productiveness and high quality of life. Before robotics will be broadly helpful in serving to with sensible day-to-day duties in people-centered areas — areas designed for folks, not machines — they want to have the ability to safely & competently present help to folks.
In 2022, we centered on challenges that include enabling robots to be extra useful to folks: 1) permitting robots and people to speak extra effectively and naturally; 2) enabling robots to grasp and apply widespread sense data in real-world conditions; and three) scaling the variety of low-level abilities robots have to successfully carry out duties in unstructured environments.
An undercurrent this previous yr has been the exploration of how giant, generalist fashions, like PaLM, can work alongside different approaches to floor capabilities permitting robots to be taught from a breadth of human data and permitting folks to have interaction with robots extra naturally. As we do that, we’re reworking robotic studying right into a scalable information downside in order that we are able to scale studying of generalized low-level abilities, like manipulation. In this weblog put up, we’ll overview key learnings and themes from our explorations in 2022.
Bringing the capabilities of LLMs to robotics
An unimaginable characteristic of huge language fashions (LLMs) is their capacity to encode descriptions and context right into a format that’s comprehensible by each folks and machines. When utilized to robotics, LLMs let folks job robots extra simply — simply by asking — with pure language. When mixed with imaginative and prescient fashions and robotics studying approaches, LLMs give robots a approach to perceive the context of an individual’s request and make selections about what actions must be taken to finish it.
One of the underlying ideas is utilizing LLMs to immediate different pretrained fashions for data that may construct context about what is occurring in a scene and make predictions about multimodal duties. This is much like the socratic methodology in educating, the place a instructor asks college students questions to steer them via a rational thought course of. In “Socratic Models”, we confirmed that this method can obtain state-of-the-art efficiency in zero-shot picture captioning and video-to-text retrieval duties. It additionally permits new capabilities, like answering free-form questions on and predicting future exercise from video, multimodal assistive dialogue, and as we’ll focus on subsequent, robotic notion and planning.
In “Towards Helpful Robots: Grounding Language in Robotic Affordances”, we partnered with Everyday Robots to floor the PaLM language mannequin in a robotics affordance mannequin to plan lengthy horizon duties. In earlier machine-learned approaches, robots have been restricted to quick, hard-coded instructions, like “Pick up the sponge,” as a result of they struggled with reasoning concerning the steps wanted to finish a job — which is even tougher when the duty is given as an summary objective like, “Can you help clean up this spill?”
| With PaLM-SayCan, the robotic acts because the language mannequin’s “arms and eyes,” whereas the language mannequin provides high-level semantic data concerning the job. |
For this method to work, one must have each an LLM that may predict the sequence of steps to finish lengthy horizon duties and an affordance mannequin representing the talents a robotic can really do in a given state of affairs. In “Extracting Skill-Centric State Abstractions from Value Functions”, we confirmed that the worth operate in reinforcement studying (RL) fashions can be utilized to construct the affordance mannequin — an summary illustration of the actions a robotic can carry out underneath completely different states. This lets us join long-horizons of real-world duties, like “tidy the living room”, to the short-horizon abilities wanted to finish the duty, like appropriately selecting, putting, and arranging gadgets.
Having each an LLM and an affordance mannequin doesn’t imply that the robotic will really be capable to full the duty efficiently. However, with Inner Monologue, we closed the loop on LLM-based job planning with different sources of knowledge, like human suggestions or scene understanding, to detect when the robotic fails to finish the duty appropriately. Using a robotic from Everyday Robots, we present that LLMs can successfully replan if the present or earlier plan steps failed, permitting the robotic to get well from failures and full advanced duties like “Put a coke within the high drawer,” as proven within the video under.
| With PaLM-SayCan, the robotic acts because the language mannequin’s “arms and eyes,” whereas the language mannequin provides high-level semantic data concerning the job. |
An emergent functionality from closing the loop on LLM-based job planning that we noticed with Inner Monologue is that the robotic can react to modifications within the high-level objective mid-task. For instance, an individual would possibly inform the robotic to vary its habits as it’s taking place, by providing fast corrections or redirecting the robotic to a different job. This habits is particularly helpful to let folks interactively management and customise robotic duties when robots are working close to folks.
