[ad_1]
ESET researchers present particulars on a beforehand undisclosed China-aligned APT group that we observe as PlushDaemon and considered one of its cyberespionage operations: the supply-chain compromise in 2023 of VPN software program developed by a South Korean firm, the place the attackers changed the reputable installer with one which additionally deployed the group’s signature implant that we’ve named SlowStepper – a feature-rich backdoor with a toolkit of greater than 30 elements.
Key factors of this blogpost:
- PlushDaemon is a China-aligned menace group, engaged in cyberespionage operations.
- PlushDaemon’s most important preliminary entry vector is hijacking reputable updates of Chinese purposes, however we’ve additionally uncovered a supply-chain assault in opposition to a South Korean VPN developer.
- We consider PlushDaemon is the unique person of a number of implants, together with SlowStepper for Windows.
- SlowStepper has a big toolkit composed of round 30 modules, programmed in C++, Python, and Go.
Overview
In May 2024, we seen detections of malicious code in an NSIS installer for Windows that customers from South Korea had downloaded from the web site of the reputable VPN software program IPany (https://ipany.kr/; see Figure 1), which is developed by a South Korean firm. Upon additional evaluation, we found that the installer was deploying each the reputable software program and the backdoor that we’ve named SlowStepper. We contacted the VPN software program developer to tell them of the compromise, and the malicious installer was faraway from their web site.
We attribute this operation to PlushDaemon – a China-aligned menace actor energetic since at the very least 2019, participating in espionage operations in opposition to people and entities in China, Taiwan, Hong Kong, South Korea, the United States, and New Zealand. PlushDaemon makes use of a customized backdoor that we observe as SlowStepper, and its most important preliminary entry method is to hijack reputable updates by redirecting site visitors to attacker-controlled servers. Additionally, we’ve noticed the group gaining entry through vulnerabilities in reputable net servers.
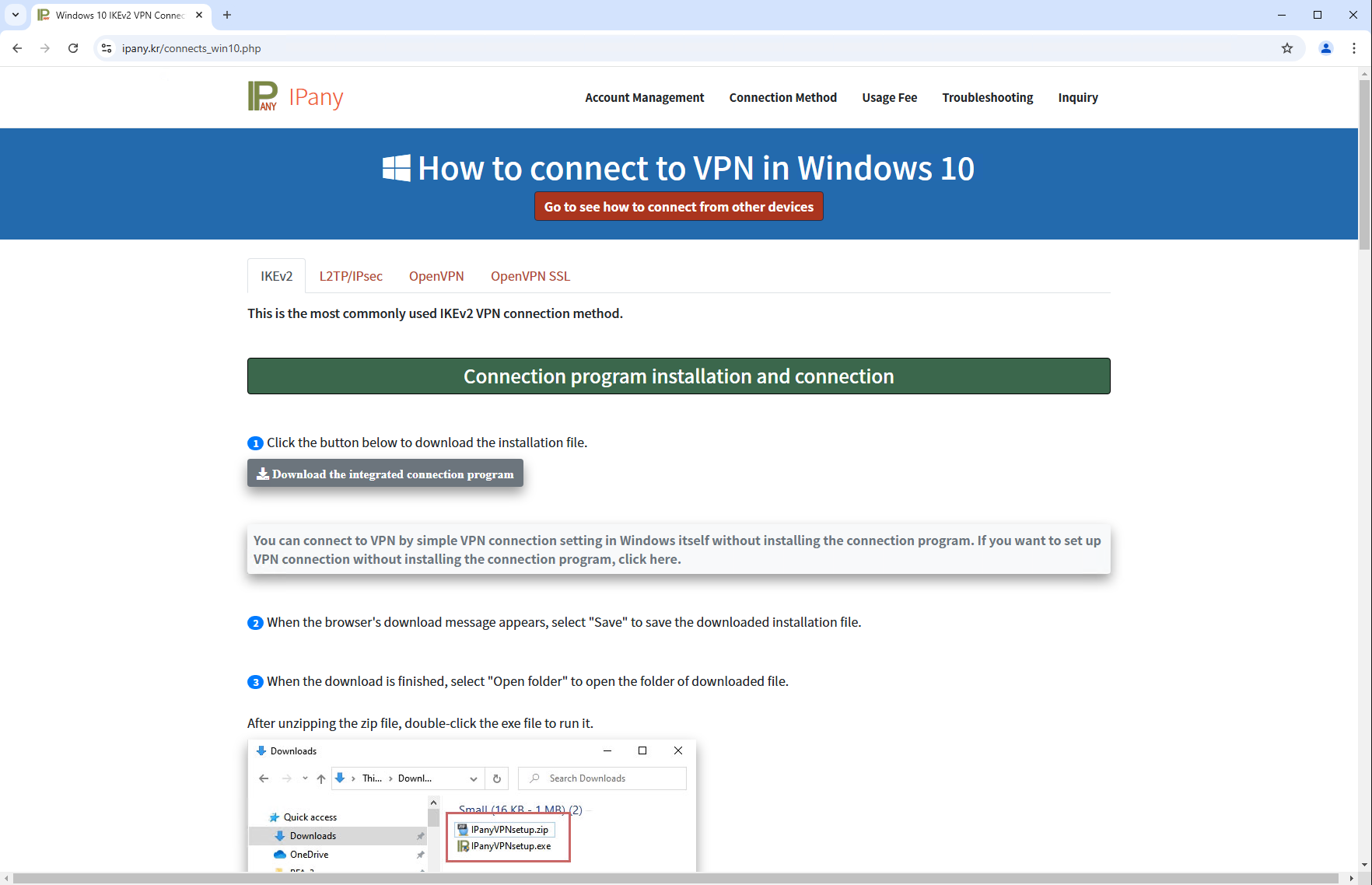
The victims seem to have manually downloaded a ZIP archive containing a malicious NSIS installer from the URL https://ipany[.]kr/download/IPanyVPNsetup.zip. We discovered no suspicious code on the obtain web page (proven in Figure 1) to provide focused downloads, for instance by geofencing to particular focused areas or IP ranges; subsequently, we consider that anybody utilizing the IPany VPN might need been a sound goal.
Via ESET telemetry, we discovered that a number of customers tried to put in the trojanized software program within the community of a semiconductor firm and an unidentified software program improvement firm in South Korea. The two oldest circumstances registered in our telemetry had been a sufferer from Japan in November 2023, and a sufferer from China in December 2023.
Technical evaluation
As illustrated in Figure 2, when the malicious IPanyVPNsetup.exe installer is executed, it creates a number of directories and deploys each reputable and malicious information.
