[ad_1]
Editor’s observe: Sophos MDR’s Johua Rawles, Mark Parsons, Jordon Olness, and Colin Cowie contributed to this report.
One of the Internet’s most prolific cybercrime-as-a-service operations not too long ago suffered a setback: In November, Sophos MDR seen that detections for the Rockstar2FA “phishing-as-a-service”(PaaS) platform had abruptly gone quiet.
Based on telemetry gathered by Sophos MDR, it seems that the group working the service skilled at the least a partial collapse of its infrastructure, with pages related to the service now not reachable. This doesn’t look like due to a takedown motion, however attributable to some technical failure on the backend of the service.
The disappearance of Rockstar2FA, an up to date model of phishing companies generally known as DadSec (beforehand related to Microsoft’s Storm-1575 menace group) got here two weeks earlier than TrustWave printed analysis detailing the phishing-as-a-service operation. Elements of the phishing service’s infrastructure at the moment are now not reachable, returning an HTTP 522 response— indicating that they have been lower off from the Cloudflare content material supply community. Telegram channels related to command and management of the service additionally seem to have gone offline.
In the weeks following the disruption of Rockstar2FA, we noticed a surge in using an analogous set of PaaS portals which were tagged by some researchers as “FlowerStorm”—the identify coming from using plant-related phrases within the HTML web page titles of most of the phishing pages themselves (“Flower,” “Sprout, “Blossom,” and “Leaf,” for instance). FlowerStorm shares a lot of options with Rockstar and with Tycoon, one other Telegram bot-powered PaaS platform.
So, you need to be a rock star
Rockstar2FA is (or maybe was) a PaaS package that mimics legit credential-request conduct of generally used cloud and software-as-a-service platforms. Would-be cybercriminals buy and management phishing campaigns by means of Telegram and are given a novel phishing web page and URL to make use of of their marketing campaign. Visits through the hyperlink delivered to the goal delivered the phish; visits to the area of the positioning itself are routed to a “decoy” web page. Rockstar’s decoy pages normally had an automotive theme.

Visitors to the URL can be routed to a counterfeit Microsoft login web page. That web page captured credentials and multifactor authentication tokens and despatched them through an HTTP POST message to an adversary-controlled “backend server” web page —a PHP web page with a seemingly random quantity for its identify (as proven in Figure 2). These back-end servers have been largely on .ru, .de and .moscow registered domains. The decoy pages have been often hosted on the identical hosts because the back-end servers.
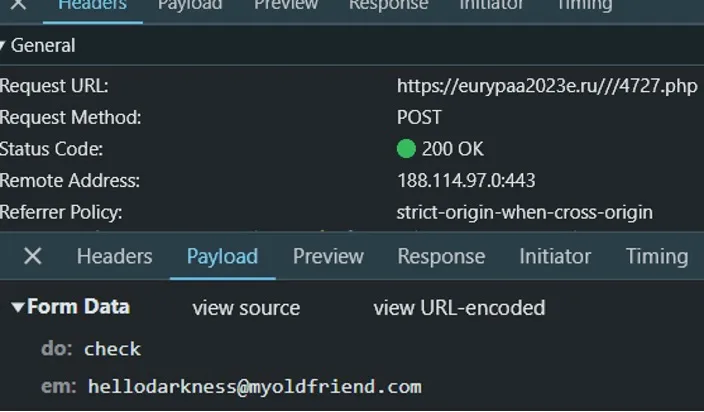
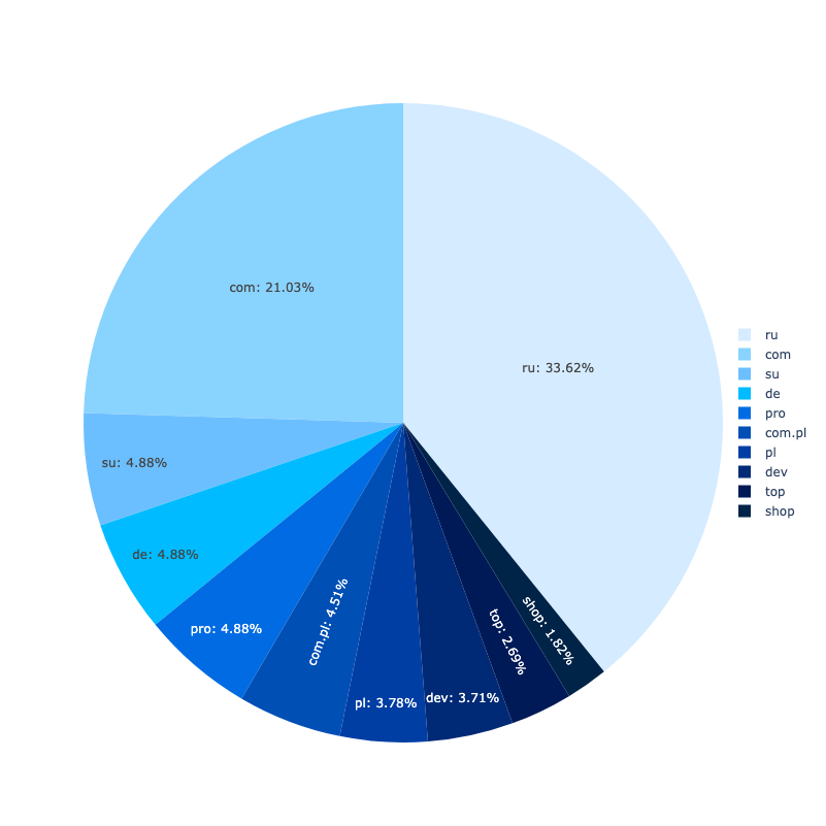
Most of the phishing pages have been on domains registered within the .com, .de, .ru. and .moscow top-level domains. At any given time, the Rockstar2FA service used about 2,000 domains throughout these and different TLDs.
