[ad_1]
A brand new evaluation of instruments put to make use of by the Black Basta ransomware operation has recognized ties between the menace actor and the FIN7 (aka Carbanak) group.
This hyperlink “might counsel both that Black Basta and FIN7 keep a particular relationship or that a number of people belong to each teams,” cybersecurity agency SentinelOne mentioned in a technical write-up shared with The Hacker News.
Black Basta, which emerged earlier this yr, has been attributed to a ransomware spree that has claimed over 90 organizations as of September 2022, suggesting that the adversary is each well-organized and well-resourced.
One notable side that makes the group stand out, per SentinelOne, is the truth that there have been no indicators of its operators trying to recruit associates or promoting the malware as a RaaS on darknet boards or crimeware marketplaces.
This has raised the chance that the Black Basta builders both reduce out associates from the chain and deploy the ransomware via their very own customized toolset or alternatively work with a detailed set of associates with out the necessity to market their warez.
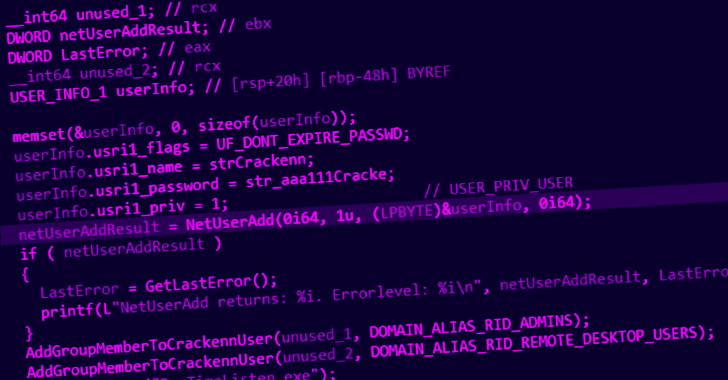
Attack chains involving Black Basta are recognized to leverage QBot (aka Qakbot), which, in flip, is delivered by the use of phishing emails containing macro-based Microsoft Office paperwork, with newer infections benefiting from ISO photographs and LNK droppers to get round Microsoft’s choice to dam macros in information downloaded from the net by default.
Once Qakbot obtains a persistent foothold within the goal setting, the Black Basta operator enters the scene to conduct reconnaissance by connecting to the sufferer via the backdoor, adopted by exploiting recognized vulnerabilities (e.g., ZeroLogon, PrintNightmare, and NoPac) to escalate privileges.
Also put to make use of at this stage are backdoors reminiscent of SystemBC (aka Coroxy) for information exfiltration and the obtain of extra malicious modules, earlier than the conducting lateral motion and taking steps to impair defenses by disabling put in safety options.
This additionally features a customized EDR evasion software that is been completely put to make use of in Black Basta incidents and comes embedded with a backdoor dubbed BIRDDOG, additionally known as as SocksBot and which has been utilized in a number of assaults beforehand attributed to the FIN7 group.
The FIN7 cybercrime syndicate, lively since 2012, has a observe file of mounting large-scale malware campaigns focusing on the point-of-sale (PoS) methods aimed on the restaurant, playing, and hospitality industries for monetary fraud.
Over the previous two years, nonetheless, the group has switched to ransomware for illicitly producing revenues, first as Darkside after which as BlackMatter and BlackCat, to not point out establishing pretend entrance corporations to recruit unwitting penetration testers to stage ransomware assaults.
“At this level, it is possible that FIN7 or an affiliate started writing instruments from scratch with a view to disassociate their new operations from the previous,” researchers Antonio Cocomazzi and Antonio Pirozzi mentioned. “It is probably going that the developer(s) behind their instruments to impair sufferer defenses is, or was, a developer for FIN7.”
The findings come weeks after the Black Basta actor was noticed utilizing the Qakbot trojan to deploy Cobalt Strike and Brute Ratel C4 frameworks as a second-stage payload in current assaults.
“The crimeware ecosystem is continually increasing, altering, and evolving,” the researchers concluded. “FIN7 (or Carbanak) is commonly credited with innovating within the felony area, taking assaults in opposition to banks and PoS methods to new heights past the schemes of their friends.”
The disclosure additionally arrives because the U.S. Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) reported a surge in ransomware assaults focusing on home entities from 487 in 2020 to 1,489 in 2021, incurring a complete value of $1.2 billion, a 188% leap from $416 million the earlier yr.
[ad_2]