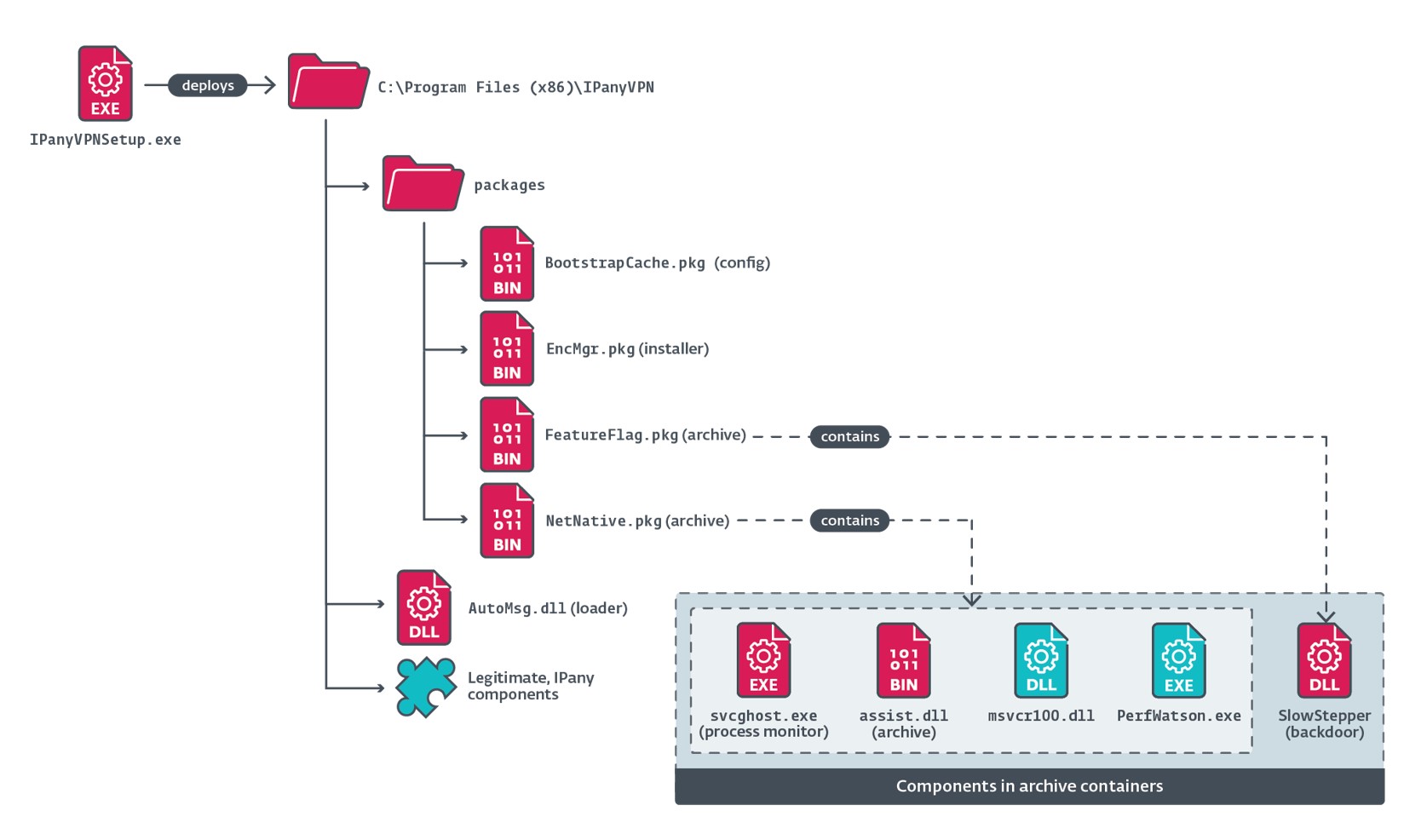
Additionally, the installer establishes persistence for SlowStepper by including an entry named IPanyVPN to a Run key, with the worth %PUBLIC%DocumentsWPSDocumentsWPSManagersvcghost.exe, in order that the malicious element svcghost.exe (later extracted and deployed by the loader in EncMgr.pkg) is launched when the working system begins.
The first malicious element that’s loaded by the installer is the AutoMsg.dll loader. Figure 3 illustrates the foremost steps taken throughout the execution of this element.
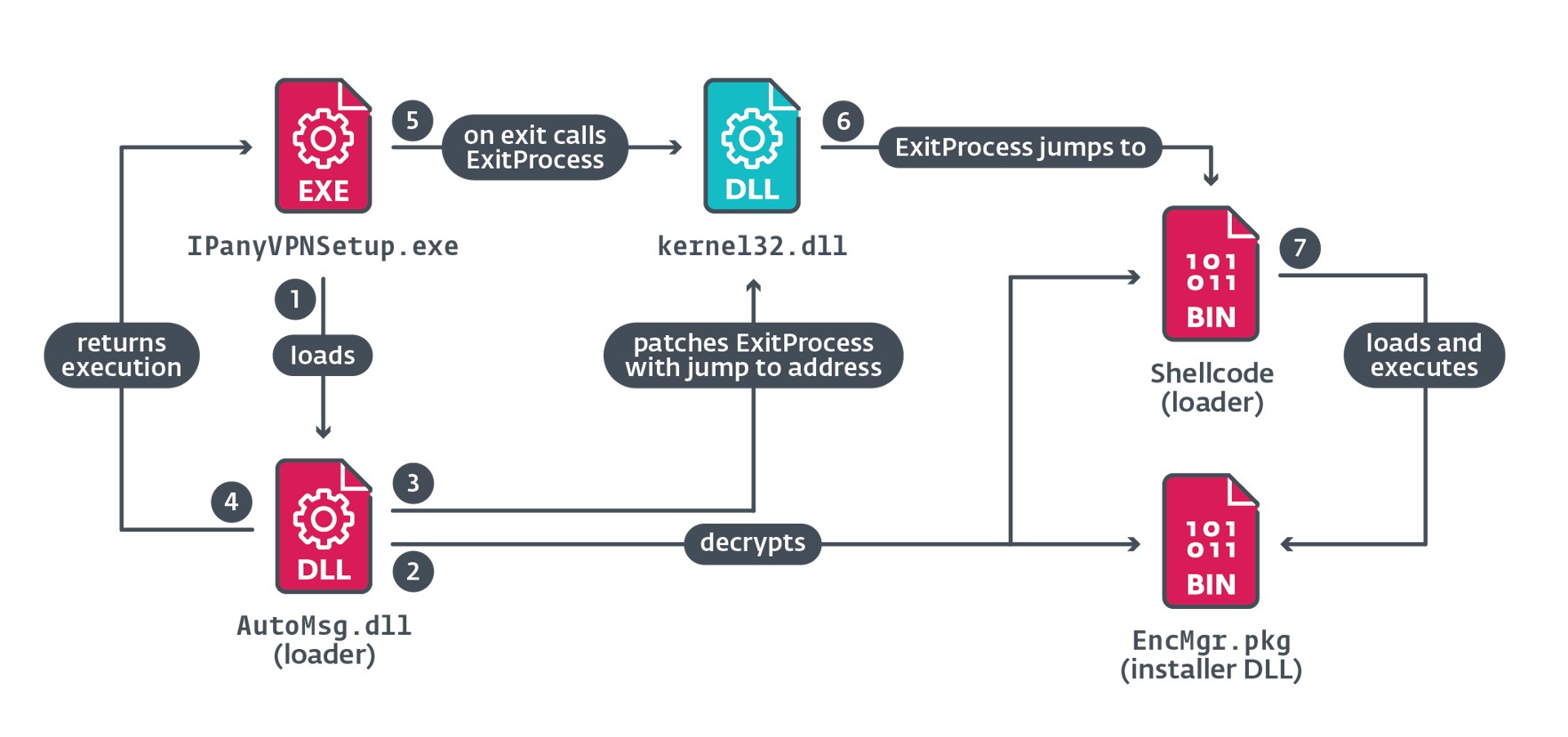
When IPanyVPNSetup.exe calls ExitProcess, the patched bytes redirect execution to the shellcode that masses EncMgr.pkg into reminiscence and executes it.