However, beginning no later than June 2024, a few of these pages used Cloudflare Pages serverless deployment (utilizing the area pages[.]dev), together with code deployed as Cloudflare employees (on the area employee[.]dev), whereas nonetheless counting on backend servers for exfiltrating phishing knowledge. These phishing pages used subdomain names that didn’t look like created with a site technology algorithm (DGA)—as an alternative, they seem to have been manually typed by the operator of the package. Some have been crafted to emulate particular goal domains (as with 4344655-proofpoint-online-secure.pages[.]dev). But others have been just like keyboard spam:
- whenyoucreatanydominsamedominusedturnslite.pages[.]dev
- pppaaaaulhaaaammmlinnnnbuiiildddeeeerrsssssnzzzzzozzzz.pages[.]dev
These domains made up solely a small variety of the general URLs associated to Rockstar, and have been usually related to the phishing portals themselves.

Technical difficulties
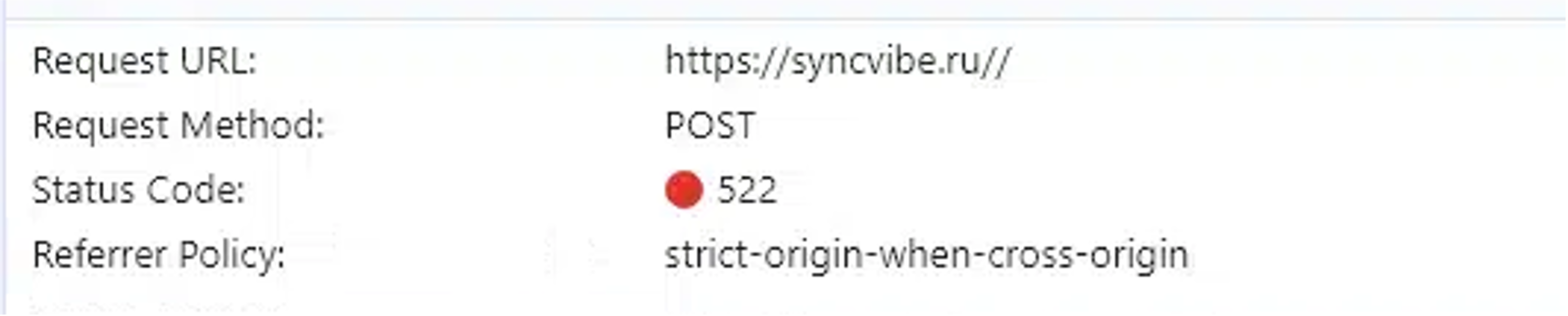
On November 11, the infrastructure of Rockstar2FA abruptly was disrupted. Redirects to decoy pages failed, yielding a Cloudflare 522 error, indicating that the server offering the web page was now not in communication with Cloudflare.
 Figure 5. A failed connection to a decoy web page area
Figure 5. A failed connection to a decoy web page area
Additionally, the portal pages started to fail. While clicking the Cloudflare “I’m human” take a look at beforehand resulted in a counterfeit Microsoft login portal being loaded, now all that loaded was the animated Outlook emblem. The the rest of the script for the portal pages fails as a result of the connection to the back-end server (through a POST request) has been severed.

The similar was true for pages[.]dev hosted portal pages, which additionally hung whereas attempting to connect with the back-end URLs. Since November, we have now continued to see new phishing portal pages arrange on pages[.]dev subdomains, however all of them fail to connect with their backend servers.
This means that the operators are persevering with to wrestle to get their infrastructure again on-line. This could also be due to a hosting downside or another technical difficulty plaguing the Rockstar2FA operators. The incontrovertible fact that the Telegram bots used to run the service additionally look like down suggests there’s some bigger type of disruption to the operation.
