[ad_1]
A brand new report from Netskope detailing the highest methods utilized by cybercriminals to assault organizations discovered that cloud apps are more and more being utilized by risk actors, representing 19% of all clicks on spearphishing hyperlinks. The report additionally make clear the attackers’ targets in keeping with their monetary or geopolitical motivations.
This Cloud and Threat report from Netskope, which is a U.S.-based firm specializing in Secure Access Service Edge, mirrored the primary three quarters of 2023.
Jump to:
Top methods utilized by cyberattackers
The most typical techniques and methods deployed by attackers to compromise programs, execute malicious code and talk with the contaminated system are break up into 4 classes by Netskope: preliminary entry, malicious payloads execution, command and management and exfiltration.
Initial entry
The simplest way for an attacker to entry a focused system is through its customers; that is very true if the focused group has patched all programs speaking with the web and is subsequently not topic to widespread vulnerabilities exploitation. Social engineering is the preferred methodology utilized by attackers to focus on organizations, whether or not it’s by e-mail (spearphishing), voice (vishing), SMS (smishing) or through social networks.
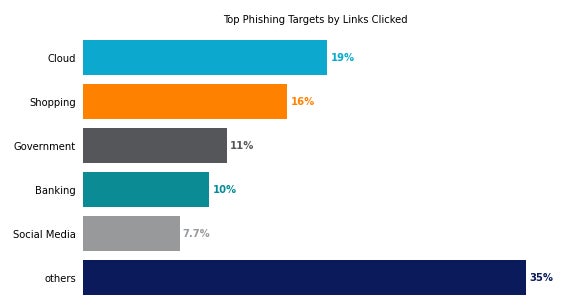
Netskope analyzed the phishing hyperlinks customers clicked on and concluded that customers most regularly clicked on phishing hyperlinks associated to cloud apps (19%), adopted by e-commerce web sites (16%) equivalent to Amazon, eBay or much less in style procuring websites (Figure A).
Figure A
According to Netskope, one third of the phishing operations focusing on cloud apps centered on Microsoft merchandise. Netskope just lately reported that Microsoft OneDrive is the preferred cloud app utilized in enterprises, so it isn’t a shock that attackers leverage this goal quite a bit, alongside Microsoft Teams, SharePoint and Outlook (Figure B).
Figure B

The second and third most-targeted apps are from Adobe (11%) and Google (8.8%).
Attackers nonetheless generally use emails to focus on customers, but the success fee of these spearphishing operations is low. For starters, organizations usually make use of superior anti-phishing filters to intercept phishing emails earlier than they attain the customers. Secondly, organizations attempt to elevate consciousness about these assault campaigns and educate their customers to identify spearphishing emails. In response to those defenses, attackers deploy varied various methods to succeed in their targets.
- Search Engine Optimization: Oftentimes, attackers create internet pages constructed round particular units of key phrases that aren’t widespread on the web, to allow them to simply deploy web optimization methods to make sure their web page is available in first in search engines like google and yahoo’ outcomes.
- Social media platforms and messaging apps: Attackers leverage in style social media platforms (e.g., Facebook) or messaging apps (e.g., WhatsApp) to succeed in targets with varied baits.
- Voicemail and textual content messages: Attackers goal customers with voicemail (vishing) or SMS (smishing) to unfold phishing hyperlinks. This methodology has the advantage of focusing on cell phones, which are sometimes much less protected than computer systems.
- Personal e-mail bins: Attackers goal customers’ private e-mail accounts, which are sometimes used on the identical programs the victims use for work and would possibly result in delicate data entry.
When it involves utilizing hooked up recordsdata for phishing, 90% of the assaults use PDF recordsdata as a result of it’s a widespread format utilized in enterprises. Ray Canzanese, director of Netskope Threat Labs, instructed TechRepublic through e-mail, that, “PDFs are popular among attackers because they are so commonly used for invoices, bills and other important correspondence. Adversaries create fake invoices and send them to their victims. Often, the only indicators that it is malicious are the URL or phone number it contains, and adversaries use obfuscation techniques to hide that from security solutions. These PDFs are created at such high volume and with so many variants that it is currently difficult for some security solutions to keep up. As with any adversary trends, security solutions will catch up and attackers will pivot to a new set of phishing techniques.”