While pure language makes it simpler for folks to specify and modify robotic duties, one of many challenges is with the ability to react in actual time to the total vocabulary folks can use to explain duties {that a} robotic is able to doing. In “Talking to Robots in Real Time”, we demonstrated a large-scale imitation studying framework for producing real-time, open-vocabulary, language-conditionable robots. With one coverage we have been in a position to handle over 87,000 distinctive directions, with an estimated common success charge of 93.5%. As a part of this undertaking, we launched Language-Table, the most important out there language-annotated robotic dataset, which we hope will drive additional analysis centered on real-time language-controllable robots.
 |
| Examples of lengthy horizon objectives reached underneath actual time human language steerage. |
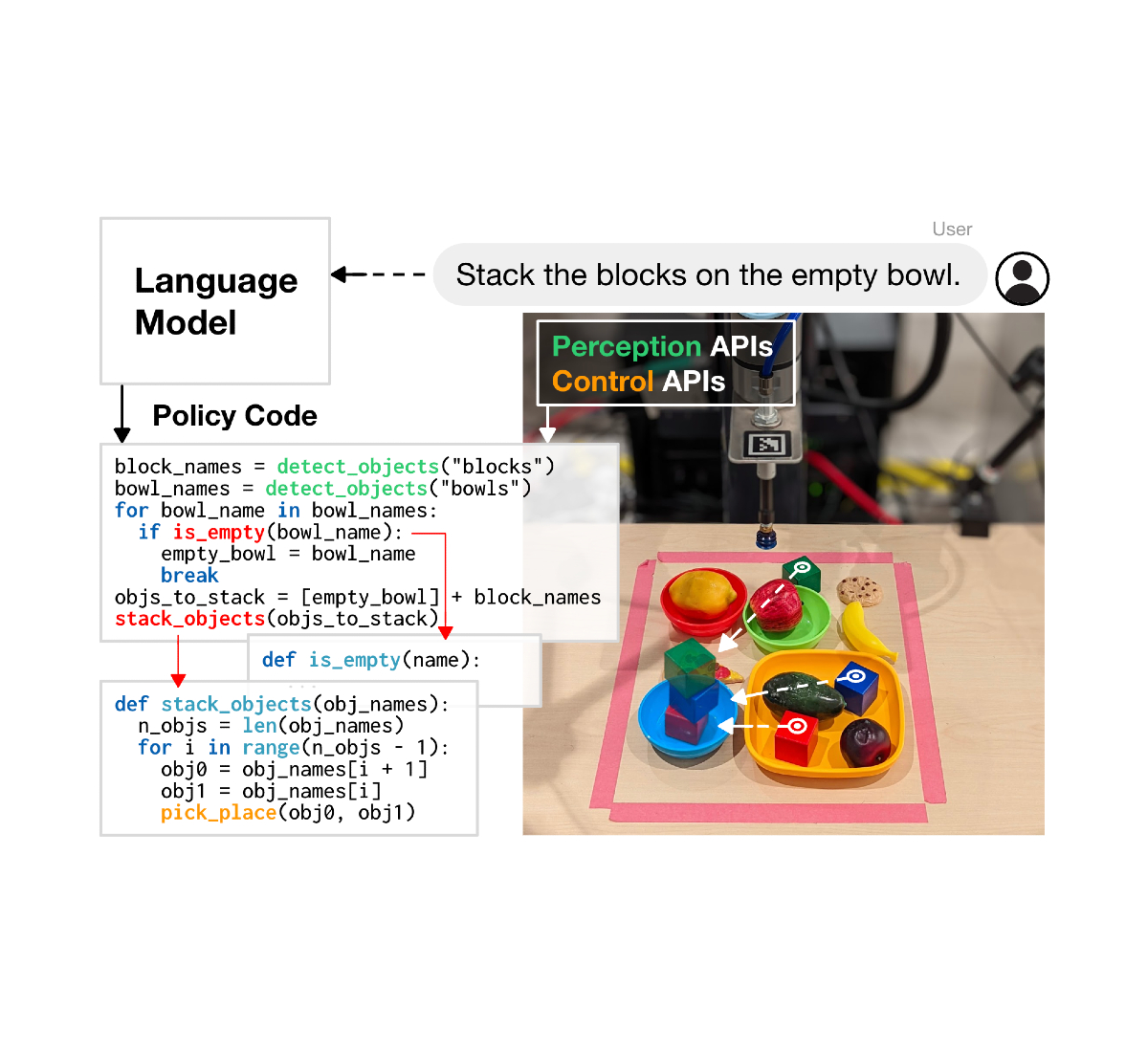
We’re additionally excited concerning the potential for LLMs to write down code that may management robotic actions. Code-writing approaches, like in “Robots That Write Their Own Code”, present promise in rising the complexity of duties robots can full by autonomously producing new code that re-composes API calls, synthesizes new capabilities, and expresses suggestions loops to assemble new behaviors at runtime.