The rising rock star (?): FlowerStorm
Within a couple of week and a half of the interruption of Rockstar, we noticed a surge in exercise from FlowerStorm, although we additionally discovered many of those websites have been being disrupted as effectively. The FlowerStorm PaaS platform has been energetic since at the least June of 2024.
Looking on the conduct of FlowerStorm samples, we discovered that the portal used the identical URL to ship an authentication request for the goal as utilized in communication requests to the “backend portal”—on this case, to a backend server using the file “next.php”.
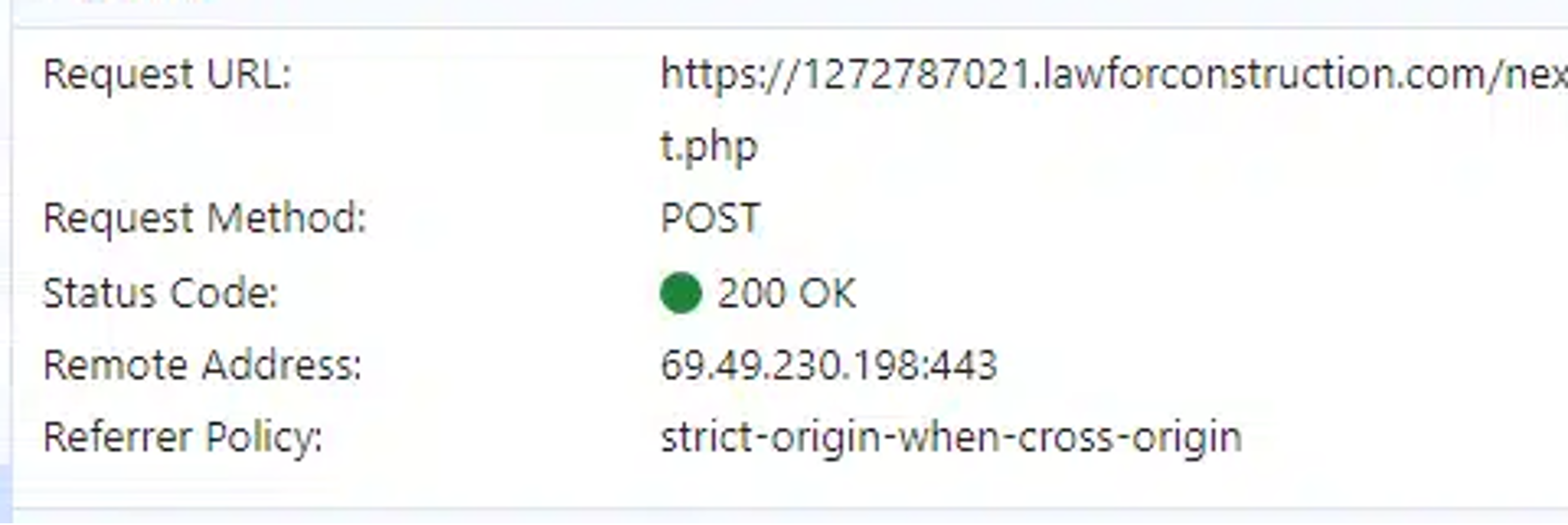
In this case, the identical IP handle utilized for the credential harvesting was additionally used for the authentication to the person account, primarily based on EntraID sign-in logs.

The phishing pages’ communication to the backend servers PHP file utilized the anticipated fields and communication under:
Field Descriptions and Expected Values
| Field/Event | Description | Value/Example |
| Do | Specifies the motion being requested. | “check” – For test operation “login” – For login occasion |
| CheckVerify | Periodic server test for authentication technique standing. | – do: “checkVerify”- token: |
| e mail | User’s e mail handle. | |
| go | User’s password, required when do is “login”. | base64_encoded_password |
| token | JWT containing session data. |
Expected Responses and Interpretations
| Action | Response | Description |
| test | { “status”: “success”, “banner”: null, “background”: null, “federationLogin”: “”, “type”: “office” } | Indicates a sound e mail and points a token. |
| login | { “status”: “verify”, “message”: “Please verify your account”, “method”: “ |
