[ad_1]
A newly created synthetic intelligence (AI) system primarily based on deep reinforcement studying (DRL) can react to attackers in a simulated surroundings and block 95% of cyberattacks earlier than they escalate.
That’s in line with the researchers from the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory who constructed an summary simulation of the digital battle between attackers and defenders in a community and educated 4 completely different DRL neural networks to maximise rewards primarily based on stopping compromises and minimizing community disruption.
The simulated attackers used a collection of ways primarily based on the MITRE ATT&CK framework’s classification to maneuver from the preliminary entry and reconnaissance part to different assault phases till they reached their objective: the impression and exfiltration part.
The profitable coaching of the AI system on the simplified assault surroundings demonstrates that defensive responses to assaults in actual time may very well be dealt with by an AI mannequin, says Samrat Chatterjee, a knowledge scientist who offered the group’s work on the annual assembly of the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence in Washington, DC on Feb. 14.
“You do not wish to transfer into extra advanced architectures when you can not even present the promise of those methods,” he says. “We needed to first exhibit that we will truly practice a DRL efficiently and present some good testing outcomes, earlier than transferring ahead.”
The software of machine studying and synthetic intelligence methods to completely different fields inside cybersecurity has grow to be a scorching pattern over the previous decade, from the early integration of machine studying in electronic mail safety gateways within the early 2010s to newer efforts to use ChatGPT to research code or conduct forensic evaluation. Now, most safety merchandise have — or declare to have — just a few options powered by machine studying algorithms educated on massive datasets.
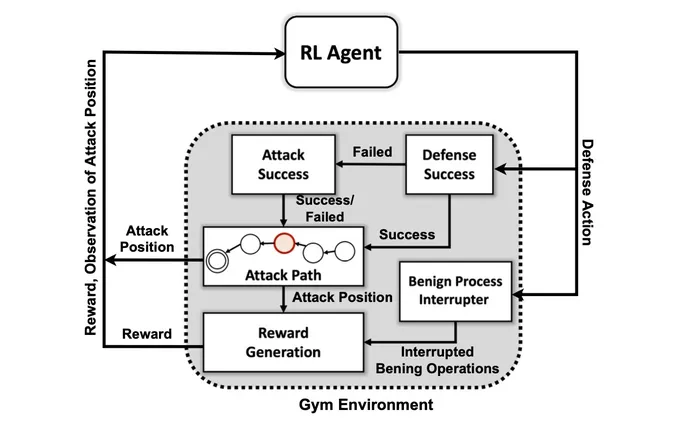
Yet creating an AI system able to proactive protection continues to be aspirational, relatively than sensible. While quite a lot of hurdles stay for researchers, the PNNL analysis exhibits that an AI defender may very well be doable sooner or later.
“Evaluating a number of DRL algorithms educated beneath numerous adversarial settings is a vital step towards sensible autonomous cyber protection options,” the PNNL analysis group acknowledged of their paper. “Our experiments recommend that model-free DRL algorithms could be successfully educated beneath multi-stage assault profiles with completely different talent and persistence ranges, yielding favorable protection outcomes in contested settings.”
How the System Uses MITRE ATT&CK
The first objective of the analysis group was to create a customized simulation surroundings primarily based on an open supply toolkit generally known as Open AI Gym. Using that surroundings, the researchers created attacker entities of various talent and persistence ranges with the flexibility to make use of a subset of seven ways and 15 methods from the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
The targets of the attacker brokers are to maneuver by way of the seven steps of the assault chain, from preliminary entry to execution, from persistence to command and management, and from assortment to impression.
For the attacker, adapting their ways to the state of the surroundings and the defender’s present actions could be advanced, says PNNL’s Chatterjee.
“The adversary has to navigate their means from an preliminary recon state all the best way to some exfiltration or impression state,” he says. “We’re not making an attempt to create a type of mannequin to cease an adversary earlier than they get contained in the surroundings — we assume that the system is already compromised.”
The researchers used 4 approaches to neural networks primarily based on reinforcement studying. Reinforcement studying (RL) is a machine studying method that emulates the reward system of the human mind. A neural community learns by strengthening or weakening sure parameters for particular person neurons to reward higher options, as measured by a rating indicating how nicely the system performs.
Reinforcement studying primarily permits the pc to create a superb, however not good, method to the issue at hand, says Mahantesh Halappanavar, a PNNL researcher and an creator of the paper.
“Without utilizing any reinforcement studying, we might nonetheless do it, however it will be a extremely large drawback that won’t have sufficient time to really give you any good mechanism,” he says. “Our analysis … provides us this mechanism the place deep reinforcement studying is type of mimicking a number of the human conduct itself, to some extent, and it will probably discover this very huge area very effectively.”
Not Ready for Prime Time
The experiments discovered {that a} particular reinforcement studying methodology, generally known as a Deep Q Network, created a powerful answer to the defensive drawback, catching 97% of the attackers within the testing information set. Yet the analysis is simply the beginning. Security professionals mustn’t search for an AI companion to assist them do incident response and forensics anytime quickly.
Among the numerous issues that stay to be solved is getting reinforcement studying and deep neural networks to clarify the elements that influenced their choices, an space of analysis known as explainable reinforcement studying (XRL).
In addition, the robustness of the AI algorithms and discovering environment friendly methods of coaching the neural networks are each issues that should be solved, says PNNL’s Chatterjee.
“Creating a product— that was not the principle motivation for this analysis,” he says. “This was extra about scientific experimentation and algorithmic discovery.”