EncMgr.pkg creates two directories – WPSDocuments and WPSManager – in %PUBLIC%Documents and the deployment begins by extracting elements from the customized archives NetNative.pkg and FeatureFlag.pkg. The elements are dropped to disk and moved to different places with new filenames. The sequence and actions taken are as follows:
1. Extracts the information from NetNative.pkg to:
a. %PUBLIC%DocumentsWPSDocumentsWPSManagerassist.dll,
b. %PUBLIC%DocumentsWPSDocumentsWPSManagermsvcr100.dll,
c. %PUBLIC%DocumentsWPSDocumentsWPSManagerPerfWatson.exe, and
d. %PUBLIC%DocumentsWPSDocumentsWPSManagersvcghost.exe.
2. Deletes NetNative.pkg.
3. Moves FeatureFlag.pkg to C:ProgramDataMicrosoft SharedFiltersSystemInfowinlogin.gif.
4. Moves help.dll to C:ProgramDataMicrosoft SharedFiltersSystemInfoWinse.gif.
5. Extracts file from Winse.gif to %PUBLIC%DocumentsWPSDocumentsWPSManagerlregdll.dll.
6. Copies information from BootstrapCache.pkg to %PUBLIC%DocumentsWPSDocumentsWPSManagerQmea.dat.
Its final actions are to execute svcghost.exe utilizing the ShellExecute API after which exit.
The svcghost.exe element performs monitoring of the PerfWatson.exe course of, the place the backdoor is loaded, making certain that it’s all the time operating. If the processes are usually not operating, it executes PerfWatson.exe (initially a reputable command line utility named regcap.exe, included in Visual Studio), which the attackers abuse to side-load lregdll.dll. The DLL’s purpose is to load the SlowStepper backdoor from the winlogin.gif file.
On a brand new thread, it creates a anonymous window that ignores all messages besides WM_CLOSE, WM_QUERYENDSESSION, and WM_ENDSESSION. When any of those three messages is acquired, the thread makes an attempt to ascertain persistence within the Windows registry, relying on the permissions of the present course of; see Table 1.
Table 1. Registry keys focused for persistence
| Requires | Registry key | Entry | Value |
| Administrator | HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentModelWinlogon | Userinit | Current path of svcghost.exe. |
| User | HKCUSoftwareMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentModelWindows | load |
The SlowStepper backdoor
SlowStepper is a backdoor developed in C++ with in depth use of object-oriented programming within the C&C communications code. Although the code comprises a whole lot of capabilities, the actual variant used within the supply-chain compromise of the IPany VPN software program seems to be model 0.2.10 Lite, in keeping with the backdoor’s code. The so-called “Lite” model certainly comprises fewer options than different earlier and newer variations.
The oldest model of the SlowStepper backdoor that we all know of is 0.1.7, compiled on 2019-01-31 in keeping with its PE timestamps; the latest one is 0.2.12, compiled on 2024-06-13, and is the complete model of the backdoor.
Both the complete and Lite variations make use of an array of instruments programmed in Python and Go, which embrace capabilities for in depth assortment of information, and spying by recording of audio and movies. The instruments had been saved in a distant code repository hosted on the Chinese platform GitCode, below the LetMeGo22 account; on the time of writing, the profile was personal (Figure 4).
C&C communications
SlowStepper doesn’t carry the C&C IP deal with in its configuration; as a substitute, it crafts a DNS question to acquire a TXT report for the area 7051.gsm.360safe[.]firm. The question is distributed to considered one of three reputable, public DNS servers:
- 8.8.8.8 – Google Public DNS,
- 114.114.114.114 – 114dns.com, or
- 223.5.5.5 – Alibaba Public DNS.
We obtained 4 such information related to that area:
- &%QT%#/zZDmb4ATTVIxwHXPLGrj0FAOV7q+P/sMG109ooj5YLnVZBs3R/eZcuQximtgLkf
- &%QT%#/zZDmb4ATTVIxwHXPLGrj0FAOV7q+P/sMG109ooj5YKQs3XiHSjM3f+h9ok9XfQ1AjoX+C4UXZsDLVqCDhvxyw==
- &%QT%#aT1sAjOFTcwzQ7hwc0iyfygP/ooo8pkIRyaNKWcqBz+QRGYBV/2v8HrVg28+aZXhfXvgDxS1vXAuhdcN2dEKxw==
- &%QT%#aT1sAjOFTcwzQ7hwc0iyfySJBEDM0z6na7BiogG0hDJqdKlUqkrb9ppOjg8epeQ6I6cUXWLKyZGZCkJwFyKD4Q==
The format of the information within the question is proven in Figure 5. The code checks whether or not the primary six bytes of the TXT report match &%QT%# and if that’s the case, it extracts the remainder of the string, which is a base64-encoded AES-encrypted blob containing an array of 10 IP addresses for use as C&C servers. The key used for decryption is sQi9&*2Uhy3Fg7se and the IV is Qhsy&7y@bsG9st#g.