Prompts for MFA utilizing the identical JWT for session monitoring. |
| Method | { “status”: true, “data”: “ |
Posts session-specific knowledge used for MFA. |
| Method (Data Decoded) | [ { “authMethodId”: “PhoneAppNotification”, “data”: “PhoneAppNotification”, “isDefault”: true }, { “authMethodId”: “PhoneAppOTP”, “data”: “PhoneAppOTP”, “phoneAppOtpTypes”: [“MicrosoftAuthenticatorBasedTOTP”] } ] | Details multi-factor authentication strategies out there to the person. |
| CheckVerify (Failure) | { “status”: false, “message”: “Verification failed”, “token”: “ |
Server begins checking for MFA acceptance. |
| CheckVerify (Success) | { “ |
MFA was accepted, response accommodates session cookies for authentication. |
Not all of the phishing pages make the most of the identical backend server construction. Some portals will make the most of a subsequent.php hosted on the identical area because the phishing touchdown web page. The IP handle in EntraID authentication logs won’t be the identical for these portals. For instance, within the case under, the phishing web page protectivewearsupplies[.]doclawfederal[.]com/wQBPg/ sends its submit request to a special host with the identical area identify:
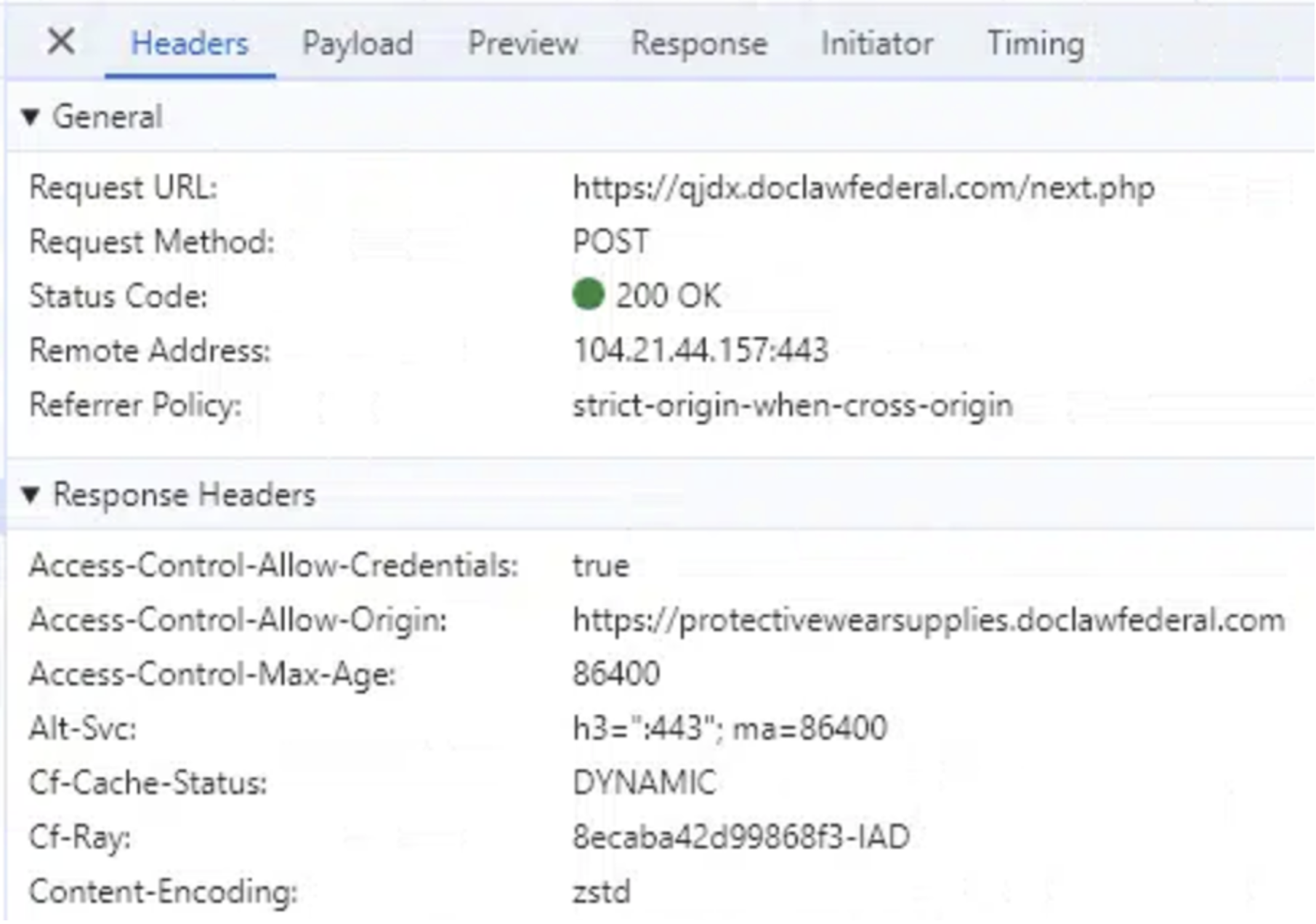
![Figure 11: A developer browser view of the phishing page protectivewearsupplies[.]doclawfederal[.]com/wQBPg/](https://news.sophos.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/FlowerstormDeveloperViewPhishportal.png)
Rockstar2FA/ FlowerStorm similarities
FlowerStorm has a major variety of similarities to Rockstar2FA, each within the format of its phishing portal pages and the connection to its backend server .
