[ad_1]
The unprecedented rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has introduced transformative potentialities throughout varied sectors, from industries and economies to societies at giant. However, this technological leap additionally introduces a set of potential challenges. In its current public assembly, the National AI Advisory Committee (NAIAC)1, which supplies suggestions on matters together with the present state of the U.S. AI competitiveness, the state of science round AI, and AI workforce points to the President and the National AI Initiative Office, has voted on a discovering primarily based on professional briefing on the potential dangers of AI and extra particularly generative AI2. This weblog put up goals to make clear these issues and delineate how DataRobot clients can proactively leverage the platform to mitigate these threats.
Understanding AI’s Potential Risks
With the swift rise of AI within the realm of know-how, it stands poised to rework sectors, streamline operations, and amplify human potential. Yet, these unmatched progressions additionally usher in a myriad of challenges that demand consideration. The “Findings on The Potential Future Risks of AI” discusses segments the danger of AI in short-term and long-term dangers of AI. The near-term dangers of AI, as described within the discovering, refers to dangers related to AI which are well-known and present issues for AI, whether or not predictive or generative AI. On the opposite hand, long-term dangers of AI underscores the potential dangers of AI that will not materialize given the present state of AI know-how or effectively understood however we must always put together for his or her potential impacts. This discovering highlights just a few classes of AI dangers – malicious goal or unintended penalties, financial and societal, and catastrophic.
Societal
While Large Language Models (LLMs) are primarily optimized for textual content prediction duties, their broader purposes don’t adhere to a singular objective. This flexibility permits them to be employed in content material creation for advertising and marketing, translation, and even in disseminating misinformation on a big scale. In some cases, even when the AI’s goal is well-defined and tailor-made for a selected objective, unexpected damaging outcomes can nonetheless emerge. In addition, as AI techniques evolve in complexity, there’s a rising concern that they may discover methods to bypass the safeguards established to watch or prohibit their habits. This is very troubling since, though people create these security mechanisms with explicit objectives in thoughts, an AI could understand them in a different way or pinpoint vulnerabilities.
Economic
As AI and automation sweep throughout varied sectors, they promise each alternatives and challenges for employment. While there’s potential for job enhancement and broader accessibility by leveraging generative AI, there’s additionally a danger of deepening financial disparities. Industries centered round routine actions may face job disruptions, but AI-driven companies might unintentionally widen the financial divide. It’s vital to spotlight that being uncovered to AI doesn’t straight equate to job loss, as new job alternatives could emerge and a few staff may see improved efficiency by AI assist. However, with out strategic measures in place—like monitoring labor tendencies, providing academic reskilling, and establishing insurance policies like wage insurance coverage—the specter of rising inequality looms, even when productiveness soars. But the implications of this shift aren’t merely monetary. Ethical and societal points are taking middle stage. Concerns about private privateness, copyright breaches, and our rising reliance on these instruments are extra pronounced than ever.
Catastrophic
The evolving panorama of AI applied sciences has the potential to achieve extra superior ranges. Especially, with the adoption of generative AI at scale, there’s rising apprehension about their disruptive potential. These disruptions can endanger democracy, pose nationwide safety dangers like cyberattacks or bioweapons, and instigate societal unrest, notably by divisive AI-driven mechanisms on platforms like social media. While there’s debate about AI reaching superhuman prowess and the magnitude of those potential dangers, it’s clear that many threats stem from AI’s malicious use, unintentional fallout, or escalating financial and societal issues.
Recently, dialogue on the catastrophic dangers of AI has dominated the conversations on AI danger, particularly with reference to generative AI. However, as was put forth by NAIAC, “Arguments about existential risk from AI should not detract from the necessity of addressing existing risks of AI. Nor should arguments about existential risk from AI crowd out the consideration of opportunities that benefit society.”3
The DataRobot Approach
The DataRobot AI Platform is an open, end-to-end AI lifecycle platform that streamlines/simplifies the way you construct, govern, and function generative and predictive AI. Designed to unify your complete AI panorama, groups and workflows, it empowers you to ship real-world worth out of your AI initiatives, whereas providing you with the flexibleness to evolve, and the enterprise management to scale with confidence.