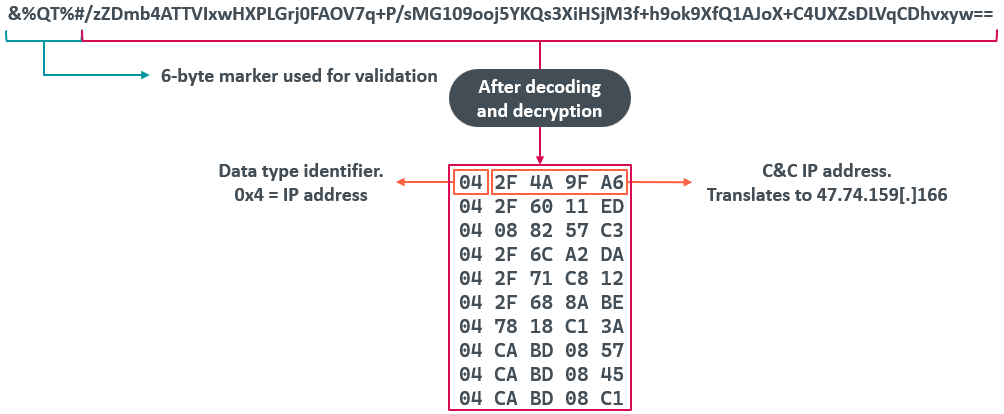
When parsing the decrypted information, the code can extract at the very least 4 information identifiers, described in Table 2.
Table 2. Data varieties processed by the backdoor’s code
| Data identifier | Size of information | Description |
| 0x04 | 4 | Data is an IP deal with. |
| 0x05 | 6 | Data is an IP deal with and port quantity. |
| 0x06 | 16 | Skips the subsequent 16 bytes of information. We suspect that, given the scale of the information, it’s attainable that it’s an IPv6 deal with. |
| 0x00–0x03 0x07–0xFF |
Data identifier worth is the worth of the information dimension. | Skips the subsequent (unknown) bytes of information. |
One of the IP addresses is chosen and SlowStepper connects to the C&C server through TCP to start its communication protocol. If, after a lot of makes an attempt, it fails to ascertain a connection to the server, it makes use of the gethostbyname API on the area st.360safe[.]firm to acquire the IP deal with mapped to that area and makes use of the obtained IP as its fallback C&C server.
Once communication is established, SlowStepper can course of the instructions listed in Table 3.
Table 3. Basic instructions supported by SlowStepper
| Command ID | Action carried out |
| 0x32 | Collects the next data from the compromised machine and sends it to the server: · model of the CPU, utilizing the CPUID instruction, · HDDs related to the pc and their serial numbers, · laptop identify, · native host identify, · public IP deal with, by querying a number of providers, · record of operating processes, · record of put in purposes, · community interface data, · further details about the pc’s drives, equivalent to quantity identify and free house, · system reminiscence, · present username, · persistence sort used, · whether or not cameras are related, · whether or not microphones are related, · whether or not the working system is operating as a digital machine, · system uptime, · HTTP proxy configuration, and · whether or not queries to the DNS server at 114.114.114.114:53 to resolve the addresses of two reputable domains, cf.duba.internet (Kingston) and f.360.cn (360 Qihoo), failed or succeeded. It is unclear to us what the aim of this data is. |
| 0x38 | Executes a Python module from its toolkit; the output and any information created by the module are despatched to the server. The process is similar to what’s used within the shell mode. |
| 0x39 | Deletes the required file. |
| 0x3A | This command can course of different instructions despatched by the operator in SlowStepper’s shell mode, which we clarify in additional element under. Alternatively, it could possibly additionally: · Run a command through cmd.exe and ship the output again to the server. · Run a command through cmd.exe with out sending the output to the server. |
| 0x3C | Uninstalls SlowStepper by eradicating its persistence mechanism and eradicating its information. |
| 0x3F | Lists information within the specified listing, and lists drives. |
| 0x5A | Downloads and executes the required file. |
SlowStepper has a moderately uncommon characteristic: the builders applied a customized shell, or command line interface, on high of its communication protocol. While the backdoor accepts and handles instructions within the conventional means, the 0x3A command prompts the interpretation of operator-written instructions (Table 4).
Table 4. Commands supported in shell mode
| Command | Parameters | Description |
| cd | Path to a listing. | Checks whether or not a listing exists. |
| gcall | Module identify and different unknown parameter(s). | This operate can carry out two duties: · Download a module from the distant code repository and execute it. The module is meant to be a console utility. · Send a file from the compromised machine to the operator. |
| pycall | Tool identify to be executed. | This command is defined intimately within the Execution of instruments through SlowStepper’s pycall shell command part. |
| restart | self | Restarts SlowStepper by rerunning the host course of and calling the ExitProcess API. Returns the message The mode of NSP does not assist restart self. when SlowStepper is operating in a course of through a persistence method that abuses Winsock namespace suppliers; nevertheless, it isn’t included on this variant of SlowStepper. |
| replace | N/A | Downloads a module from the distant code repository, changing a earlier present model. |
| gconfig | present | Displays the worth of ServerIP (the C&C IP deal with). |
| set | Changes the worth of ServerIP. The console suggests the next to the operator: If you need make the Configuration efficient instantly, please command “gconfig reload”. |
|
| reload | Reloads the configuration. | |
| getname | Returns the identify of the present course of wherein SlowStepper is operating. | |
| getdll | Returns the identify of the SlowStepper DLL within the present course of. | |
| getpid | Returns the method ID of the present course of wherein SlowStepper is operating. | |
| getsid | Returns the Remote Desktop Services session ID of the present course of. This means that SlowStepper may additionally be supposed to compromise machines operating Windows Server. | |
| getpwd | Downloads getcode.mod from the distant code repository and executes it utilizing rundll32.exe. The module generates a file, named psf.bin, that comprises the collected information. | |
| gcmd | question | Creates an entire report of details about the required file or listing. |
| delete | Deletes the required file, listing, or all information in a listing. | |
| set | Sets configuration parameters. | |
| terminate | Terminates the required course of. | |
| cancel | Creates a file with the .delete extension. |
Execution of instruments through SlowStepper’s pycall shell command
Figure 6 illustrates the execution chain, beginning when the operator points a pycall command to request the execution of a Python module on the compromised machine; right here, for example, the module CollectInfo.
