[ad_1]
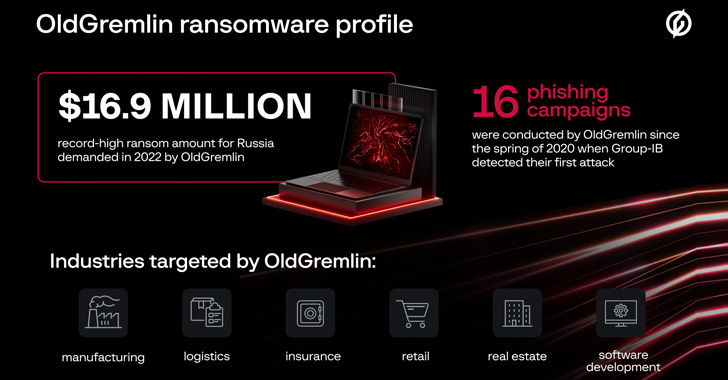
A Russian-speaking ransomware group dubbed OldGremlin has been attributed to 16 malicious campaigns geared toward entities working within the transcontinental Eurasian nation over the course of two and a half years.
“The group’s victims embody firms in sectors comparable to logistics, business, insurance coverage, retail, actual property, software program improvement, and banking,” Group-IB mentioned in an exhaustive report shared with The Hacker News. “In 2020, the group even focused an arms producer.”
In what’s a rarity within the ransomware panorama, OldGremlin (aka TinyScouts) is without doubt one of the only a few financially motivated cybercrime gangs that primarily focuses on Russian firms.
Other notable teams include Dharma, Crylock, and Thanos, contributing to an uptick in ransomware assaults concentrating on companies within the nation by over 200% in 2021.
OldGremlin first got here to mild in September 2020 when the Singapore-headquartered cybersecurity firm disclosed 9 campaigns orchestrated by the actor between May and August. The first assault was detected in early April 2020.
In all, the group is claimed to have carried out 10 phishing electronic mail campaigns in 2020, adopted by one extremely profitable assault in 2021 and 5 extra in 2022, with ransom calls for touching a document $16.9 million and permitting the actor to internet as a lot as $30 million in illicit revenues.
“OldGremlin totally research their victims,” Group-IB defined. “The demanded ransom is subsequently typically proportional to the corporate’s dimension and income and is clearly increased than the price range essential for making certain an acceptable stage of knowledge safety.”
Known to primarily goal enterprise networks operating on Windows, assaults mounted by OldGremlin have leveraged phishing emails masquerading as tax and authorized companies firms to dupe victims into clicking on fraudulent hyperlinks and downloading malicious recordsdata, permitting the attackers to worm their manner contained in the networks.
“The risk actors typically pose as well-known firms, together with the media group RBC, the authorized help system Consultant Plus, the corporate 1C-Bitrix, the Russian Union of Industrialists and Entrepreneurs, and Minsk Tractor Works,” Group-IB mentioned.
Upon gaining an preliminary foothold, OldGremlin strikes to ascertain persistence by creating scheduled duties, gaining elevated privileges utilizing Cobalt Stroke, and even flaw in Cisco AnyConnect (CVE-2020-3153 and CVE-2020-3433), whereas additionally gaining distant entry to the compromised infrastructure utilizing instruments comparable to TeamViewer.
“Around 30% of assaults allowed OldGremlin to achieve preliminary entry and begin post-exploitation,” Oleg Skulkin, head of digital forensics and incident response staff at Group-IB, advised The Hacker News. “In roughly 10%, the risk actor was in a position to deploy ransomware enterprise-wide.”
Some of the points that make the crew stand out from different ransomware teams is that it does not depend on double extortion to coerce focused firms into paying up regardless of exfiltrating the information. It has additionally been noticed taking lengthy breaks after every profitable assault.
What’s extra, the common dwell time till ransomware deployment has been pegged at 49 days, effectively above the reported 11 day median dwell time, suggesting prolonged efforts on a part of the actor to look at the breached area (which is achieved utilizing a device referred to as TinyScout).
OldGremlin’s most up-to-date phishing wave occurred on August 23, 2022, with emails embedding hyperlinks pointing to a ZIP archive payload hosted on Dropbox to activate the killchain.
These archive recordsdata, in flip, harbor a rogue LNK file (dubbed TinyLink) that downloads a backdoor referred to as TinyFluff, which is one among the many 4 implants utilized by the group: TinyPosh, TinyNode, and TinyShell, earlier than deleting knowledge backups and dropping the .NET-based TinyCrypt ransomware.
- TinyPosh: A PowerShell trojan engineered to gather and switch delicate details about the contaminated system to a distant server, and launch extra PowerShell scripts.
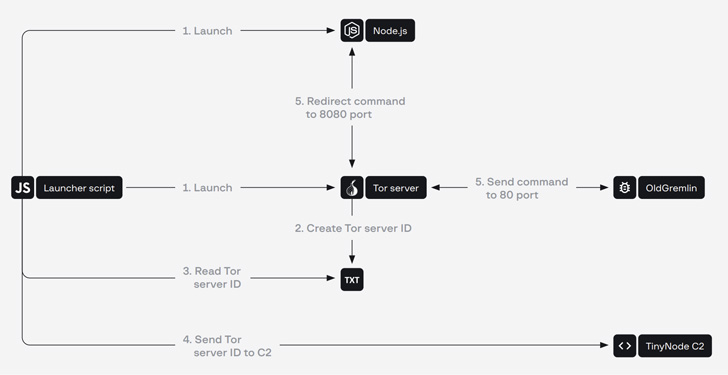
- TinyNode: A backdoor that runs the Node.js interpreter to execute instructions acquired from a command-and-control (C2) server over the Tor community.
- TinyFluff: A successor to TinyNode, which is used as the first downloader for receiving and operating malicious scripts.
Also put to make use of by OldGremlin are different instruments comparable to TinyShot, a console utility for capturing screenshots, TinyKiller, which kills antivirus processes through a deliver your individual weak driver (BYOVD) assault concentrating on gdrv.sys and RTCore64.sys drivers.
It’s value noting that the operators behind the BlackByte ransomware group had been additionally just lately discovered leveraging the identical flaw within the RTCore64.sys driver to show off safety options within the hacked machines.
One different uncommon software utilized by OldGremlin in its assaults is a .NET console app referred to as TinyIsolator, which briefly cuts off the host from the community by disabling community adaptors previous to executing the ransomware.
On high of that, the group’s malware arsenal encompasses a Linux model of TinyCrypt, which is written within the Go programming language and launched after deleting .bash_history recordsdata, altering person passwords to restrict entry to the compromised host, and disabling SSH.
“OldGremlin has debunked the parable that ransomware teams are detached to Russian firms,” Ivan Pisarev, head of dynamic malware evaluation staff at Group-IB, mentioned.
“Despite the truth that OldGremlin has been specializing in Russia to this point, they shouldn’t be underestimated elsewhere. Many Russian-speaking gangs began off by concentrating on firms in post-Soviet house after which switched to different geographies.”