DataRobot serves as a beacon in navigating these challenges. By championing clear AI fashions by automated documentation in the course of the experimentation and in manufacturing, DataRobot allows customers to overview and audit the constructing technique of AI instruments and its efficiency in manufacturing, which fosters belief and promotes accountable engagement. The platform’s agility ensures that customers can swiftly adapt to the quickly evolving AI panorama. With an emphasis on coaching and useful resource provision, DataRobot ensures customers are well-equipped to grasp and handle the nuances and dangers related to AI. At its core, the platform prioritizes AI security, guaranteeing that accountable AI use is not only inspired however integral from improvement to deployment.
With regards to generative AI, DataRobot has integrated a reliable AI framework in our platform. The chart beneath highlights the excessive degree view of this framework.
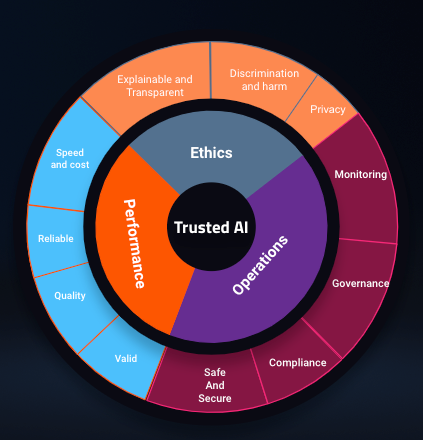
Pillars of this framework, Ethics, Performance, and Operations, have guided us to develop and embed options within the platform that help customers in addressing among the dangers related to generative AI. Below we delve deeper into every of those parts.
Ethics
AI Ethics pertains to how an AI system aligns with the values held by each its customers and creators, in addition to the real-world penalties of its operation. Within this context, DataRobot stands out as an trade chief by incorporating varied options into its platform to deal with moral issues throughout three key domains: Explainability, Discrimination and hurt mitigation, and Privacy preservation.
DataRobot straight tackles these issues by providing cutting-edge options that monitor mannequin bias and equity, apply progressive prediction rationalization algorithms, and implement a platform structure designed to maximise knowledge safety. Additionally, when orchestrating generative AI workflows, DataRobot goes a step additional by supporting an ensemble of “guard” fashions. These guard fashions play an important function in safeguarding generative use circumstances. They can carry out duties akin to subject evaluation to make sure that generative fashions keep on subject, establish and mitigate bias, toxicity, and hurt, and detect delicate knowledge patterns and identifiers that shouldn’t be utilized in workflows.
What’s notably noteworthy is that these guard fashions may be seamlessly built-in into DataRobot’s modeling pipelines, offering an additional layer of safety round Language Model (LLM) workflows. This degree of safety instills confidence in customers and stakeholders relating to the deployment of AI techniques. Furthermore, DataRobot’s sturdy governance capabilities allow steady monitoring, governance, and updates for these guard fashions over time by an automatic workflow. This ensures that moral issues stay on the forefront of AI system operations, aligning with the values of all stakeholders concerned.
Performance
AI Performance pertains to evaluating how successfully a mannequin accomplishes its supposed objective. In the context of an LLM, this might contain duties akin to responding to consumer queries, summarizing or retrieving key info, translating textual content, or avarious different use-cases. It is price noting that many current LLM deployments typically lack real-time evaluation of validity, high quality, reliability, and price. DataRobot, nonetheless, has the aptitude to watch and measure efficiency throughout all of those domains.
DataRobot’s distinctive mix of generative and predictive AI empowers customers to create supervised fashions able to assessing the correctness of LLMs primarily based on consumer suggestions. This leads to the institution of an LLM correctness rating, enabling the analysis of response effectiveness. Every LLM output is assigned a correctness rating, providing customers insights into the arrogance degree of the LLM and permitting for ongoing monitoring by the DataRobot LLM Operations (LLMOps) dashboard. By leveraging domain-specific fashions for efficiency evaluation, organizations could make knowledgeable selections primarily based on exact info.
DataRobot’s LLMOps presents complete monitoring choices inside its dashboard, together with velocity and price monitoring. Performance metrics akin to response and execution instances are repeatedly monitored to make sure well timed dealing with of consumer queries. Furthermore, the platform helps using customized metrics, enabling customers to tailor their efficiency evaluations. For occasion, customers can outline their very own metrics or make use of established measures like Flesch reading-ease to gauge the standard of LLM responses to inquiries. This performance facilitates the continued evaluation and enchancment of LLM high quality over time.