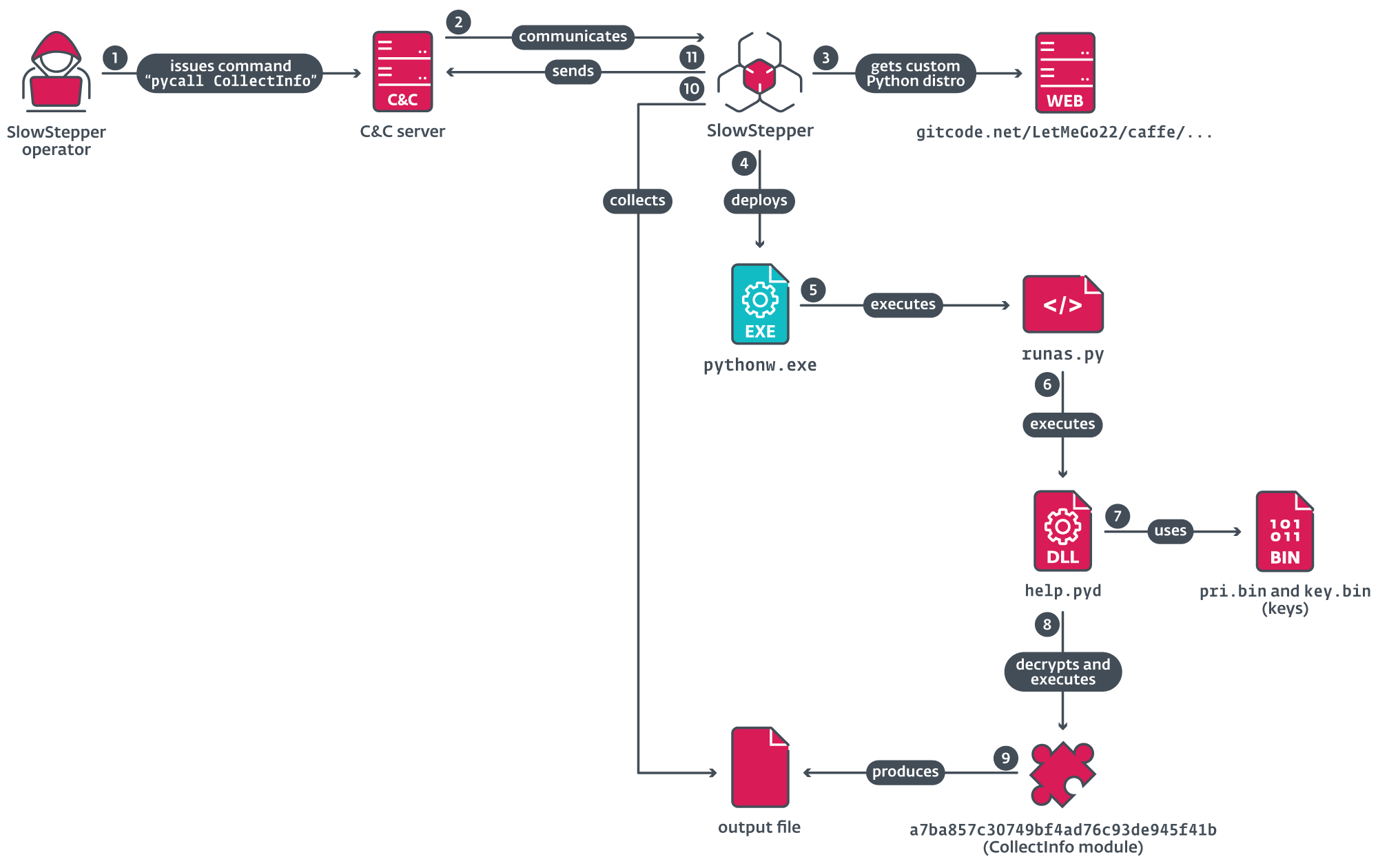
From the distant repository, the pycall command downloads a ZIP archive that comprises the Python interpreter and its supporting libraries. One of three attainable custom-made distributions is downloaded, as outlined in Table 5.
Table 5. List of custom-made Python distributions and the circumstances below which they’re downloaded
| Condition | Archive identify | Description |
| Windows working system is XP. | winxppy.org | Python 3.4 |
| All required Windows API set (stub) DLLs and the Microsoft C runtime are current. | winpy_no_rundll.org | Python 3.7 |
| Neither of the previous circumstances are met. | win7py.org | Python 3.7; contains Windows API set (stub) DLLs and the Microsoft C runtime library. |
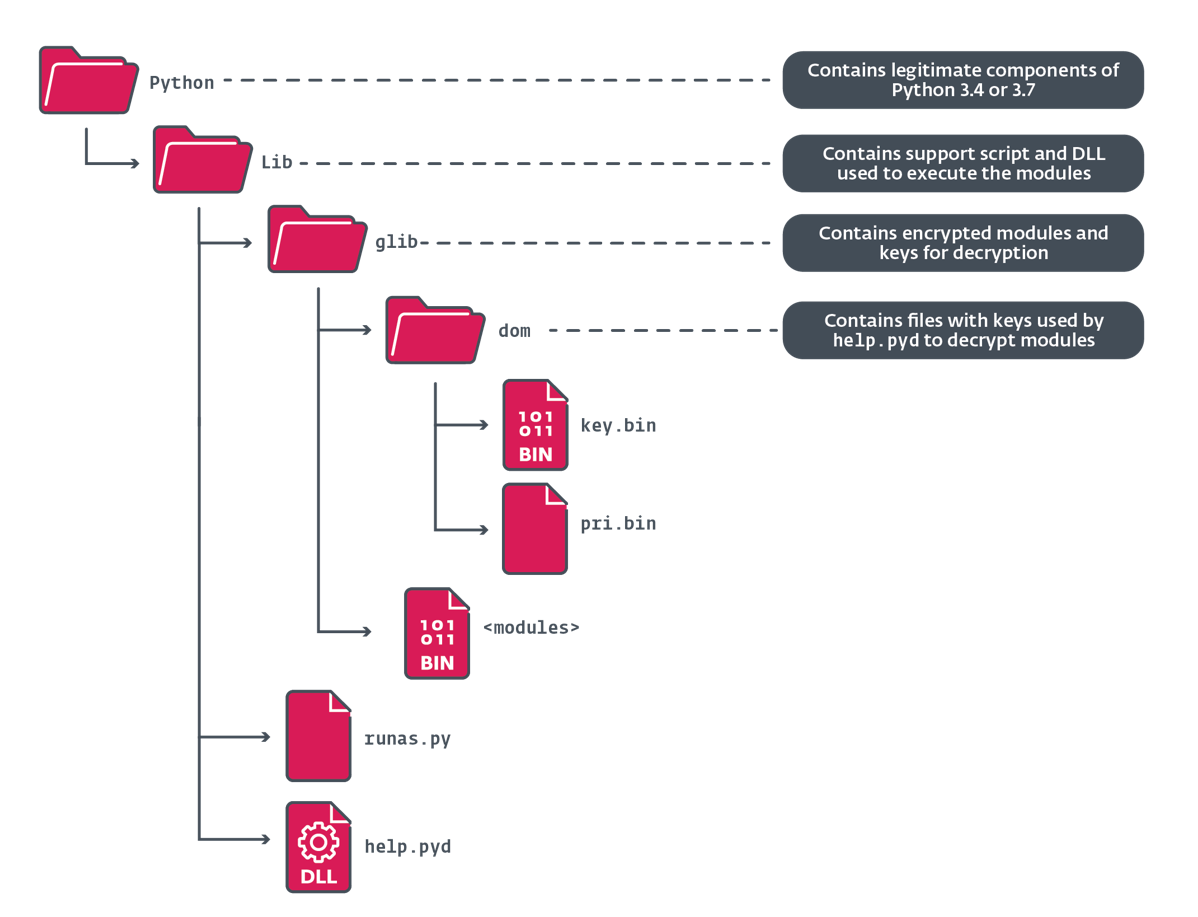
Figure 7 reveals the listing construction of the decompressed archive containing the Python distribution, itemizing solely the malicious information which might be included inside.