Turning robotic studying right into a scalable information downside
Large language and multimodal fashions assist robots perceive the context wherein they’re working, like what’s taking place in a scene and what the robotic is anticipated to do. But robots additionally want low-level bodily abilities to finish duties within the bodily world, like selecting up and exactly putting objects.
While we frequently take these bodily abilities without any consideration, executing them tons of of occasions day-after-day with out even considering, they current vital challenges to robots. For instance, to select up an object, the robotic must understand and perceive the surroundings, motive concerning the spatial relation and call dynamics between its gripper and the article, actuate the excessive degrees-of-freedom arm exactly, and exert the correct quantity of pressure to stably grasp the article with out breaking it. The problem of studying these low-level abilities is called Moravec’s paradox: reasoning requires little or no computation, however sensorimotor and notion abilities require huge computational assets.
Inspired by the current success of LLMs, which reveals that the generalization and efficiency of huge Transformer-based fashions scale with the quantity of information, we’re taking a data-driven method, turning the issue of studying low-level bodily abilities right into a scalable information downside. With Robotics Transformer-1 (RT-1), we skilled a robotic manipulation coverage on a large-scale, real-world robotics dataset of 130k episodes that cowl 700+ duties utilizing a fleet of 13 robots from Everyday Robots and confirmed the identical pattern for robotics — rising the size and variety of information improves the mannequin capacity to generalize to new duties, environments, and objects.
 |
| Example PaLM-SayCan-RT1 executions of long-horizon duties in actual kitchens. |
Behind each language fashions and lots of of our robotics studying approaches, like RT-1, are Transformers, which permit fashions to make sense of Internet-scale information. Unlike LLMs, robotics is challenged by multimodal representations of regularly altering environments and restricted compute. In 2020, we launched Performers as an method to make Transformers extra computationally environment friendly, which has implications for a lot of functions past robotics. In Performer-MPC, we utilized this to introduce a brand new class of implicit management insurance policies combining the advantages of imitation studying with the sturdy dealing with of system constraints from Model Predictive Control (MPC). We present a >40% enchancment on the robotic reaching its objective and a >65% enchancment on social metrics when navigating round people compared to a regular MPC coverage. Performer-MPC gives 8 ms latency for the 8.3M parameter mannequin, making on-robot deployment of Transformers sensible.
 |
| Navigation robotic maneuvering via extremely constrained areas utilizing: Regular MPC, Explicit Policy, and Performer-MPC. |
In the final yr, our staff has proven that data-driven approaches are usually relevant on completely different robotic platforms in various environments to be taught a variety of duties, together with cellular manipulation, navigation, locomotion and desk tennis. This reveals us a transparent path ahead for studying low-level robotic abilities: scalable information assortment. Unlike video and textual content information that’s ample on the Internet, robotic information is extraordinarily scarce and exhausting to amass. Finding approaches to gather and effectively use wealthy datasets consultant of real-world interactions is the important thing for our data-driven approaches.