Operations
AI Operations focuses on guaranteeing ith the reliability of the system or the surroundings housing the AI know-how. This encompasses not solely the reliability of the core system but in addition the governance, oversight, upkeep, and utilization of that system, all with the overarching objective of guaranteeing environment friendly, efficient, and secure and safe operations.
With over 1 million AI tasks operationalized and delivering over 1 trillion predictions, the DataRobot platform has established itself as a sturdy enterprise basis able to supporting and monitoring a various array of AI use circumstances. The platform boasts built-in governance options that streamline improvement and upkeep processes. Users profit from customized environments that facilitate the deployment of data bases with pre-installed dependencies, expediting improvement lifecycles. Critical data base deployment actions are logged meticulously to make sure that key occasions are captured and saved for reference. DataRobot seamlessly integrates with model management, selling greatest practices by steady integration/steady deployment (CI/CD) and code upkeep. Approval workflows may be orchestrated to make sure that LLM techniques endure correct approval processes earlier than reaching manufacturing. Additionally, notification insurance policies preserve customers knowledgeable about key deployment-related actions.
Security and security are paramount issues. DataRobot employs two-factor authentication and entry management mechanisms to make sure that solely approved builders and customers can make the most of LLMs.
DataRobot’s LLMOps monitoring extends throughout varied dimensions. Service well being metrics observe the system’s means to reply rapidly and reliably to prediction requests. Crucial metrics like response time present important insights into the LLM’s capability to deal with consumer queries promptly. Furthermore, DataRobot’s customizable metrics functionality empowers customers to outline and monitor their very own metrics, guaranteeing efficient operations. These metrics might embody general value, readability, consumer approval of responses, or any user-defined standards. DataRobot’s textual content drift characteristic allows customers to watch adjustments in enter queries over time, permitting organizations to investigate question adjustments for insights and intervene in the event that they deviate from the supposed use case. As organizational wants evolve, this textual content drift functionality serves as a set off for brand new improvement actions.
DataRobot’s LLM-agnostic method presents customers the flexibleness to pick out probably the most appropriate LLM primarily based on their privateness necessities and knowledge seize insurance policies. This accommodates companions, which implement enterprise privateness, in addition to privately hosted LLMs the place knowledge seize just isn’t a priority and is managed by the LLM house owners. Additionally, it facilitates options the place community egress may be managed. Given the varied vary of purposes for generative AI, operational necessities could necessitate varied LLMs for various environments and duties. Thus, an LLM-agnostic framework and operations are important.
It’s price highlighting that DataRobot is dedicated to repeatedly enhancing its platform by incorporating extra accountable AI options into the AI lifecycle for the advantage of finish customers.
Conclusion
While AI is a beacon of potential and transformative advantages, it’s important to stay cognizant of the accompanying dangers. Platforms like DataRobot are pivotal in guaranteeing that the facility of AI is harnessed responsibly, driving real-world worth, whereas proactively addressing challenges.
1 The White House. n.d. “National AI Advisory Committee.” AI.Gov. https://ai.gov/naiac/.
2 “FINDINGS: The Potential Future Risks of AI.” October 2023. National Artificial Intelligence Advisory Committee (NAIAC). https://ai.gov/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Findings_The-Potential-Future-Risks-of-AI.pdf.
3 “STATEMENT: On AI and Existential Risk.” October 2023. National Artificial Intelligence Advisory Committee (NAIAC). https://ai.gov/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Statement_On-AI-and-Existential-Risk.pdf.
About the creator

Haniyeh is a Global AI Ethicist on the DataRobot Trusted AI staff and a member of the National AI Advisory Committee (NAIAC). Her analysis focuses on bias, privateness, robustness and stability, and ethics in AI and Machine Learning. She has a demonstrated historical past of implementing ML and AI in quite a lot of industries and initiated the incorporation of bias and equity characteristic into DataRobot product. She is a thought chief within the space of AI bias and moral AI. Haniyeh holds a PhD in Astronomy and Astrophysics from the Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn.
[ad_2]