SlowStepper runs the Python interpreter utilizing the next command line:
%PUBLIC%DocumentsWPSDocumentsWPSManagerPythonPythonw.exe -m runas
The module named runas is a customized Python script (Figure 8) that masses one other customized Python module named assist from which it makes use of the operate named run to decrypt the module and execute it.
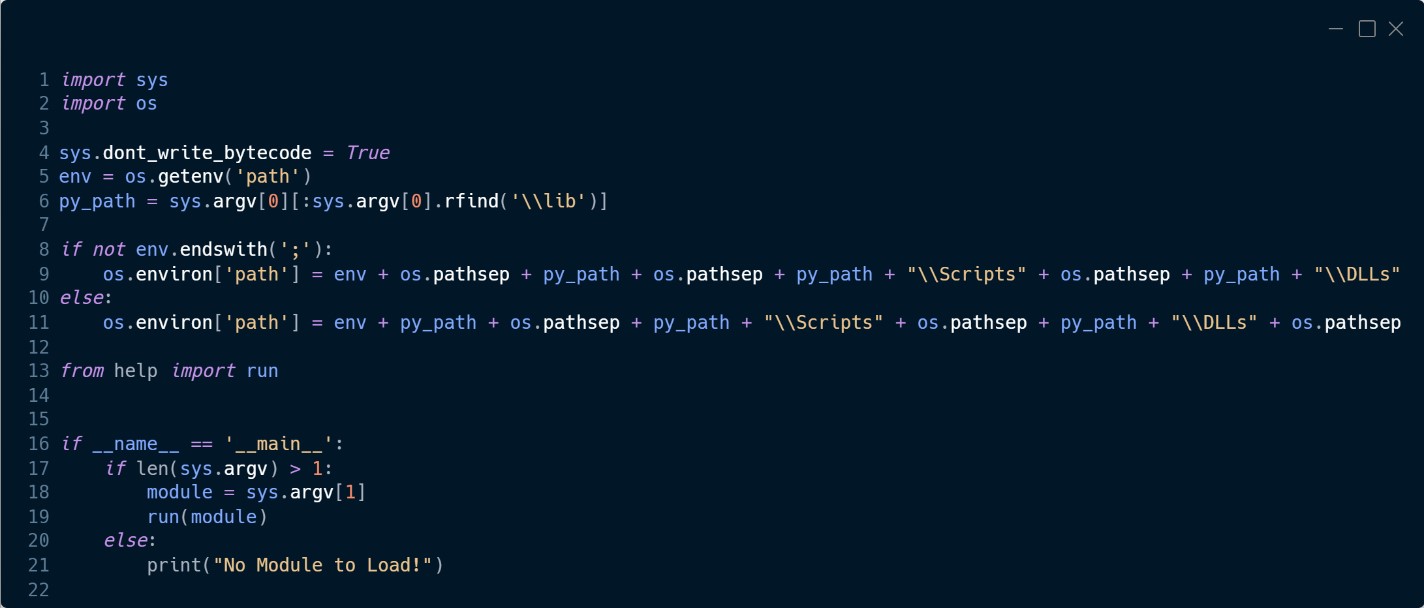
Table 6 lists the modules that we recovered from the distant repository throughout the time it was accessible.
Table 6. List of Python modules and their function
| Filename on disk | Original module identify | Purpose |
| 900150983cd24fb0 |
abc | Test module that prints howdy world. |
| ef15fd2f45e6bb5c |
Browser | Collects a variety of information from net browsers: Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Opera, Brave, Vivaldi, Cốc Cốc browser, UC Browser, 360 Browser, and Mozilla Firefox. |
| 967d35e40f3f95b1 |
Camera | If the pc has a digital camera related, it takes images. |
| a7ba857c30749bf4 |
CollectInfo | Scans the disk for information with extensions .txt, .doc, .docx, .xls, .xlsx, .ppt, and .pptx. Collects data from a number of software program titles, together with: LetsVPN, Tencent QQ, WeChat, Kingsoft WPS, e2eSoft VCam, KuGou, Oray Sunlogin, and ToDesk. |
| 6002396e8a3e3aa7 |
Decode | Downloads a module from the distant repository and decrypts it. |
| 9348a97af6e8a2f4 |
DingTalk | Collects a variety of information from DingTalk (a company administration software developed in China), together with chat messages, audio, video, contact data, and teams the person has joined. |
| 801ab24683a4a8c4 |
Download | Downloads (non-malicious) Python packages. |
| 16654b501ac48e46 |
FileScanner | Scans the disk for information, utilizing the identical code as CollectInfo. |
| 7d3b40764db47a45 |
FileScannerAllDisk | |
| 3582f6ebaf9b6129 |
getOperaCookie | Gets cookies from the Opera browser. |
| 10ae9fc7d453b0dd |
record | Lists modules with a .py extension. |
| ce5bf551379459c1 |
Location | Obtains the IP deal with of the pc and the GPS coordinates, utilizing on-line providers. |
| 68e36962b09c99d6 |
Location1 | |
| 5e0a529f8acc19b4 |
LocationByIP | |
| c84fcb037b480bd2 |
PackDir | Creates a ZIP archive of the required file. |
| 4518dc0ae0ff517b |
qpass | This script seems to be unfinished. It obtains and decrypts passwords from Tencent QQ Browser. Probably changed by the qqpass module. |
| 5fbf04644f45bb2b |
qqpass | Obtains and decrypts passwords from Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Tencent QQ Browser, 360 Chrome, and UC Browser. |
| 874f5aaef6ec4af8 |
ScreenDocument | Records the display screen, saving the end result as an AVI file inside a ZIP archive. |
| c915683f3ec888b8 |
Telegram | Collects account data from the Telegram desktop utility. |
| 104be797a980bcbd |
Webpass | Similar to the qqpass module. |
| e5b152ed6b4609e9 |
One of the biggest modules, it collects a variety of information from WeChat. | |
| 6d07a4ebf4dff8e5 |
Wechat_all_file | Collects information from WeChat. |
| 17cf4a6dd339a131 |
Wechat_src | |
| 8326cef49f458c94 |
Wechat1 | Similar to WeChat. |
| 427f01be70f46f02 |
WechatFile | |
| 72704d83b916fa1f |
WirelessKey | Collects wi-fi community data and passwords, and output from the ipconfig /all command. |
In addition to the Python toolkit, we discovered, saved within the distant code repository different instruments (Table 7) that aren’t encrypted; a few of these had been programmed in C/C++ and others in Go, as famous under.