Document object mannequin
The HTML of FlowerStorm’s portal pages has modified over the previous six months however nonetheless retains an analogous Document Object Model (DOM) content material to that of Rockstar pages. The HTML pages of older and newer FlowerStorm phishing pages, like these of Rockstar2FA, have strings of random, unrelated textual content in HTML feedback, use Cloudflare “turnstile” keys to immediate a test of the incoming web page request, and produce other comparable buildings and content material, as proven under:
| New FlowerStorm | Old Rockstar2FA | Old FlowerStorm | |
| Title | OreganoLeaf | Unalike | Elderberry |
| Turnstile Sitekey | 0x4AAAAAAA0_fAGSk-ZDbrja | 0x4AAAAAAAhiG1SBeMjCx4fG | 0x4AAAAAAAceMeRudDiJWXJJ |
| Form Submission Script | FennelBlossom | Nautili | Bravery |
| Comments Themes | Literary/educational | Cars, health, fruits | Cars, way of life, fruits |
| Visible Security Text | “Initializing browser security protocols” | “Running browser verification to protect your safety” | “Browser security verification ongoing for your safety” |
The components within the chart above are referred to as out within the screenshots under, displaying the HTML code of every of the phishing portals. The HTML doc title tags are highlighted with a purple field, feedback are highlighted with orange, turnstyle key with yellow, the script operate identify in inexperienced, and the seen “security” textual content in blue. All seem to observe the identical type of template for producing HTML, although the remark and title naming schemes reference totally different textual content arrays.
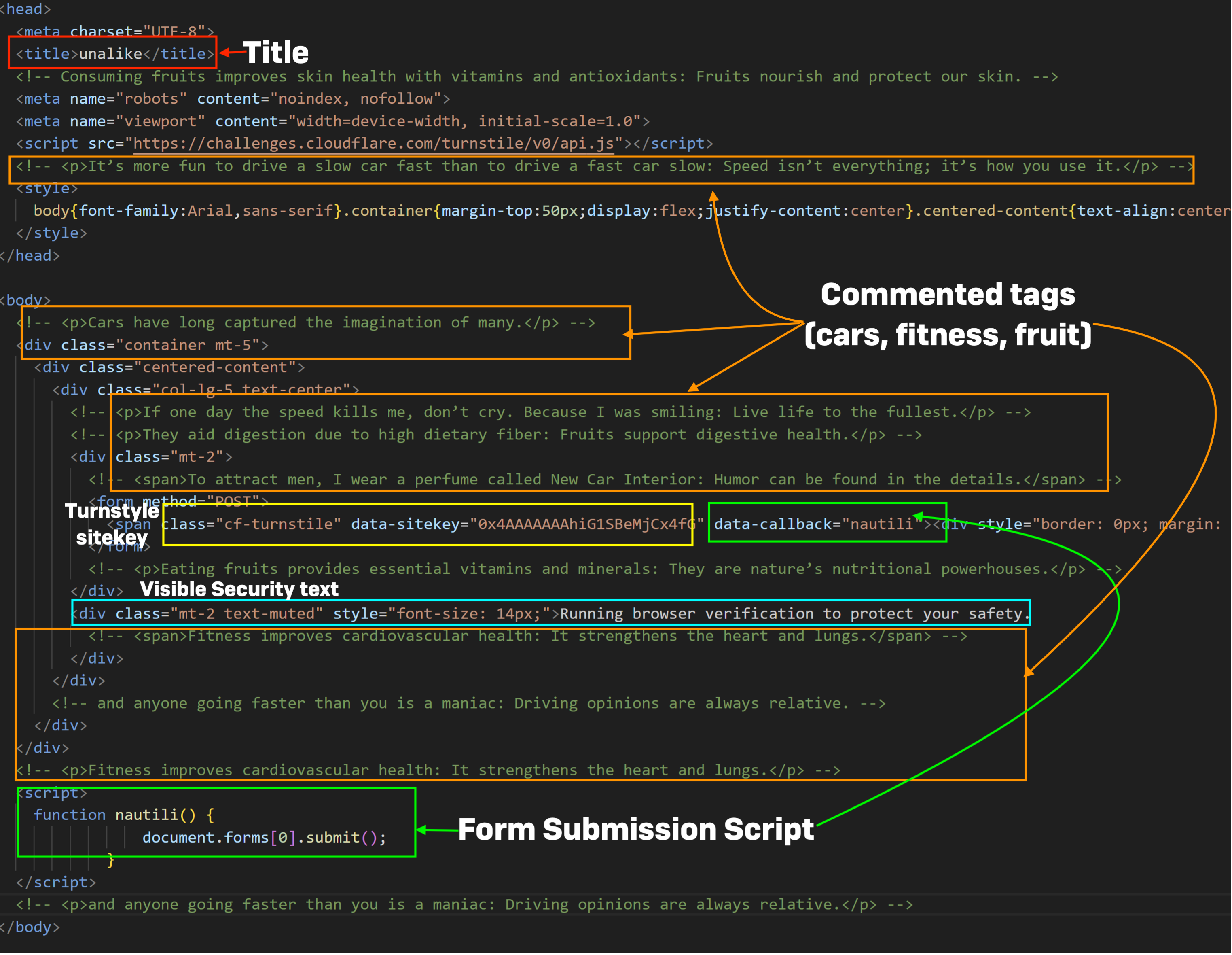
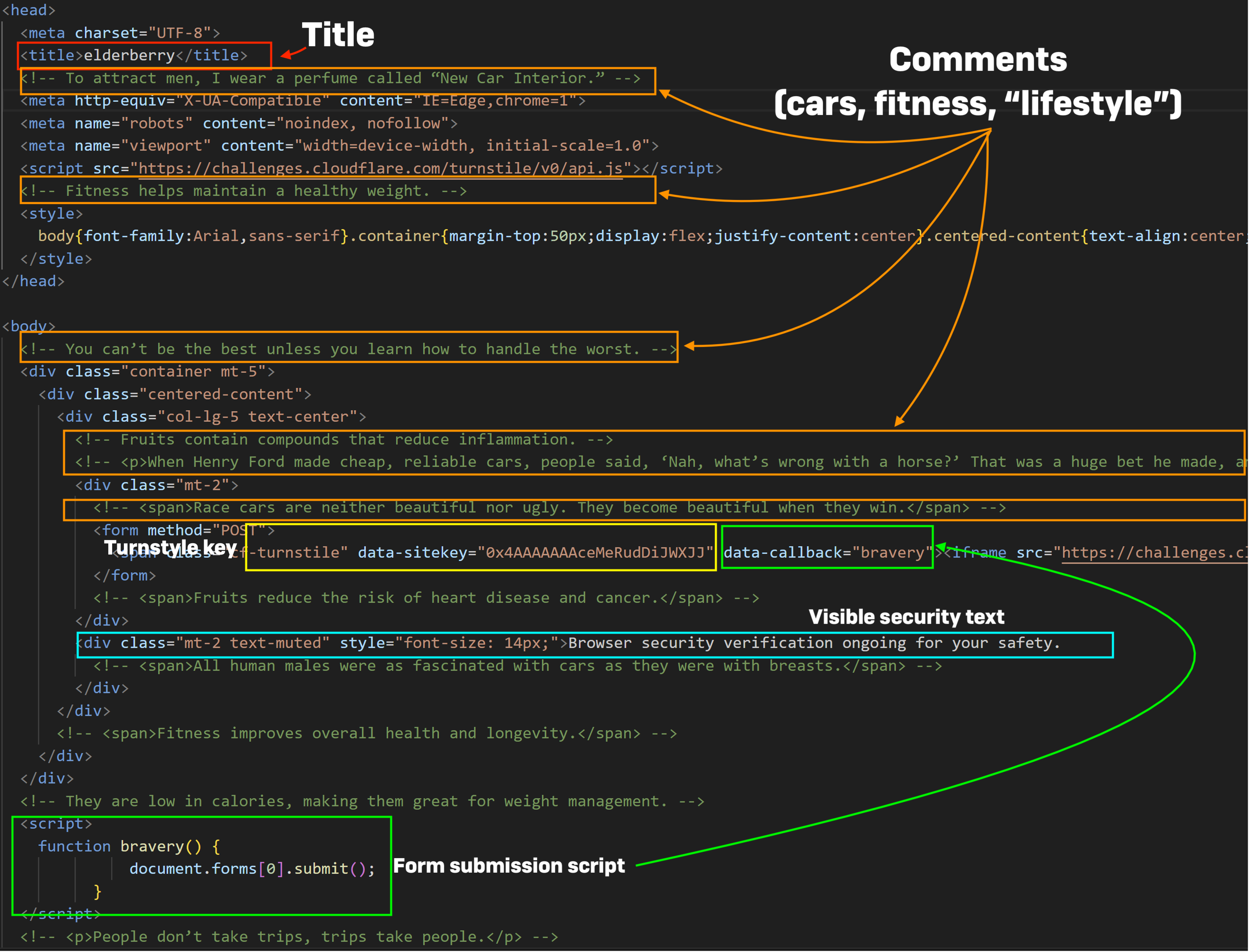

While abuse of the Cloudflare CDN’s safety turnstyles has been current in different adversary-in-the-middle phishing kits, the construction of FlowerStorm and Rockstar phishing portals suggests at the least a typical ancestry.
