[ad_1]
Microsoft on Tuesday disclosed it took steps to implement blocking protections and droop accounts that had been used to publish malicious drivers that had been licensed by its Windows Hardware Developer Program.
The tech large stated its investigation revealed the exercise was restricted to a variety of developer program accounts and that no additional compromise was detected.
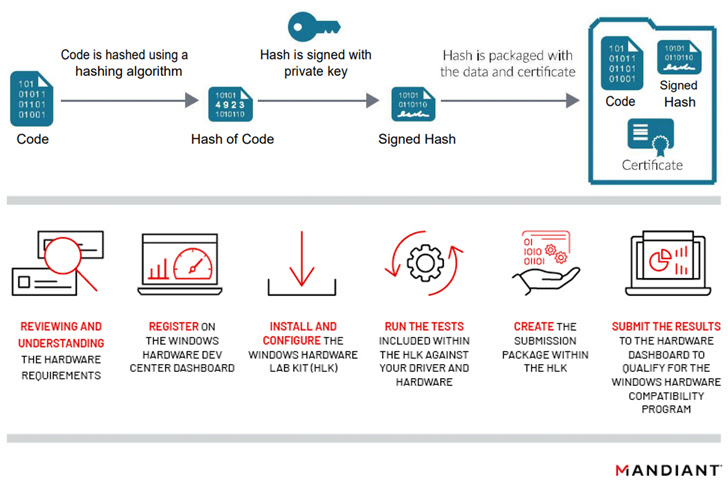
Cryptographically signing malware is regarding not least as a result of it not solely undermines a key safety mechanism but additionally permits risk actors to subvert conventional detection strategies and infiltrate goal networks to carry out extremely privileged operations.
The probe, Redmond acknowledged, was initiated after it was notified of rogue drivers being utilized in post-exploitation efforts, together with deploying ransomware, by cybersecurity companies Mandiant, SentinelOne, and Sophos on October 19, 2022.
One notable side of those assaults was that the adversary had already obtained administrative privileges on compromised techniques earlier than utilizing the drivers.
“Several developer accounts for the Microsoft Partner Center had been engaged in submitting malicious drivers to acquire a Microsoft signature,” Microsoft defined. “A brand new try at submitting a malicious driver for signing on September 29, 2022, led to the suspension of the sellers’ accounts in early October.”
According to an evaluation from Sophos, risk actors affiliated with the Cuba ransomware (aka COLDDRAW) planted a malicious signed driver in a failed try at disabling endpoint detection instruments by way of a novel malware loader dubbed BURNTCIGAR, which was first revealed by Mandiant in February 2022.
The firm additionally recognized three variants of the driving force signed by code signing certificates that belong to 2 Chinese firms, Zhuhai Liancheng Technology and Beijing JoinHope Image Technology.
The reasoning behind utilizing signed drivers is that it presents a approach for risk actors to get round essential safety measures which require kernel-mode drivers to be signed to ensure that Windows to load the bundle. What’s extra, the method misuses the de facto belief safety instruments place in Microsoft-attested drivers to their benefit.
“Threat actors are shifting up the belief pyramid, making an attempt to make use of more and more extra well-trusted cryptographic keys to digitally signal their drivers,” Sophos researchers Andreas Klopsch and Andrew Brandt stated. “Signatures from a big, reliable software program writer make it extra possible the driving force will load into Windows with out hindrance.”
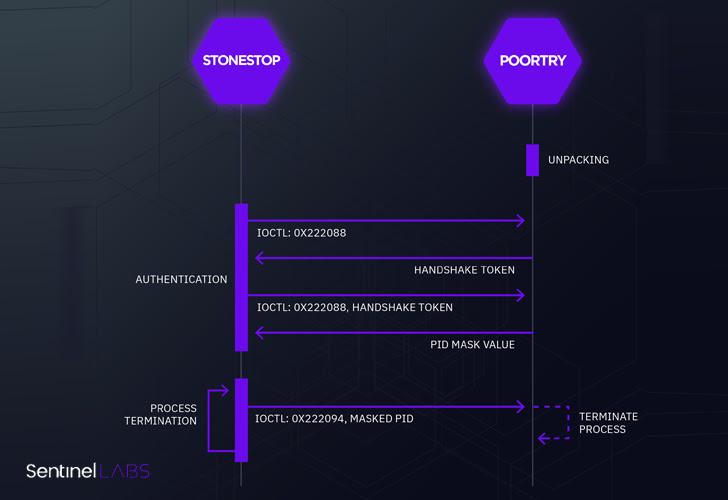
Google-owned Mandiant, in a coordinated disclosure, stated it noticed a financially motivated risk group often called UNC3944 using a loader named STONESTOP to put in a malicious driver dubbed POORTRY that is designed to terminate processes related to safety software program and delete recordsdata.
Stating that it has “regularly noticed risk actors use compromised, stolen, and illicitly bought code-signing certificates to signal malware,” the risk intelligence and incident response agency famous that “a number of distinct malware households, related to distinct risk actors, have been signed with this course of.”
This has given rise to the likelihood that these hacking teams might be leveraging a prison service for code signing (i.e., malicious driver signing as a service), whereby the supplier will get the malware artifacts signed via Microsoft’s attestation course of on behalf of the actors.
STONESTOP and POORTRY are stated to have been utilized by UNC3944 in assaults aimed toward telecommunication, BPO, MSSP, monetary providers, cryptocurrency, leisure, and transportation sectors, SentinelOne stated, including a distinct risk actor utilized an identical signed driver that resulted within the deployment of Hive ransomware.
The intrusion set recognized by SentinelOne additionally possible overlaps with a “persistent” marketing campaign orchestrated by a risk actor tracked by CrowdStrike as Scattered Spider concentrating on the identical verticals since June 2022, with a few of the assaults penetrating cellular provider networks to offer SIM swapping providers.
When reached for remark, SentinelOne instructed The Hacker News that “related targets, TTPs, and malware recommend the opportunity of a linkage with this exercise,” however emphasised that it can not affirm the analysis and that it would not have “additional particulars” to share right now.
Microsoft has since revoked the certificates for impacted recordsdata and suspended the companions’ vendor accounts to counter the threats as a part of its December 2022 Patch Tuesday replace.
This isn’t the primary time digital certificates have been abused to signal malware. Last yr, a Netfilter driver licensed by Microsoft turned out to be a malicious Windows rootkit that was noticed speaking with command-and-control (C2) servers positioned in China.
It’s not a Windows-only phenomenon, nonetheless, as Google this month revealed findings that compromised platform certificates managed by Android system makers together with Samsung and LG had been used to signal malicious apps distributed via unofficial channels.
The improvement additionally comes amid a broader abuse of signed drivers to sabotage safety software program in current months. The assault, known as Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver (BYOVD), includes exploiting official drivers that include recognized shortcomings to escalate privileges and execute post-compromise actions.
Microsoft, in late October, stated it is enabling the weak driver blocklist (saved within the “DriverSiPolicy.p7b” file) by default for all gadgets with Windows 11 2022 replace, alongside validating that it is the identical throughout completely different working system variations, following an Ars Technica report that highlighted inconsistencies in updating the blocklist for Windows 10 machines.
“Code signing mechanisms are an necessary characteristic in trendy working techniques,” SentinelOne stated. “The introduction of driver signing enforcement was key in stemming the tide of rootkits for years. The receding effectiveness of code signing represents a risk to safety and verification mechanisms in any respect OS layers.”
[ad_2]