Table 7. Tools and their operate
| Tool filename | Description |
| agent.mod | Reverse proxy programmed in Go. |
|
getcode.mod getcode64.mod |
Mimikatz. This software is a DLL downloaded by the getpwd command. |
| InitPython.mod | Old downloader to put in the custom-made Python distribution on the compromised machine. This software is a DLL. |
| Remote.mod | RealVNC server that permits the attackers to remotely management the compromised machine. This software is a DLL. |
| soc.mod |
Reverse proxy programmed in Go. Signed with a certificates from a Chinese firm referred to as Hangzhou Fuyang Qisheng Information Technology Service Department. We had been unable to seek out any details about the corporate. |
| stoll.mod |
Tool used to carry out downloads, written in Go. Signed with a certificates from the Chinese firm Zhoushan Xiaowen Software Development Studio. We had been unable to seek out any details about the corporate. |
Conclusion
In this blogpost, we’ve analyzed a supply-chain assault in opposition to a Korean VPN supplier, focusing on customers in East Asia, as evident by the precise software program focused for data assortment and confirmed through ESET telemetry. We additionally documented the SlowStepper backdoor, used completely by PlushDaemon. This backdoor is notable for its multistage C&C protocol utilizing DNS, and its capacity to obtain and execute dozens of further Python modules with espionage capabilities.
The quite a few elements within the PlushDaemon toolset, and its wealthy model historical past, present that, whereas beforehand unknown, this China-aligned APT group has been working diligently to develop a wide selection of instruments, making it a major menace to observe for.
For any inquiries about our analysis printed on WeLiveSecurity, please contact us at threatintel@eset.com.ESET Research gives personal APT intelligence studies and information feeds. For any inquiries about this service, go to the ESET Threat Intelligence web page.
IoCs
A complete record of indicators of compromise and samples could be present in our GitHub repository.
Files
| SHA-1 | Filename | Detection | Description |
| A8AE42884A8EDFA17E9D |
AutoMsg.dll | Win32/ShellcodeRunner.GZ | Initial loader DLL. |
| 2DB60F0ADEF14F4AB357 |
lregdll.dll | Win32/Agent.AGUU | Loader DLL for the SlowStepper backdoor. |
| 846C025F696DA1F6808B |
OldLJM.dll | Win32/Agent.AGXL | Installer DLL, internally named OldLJM.dll. It is extracted from EncMgr.pkg and executed in reminiscence. |
| AD4F0428FC9290791D55 |
svcghost.exe | Win32/Agent.AGUU | Process monitor element that launches PerfWatson.exe or RuntimeSvc.exe to side-load lregdll.dll. |
| 401571851A7CF71783A4 |
most important.dll | Win32/Agent.AEIJ | Decrypted SlowStepper backdoor element. |
| 068FD2D209C0BBB0C6FC |
IPanyVPNsetup |
Win32/ShellcodeRunner.GZ | Malicious IPany installer. Contains the SlowStepper implant and the reputable IPany VPN software program. |
Network
| IP | Domain | Hosting supplier | First seen | Details |
| 202.189.8[.]72 | reverse.wcsset |
Shandong eshinton Network Technology Co., Ltd. | 2024‑10‑14 | Server utilized by the (reverse proxy) soc.mod software. |
| 47.96.17[.]237 | agt.wcsset[.]com | Hangzhou Alibaba Advertising Co.,Ltd. | 2024‑10‑14 | Server utilized by agent.mod software. |
| N/A | 7051.gsm.360safe |
N/A | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper queries this area to acquire its related DNS TXT report. |
| 202.105.1[.]187 | st.360safe |
IRT-CHINANET-CN | 2021‑03‑11 | Fallback C&C server contacted by SlowStepper. |
| 47.74.159[.]166 | N/A | Alibaba (US) Technology Co., Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 8.130.87[.]195 | N/A | Hangzhou Alibaba Advertising Co.,Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 47.108.162[.]218 | N/A | Hangzhou Alibaba Advertising Co.,Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 47.113.200[.]18 | N/A | Hangzhou Alibaba Advertising Co.,Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 47.104.138[.]190 | N/A | Guowei Pan | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 120.24.193[.]58 | N/A | Hangzhou Alibaba Advertising Co.,Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 202.189.8[.]87 | N/A | Shandong eshinton Network Technology Co., Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 202.189.8[.]69 | N/A | Shandong eshinton Network Technology Co., Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 202.189.8[.]193 | N/A | Shandong eshinton Network Technology Co., Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 47.92.6[.]64 | N/A | Hangzhou Alibaba Advertising Co.,Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
MITRE ATT&CK strategies
This desk was constructed utilizing model 16 of the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
| Tactic | ID | Name | Description |
| Resource Development | T1583.001 | Acquire Infrastructure: Domains | PlushDaemon has acquired domains for its C&C infrastructure. |
| T1583.004 | Acquire Infrastructure: Server | PlushDaemon has acquired servers for use as C&C servers. | |
| T1608.001 | Stage Capabilities: Upload Malware | PlushDaemon has staged its toolkit within the code repository web site GitCode. | |
| T1608.002 | Stage Capabilities: Upload Tool | PlushDaemon has staged its toolkit within the code repository web site GitCode. | |
| T1588.001 | Obtain Capabilities: Malware | PlushDaemon has entry to SlowStepper. | |
| T1588.002 | Obtain Capabilities: Tool | PlushDaemon instruments getcode.mod and getcode64.mod use Mimikatz. | |
| T1588.003 | Obtain Capabilities: Code Signing Certificates | PlushDaemon instruments soc.mod and stoll.mod are signed. | |
| T1588.005 | Obtain Capabilities: Exploits | PlushDaemon has used an unidentified exploit for Apache HTTP server. | |
| Initial Access | T1659 | Content Injection | PlushDaemon can intercept community site visitors to hijack replace protocols and ship its SlowStepper implant. |
| T1190 | Exploit Public-Facing Application | PlushDaemon exploited an unidentified vulnerability in Apache HTTP Server. | |
| T1195.002 | Supply Chain Compromise: Compromise Software Supply Chain | PlushDaemon has compromised the provision chain of a VPN developer and changed the unique installer with a trojanized one containing the SlowStepper implant. | |