Simulation is a quick, protected, and simply parallelizable choice, however it’s tough to duplicate the total surroundings, particularly physics and human-robot interactions, in simulation. In i-Sim2Real, we confirmed an method to deal with the sim-to-real hole and be taught to play desk tennis with a human opponent by bootstrapping from a easy mannequin of human habits and alternating between coaching in simulation and deploying in the actual world. In every iteration, each the human habits mannequin and the coverage are refined.
 |
| Learning to play desk tennis with a human opponent. |
While simulation helps, collecting information in the actual world is crucial for fine-tuning simulation insurance policies or adapting current insurance policies in new environments. While studying, robots are liable to failure, which may trigger harm to itself and environment — particularly within the early phases of studying the place they’re exploring work together with the world. We want to gather coaching information safely, even whereas the robotic is studying, and allow the robotic to autonomously get well from failure. In “Learning Locomotion Skills Safely in the Real World”, we launched a protected RL framework that switches between a “learner policy” optimized to carry out the specified job and a “safe recovery policy” that forestalls the robotic from unsafe states. In “Legged Robots that Keep on Learning”, we skilled a reset coverage so the robotic can get well from failures, like studying to face up by itself after falling.
| Automatic reset insurance policies allow the robotic to proceed studying in a lifelong style with out human supervision. |
While robotic information is scarce, movies of individuals performing completely different duties are ample. Of course, robots aren’t constructed like folks — so the thought of robotic studying from folks raises the issue of transferring studying throughout completely different embodiments. In “Robot See, Robot Do”, we developed Cross-Embodiment Inverse Reinforcement Learning to be taught new duties by watching folks. Instead of attempting to duplicate the duty precisely as an individual would, we be taught the high-level job goal, and summarize that data within the type of a reward operate. This kind of demonstration studying may permit robots to be taught abilities by watching movies available on the web.
We’re additionally progressing in the direction of making our studying algorithms extra information environment friendly in order that we’re not relying solely on scaling information assortment. We improved the effectivity of RL approaches by incorporating prior data, together with predictive data, adversarial movement priors, and information insurance policies. Further enhancements are gained by using a novel structured dynamical methods structure and combining RL with trajectory optimization, supported by novel solvers. These kinds of prior data helped alleviate the exploration challenges, served pretty much as good regularizers, and considerably diminished the quantity of information required. Furthermore, our staff has invested closely in additional data-efficient imitation studying. We confirmed {that a} easy imitation studying method, BC-Z, can allow zero-shot generalization to new duties that weren’t seen throughout coaching. We additionally launched an iterative imitation studying algorithm, GoalsEye, which mixed Learning from Play and Goal-Conditioned Behavior Cloning for high-speed and high-precision desk tennis video games. On the theoretical entrance, we investigated dynamical-systems stability for characterizing the pattern complexity of imitation studying, and the function of capturing failure-and-recovery inside demonstration information to higher situation offline studying from smaller datasets.
Closing
Advances in giant fashions throughout the sphere of AI have spurred a leap in capabilities for robotic studying. This previous yr, we’ve seen the sense of context and sequencing of occasions captured in LLMs assist clear up long-horizon planning for robotics and make robots simpler for folks to work together with and job. We’ve additionally seen a scalable path to studying sturdy and generalizable robotic behaviors by making use of a transformer mannequin structure to robotic studying. We proceed to open supply information units, like “Scanned Objects: A Dataset of 3D-Scanned Common Household Items”, and fashions, like RT-1, within the spirit of taking part within the broader analysis group. We’re enthusiastic about constructing on these analysis themes within the coming yr to allow useful robots.
Acknowledgements
We want to thank everybody who supported our analysis. This consists of the complete Robotics at Google staff, and collaborators from Everyday Robots and Google Research. We additionally wish to thank our exterior collaborators, together with UC Berkeley, Stanford, Gatech, University of Washington, MIT, CMU and U Penn.
Google Research, 2022 & past
This was the sixth weblog put up within the “Google Research, 2022 & Beyond” collection. Other posts on this collection are listed within the desk under:
| * Articles might be linked as they’re launched. |