Credential harvesting
The strategies utilized by FlowerStorm for communication bear shut resemblance to the earlier Rockstar2FA portals, with some minor variation within the discipline names and responses:
Common Fields
| FlowerStorm | Rockstar2FA | Commonality | |
| PHP Communication | Next.php | Both talk to a backend server internet hosting a PHP file. Used for exfiltration and knowledge communication. | |
| Email Validation | “do”:
“check” for e mail validation |
“do”: “check” for e mail validation | Both assist e mail validation as a elementary characteristic. |
| Login Event | “do”: “login” for authentication | “do”: “le” for authentication | Both facilitate login operations. |
| Password | “pass”: accommodates base64 encoded password | “px”: accommodates plaintext password | Both talk passwords to backend server. |
| Session Tracking | “token” for session monitoring. | “sec” for session monitoring | Both present session monitoring tokens. |
Domain Registration and Discovery
The patterns of area registration and the detection of latest pages by means of URLScan submissions for each phishing kits’ infrastructure seem to observe a definite sample, particularly when evaluating the area exercise and identification of the 2.
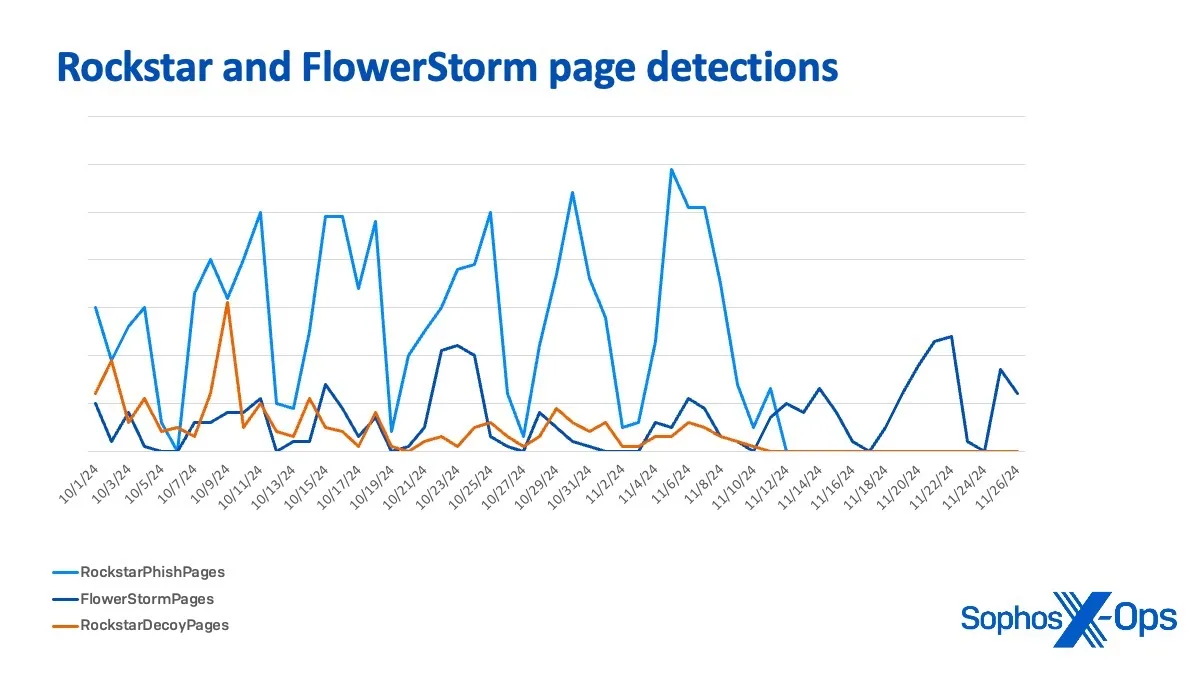
From October 1 to November 11 the peaks and valleys of FlowerStorm and Rockstar Decoy web page detections and area registrations observe a remarkably comparable development, usually rising and falling in tandem. This conduct may point out a shared infrastructure, overlapping operational goals, or coordinated timing between the 2 actions.
After November eleventh, the 2 patterns diverge:
- FlowerStorm begins to point out stronger unbiased peaks, particularly round November 22–26
- Rockstar Decoy web page exercise dwindles considerably after November 11, which is consistent with the ceasing of operations beforehand talked about.
FlowerStorm focusing on
The total nature of FlowerStorm as a paid phishing service implies that FlowerStorm’s operators don’t select who will get focused for phishing assaults. That’s the choice of their clients. But an evaluation of what actors are doing as soon as they’ve entry to the system may be helpful for defenders.
Based on our detection data for FlowerStorm, the overwhelming majority of the targets chosen by FlowerStorm customers (84%) are within the United States, Canada, United Kingdom, Australia, and Italy. Organizations within the United States have been essentially the most often focused, with over 60% of instances related to organizations primarily situated throughout the US. Canada was the following most focused nation, at solely 8.96%. Overall, 94% of the targets of FlowerStorm phishing makes an attempt Sophos has detected have been workers of North American and European organizations. Beyond these areas, Singapore, India, Israel, New Zealand, and the United Arab Emirates make up the remaining 5% of targets.