| Execution | T1059.003 | Command-Line Interface: Windows Command Shell | SlowStepper makes use of cmd.exe to execute instructions on a compromised machine. |
| T1059.006 | Command-Line Interface: Python | SlowStepper for Windows can use the Python console to execute the Python elements of its toolkit. | |
| Persistence | T1547.001 | Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder | The SlowStepper installer establishes persistence by including an entry in HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows |
| T1547.004 | Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Winlogon Helper DLL | The SlowStepper course of monitor element can set up persistence by including an entry in HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentModelWinlogonUserinit or HKCUSoftwareMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentModelWinlogonload. | |
| T1574.002 | Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Side-Loading | PlushDaemon has abused a reputable command line utility included in Visual Studio referred to as regcap.exe to side-load a malicious DLL named lregdll.dll. | |
| Defense Evasion | T1222.001 | File Permissions Modification: Windows File and Directory Permissions Modification | SlowStepper modifies the entry rights of the listing the place its elements are saved on disk. |
| T1070.004 | Indicator Removal: File Deletion | SlowStepper can take away its personal information. | |
| T1036.005 | Masquerading: Match Legitimate Name or Location | SlowStepper makes use of folder names and filenames from reputable software program. | |
| T1112 | Modify Registry | SlowStepper can modify the registry. | |
| T1027.007 | Obfuscated Files or Information: Dynamic API Resolution | SlowStepper dynamically resolves Windows API capabilities. | |
| T1027.009 | Obfuscated Files or Information: Embedded Payloads | SlowStepper loader DLLs include embedded, position-independent code, executed in reminiscence, to load elements. | |
| T1027.013 | Obfuscated Files or Information: Encrypted/Encoded File | SlowStepper elements are saved encrypted on disk. | |
| T1553.002 | Subvert Trust Controls: Code Signing | PlushDaemon instruments soc.mod and stoll.mod are signed. | |
| Discovery | T1217 | Browser Bookmark Discovery | SlowStepper’s Browser software collects data from browsers. |
| T1083 | File and Directory Discovery | SlowStepper and its instruments can seek for information with particular extensions, or enumerate information in directories. | |
| T1120 | Peripheral Device Discovery | SlowStepper and its toolkit can uncover units related to the compromised machine. | |
| T1057 | Process Discovery | SlowStepper can create a listing of operating processes. | |
| T1012 | Query Registry | SlowStepper can question the registry. | |
| T1518 | Software Discovery | SlowStepper can create a listing of software program put in on the compromised machine. | |
| T1082 | System Information Discovery | SlowStepper can acquire system data. | |
| T1614 | System Location Discovery | SlowStepper’s Location software makes an attempt to find the attainable geolocation of the compromised machine by querying a number of on-line providers. | |
| T1016 | System Network Configuration Discovery | SlowStepper collects data from the community adapters. | |
| T1016.002 | System Network Configuration Discovery: Wi-Fi Discovery | SlowStepper’s Wireless software and its variants collects a variety of data from the Wi-Fi community. | |
| T1033 | System Owner/User Discovery | SlowStepper obtains the username. | |
| Collection | T1560.002 | Archive Collected Data: Archive through Library | SlowStepper instruments can compress the collected information in ZIP archives. |
| T1123 | Audio Capture | SlowStepper can seize audio if the compromised machine has a microphone. | |
| T1005 | Data from Local System | SlowStepper and its instruments acquire a variety of information from the compromised system. | |
| T1074.001 | Data Staged: Local Data Staging | SlowStepper and its instruments stage information regionally earlier than exfiltrating it to the C&C server. | |
| T1113 | Screen Capture | SlowStepper’s ScreenDocument software can take screenshots. | |
| T1125 | Video Capture | SlowStepper’s Camera software can report movies if the compromised machine has a digital camera. | |
| Command and Control | T1071.004 | Standard Application Layer Protocol: DNS | SlowStepper retrieves a DNS TXT report that comprises an AES-encrypted record of C&C servers. |
| T1132.001 | Data Encoding: Standard Encoding | SlowStepper retrieves a DNS TXT report that comprises an AES-encrypted record of C&C servers. The report is base64 encoded. | |
| T1573.001 | Encrypted Channel: Symmetric Cryptography | SlowStepper’s communication protocol with its C&C is encrypted with AES. | |
| T1008 | Fallback Channels | SlowStepper will get a fallback C&C server IP deal with by resolving another area managed by the attackers. | |
| T1105 | Remote File Copy | SlowStepper downloads further instruments from a distant code repository at GitCode. | |
| T1104 | Multi-Stage Channels | SlowStepper obtains a listing of C&C servers by querying the DNS TXT report from a website managed by the attackers; if no communication could be established with the servers, it resolves the IP deal with of one other area managed by the attackers to acquire a backup server. SlowStepper instruments use completely different servers from PlushDaemon infrastructure. |
|
| T1095 | Standard Non-Application Layer Protocol | SlowStepper communicates with its C&C through TCP. | |
| T1090 | Connection Proxy | SlowStepper instruments agent.mod and soc.mod are reverse proxies. | |
| T1219 | Remote Access Tools | SlowStepper software Remote.mod permits its operator to remotely management the compromised machine through VNC. | |
| Exfiltration | T1020 | Automated Exfiltration | SlowStepper can exfiltrate staged information. |
| T1041 | Exfiltration Over C2 Channel | SlowStepper exfiltrates collected information when related to considered one of its C&C servers. |

