[ad_1]
Security researchers have disclosed a number of architectural vulnerabilities in Siemens SIMATIC and SIPLUS S7-1500 programmable logic controllers (PLCs) that may very well be exploited by a malicious actor to stealthily set up firmware on affected gadgets and take management of them.
Discovered by Red Balloon Security, the problems are tracked as CVE-2022-38773 (CVSS rating: 4.6), with the low severity stemming from the prerequisite that exploitation requires bodily tampering of the machine.
The flaws “may enable attackers to bypass all protected boot options, leading to persistent arbitrary modification of working code and information,” the corporate stated. More than 100 fashions are inclined.
Put in a different way, the weaknesses are the results of an absence of uneven signature verifications for firmware at bootup, successfully allowing the attacker to load tainted bootloader and firmware whereas undermining integrity protections.
A extra extreme consequence of loading such modified firmware is that it may give the risk actor the power to persistently execute malicious code and achieve whole management of the gadgets with out elevating any pink flags.
“This discovery has doubtlessly vital implications for industrial environments as these unpatchable {hardware} root-of-trust vulnerabilities may lead to persistent arbitrary modification of S7-1500 working code and information,” the researchers stated.
Siemens, in an advisory launched this week, stated it has no patches deliberate however urged clients to restrict bodily entry to the affected PLCs to trusted personnel to keep away from {hardware} tampering.
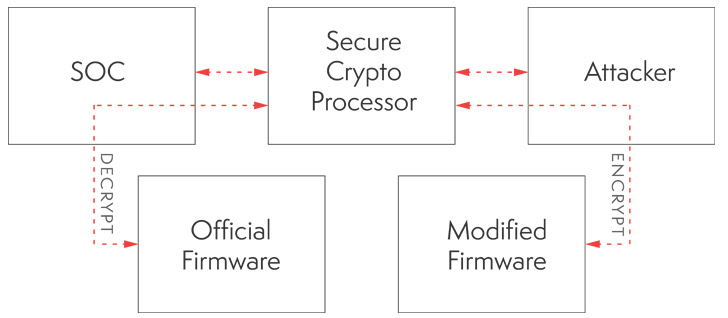
The lack of a firmware replace is attributed to the truth that the cryptographic scheme that undergirds the protected boot options is baked right into a devoted bodily safe aspect chip (known as the ATECC108 CryptoAuthentication coprocessor), which decrypts the firmware in reminiscence throughout startup.
An attacker with bodily entry to the machine may subsequently leverage the problems recognized within the cryptographic implementation to decrypt the firmware, make unauthorized adjustments, and flash the trojanized firmware onto the PLC both bodily or by exploiting a identified distant code execution flaw.
“The elementary vulnerabilities — improper {hardware} implementations of the [Root of Trust] utilizing devoted cryptographic-processor — are unpatchable and can’t be fastened by a firmware replace because the {hardware} is bodily unmodifiable,” the researchers defined.
However, the German automation large stated it is within the technique of releasing new {hardware} variations for the S7-1500 product household that include a revamped “safe boot mechanism” that resolves the vulnerability.
The findings come as industrial safety agency Claroty final 12 months disclosed a crucial flaw impacting Siemens SIMATIC gadgets that may very well be exploited to retrieve the hard-coded, international non-public cryptographic keys and utterly compromise the product.
[ad_2]