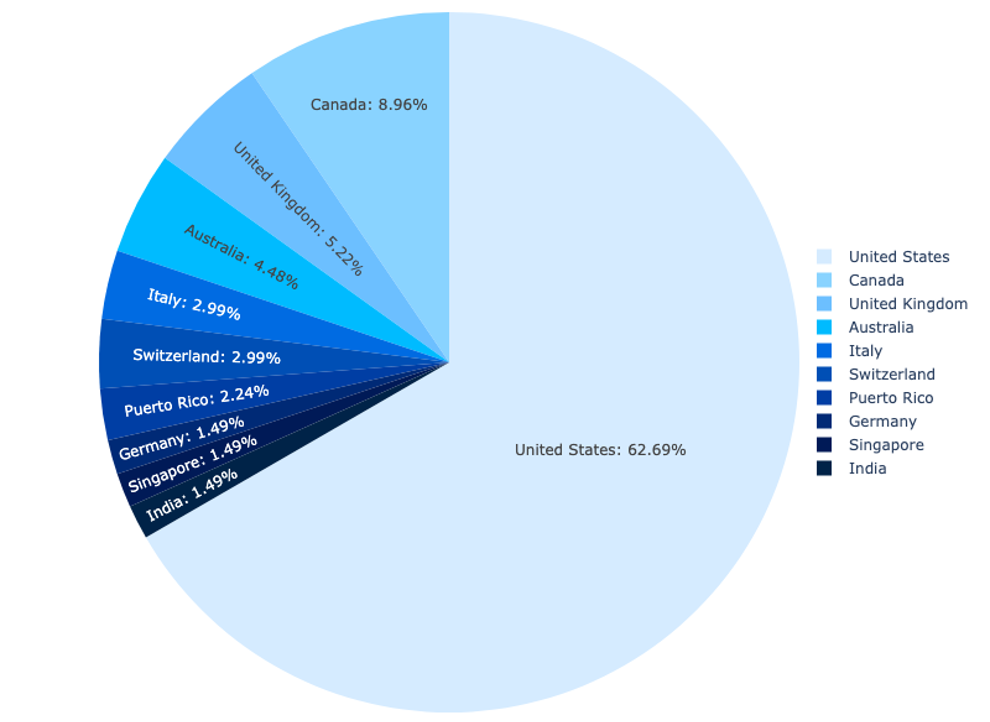
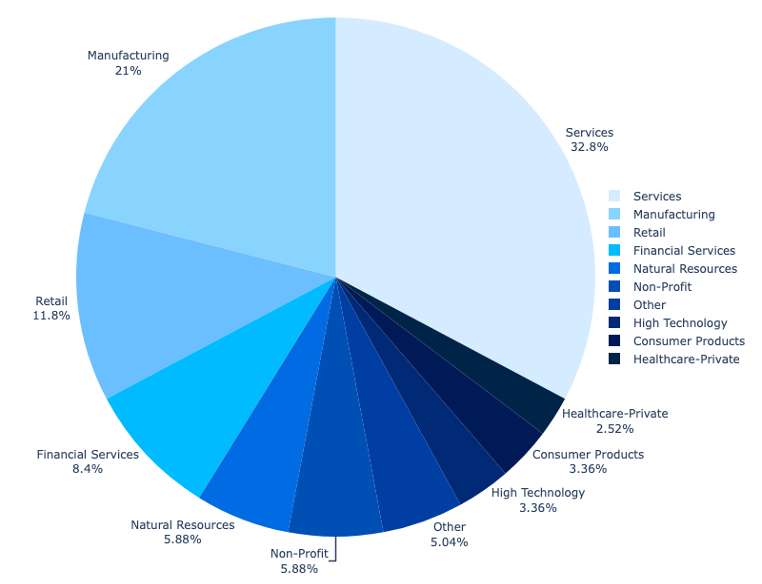
The most closely focused sector is the service business, with specific deal with companies offering engineering, building, actual property, and authorized companies and consulting.
Conclusions
We can not with excessive confidence hyperlink Rockstar2FA and FlowerStorm, apart from to notice that the kits replicate a typical ancestry at a minimal as a result of comparable contents of the kits deployed The comparable patterns of area registration could possibly be a mirrored image of FlowerStorm and Rockstar working in coordination, although it’s also doable that these matching patterns have been pushed by market forces greater than the platforms themselves. The diverging exercise post-November 11might replicate:
- A strategic pivot in one of many teams
- A change in personnel impacting operations
- A disruption in shared infrastructure
- A deliberate decoupling of operations to keep away from detection
Furthermore, the speedy ramp-up of FlowerStorm has led to some errors and misconfigurations of their operations which have allowed them to additionally simply be disrupted. Those errors have additionally supplied us with a chance to extra carefully look at their back-end operations—which we’ll proceed to do.
A listing of indicators of compromise associated to FlowerStorm is on the market on Sophos X-Ops’ Github repository.
[ad_2]