Malicious payloads execution
Malicious payloads could be executed by unsuspecting customers with the impact of offering the attacker with distant entry to programs inside the group to function extra malicious actions, equivalent to deploying ransomware or stealing data.
Attackers now use cloud storage apps a bit extra (55%) than internet storage (45%) on common for the primary quarters of 2023 (Figure C).
Figure C
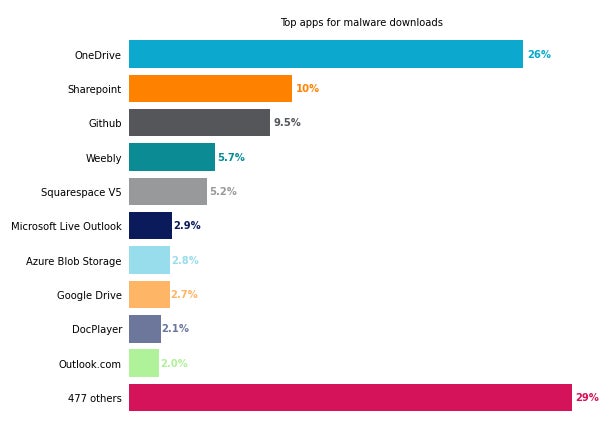
Microsoft OneDrive represents greater than 1 / 4 of the general utilization of cloud storage apps to host malware (26%), forward of SharePoint (10%) and GitHub (9.5%).
Malware communications and information exfiltration
Attackers largely use the HTTP (67%) and HTTPS (52%) protocols for communications between their malicious payloads and their command and management servers; these two protocols are usually totally allowed for customers, as they’re the primary vector for searching the web and will not be filtered by firewalls.
Far behind HTTP and HTTPS, the Domain Name System protocol is utilized in 5.5% of malware communications. The DNS protocol, which isn’t blocked and filtered in organizations, will not be as stealthy as HTTP and HTTPS when transmitting information. Also, DNS makes it more durable for attackers to mix with reliable site visitors from the group and may transmit much less information at a time than HTTP or HTTPS.
Most prevalent risk actors and their motivations
WizardSpider is essentially the most prevalent risk actor
The most prevalent risk actor as noticed by Netskope is Wizard Spider, who additionally goes by the aliases of UNC1878, TEMP.MixMaster or Grim Spider. Wizard Spider is chargeable for the TrickBot malware, which initially was a banking trojan however advanced to a fancy malware that additionally deployed extra third-parties’ malware equivalent to ransomware.
Regarding potential affiliation, Canzanese instructed TechRepublic that “nearly every major cybercrime group today uses an affiliate model where anyone can become an affiliate and use the group’s tools against targets of their choosing. Wizard Spider is no different, with affiliates using their TrickBot malware and multiple ransomware families.”
Threat actors’ main motivations and targets
According to Netskope’s report, most risk actors motivated by monetary acquire originate from Russia and Ukraine; these risk actors have largely unfold ransomware slightly than another form of malware.
On the geopolitical aspect, Netskope noticed that the largest threats come from China, led by menuPass (also called APT10, Stone Panda or Red Apollo) and Aquatic Panda.
The most focused industries range between financially-motivated actors and geopolitical ones, with monetary providers and healthcare being essentially the most focused by geopolitical actors.
Australia and North America are the 2 most-targeted areas for monetary crime as in comparison with geopolitical focusing on. When we requested Canzanese why Australia and North America have been focused, he replied, “If asked a different way, the answer perhaps becomes more readily apparent: Why is the relative percentage of geopolitical adversary group activity higher in the rest of the world? Such activity mirrors broader political, economic, military or social conflicts. So the higher percentage of geopolitical adversary activity in the rest of the world appears to be the result of active conflicts and the broader geopolitical climate in those regions.”
How to mitigate these cloud safety threats
Companies ought to take these steps to mitigate such cloud safety threats:
- Deploy e-mail safety options that may analyze hooked up recordsdata and hyperlinks to detect phishing and malware.
- Educate customers on easy methods to detect phishing and social engineering schemes which may put them or the corporate in danger. In explicit, customers shouldn’t obtain any content material from the web, even when saved on cloud apps, that doesn’t originate from a trusted contact.
- Keep all software program and working programs updated and patched as a way to keep away from being compromised by a standard vulnerability.
Disclosure: I work for Trend Micro, however the views expressed on this article are mine.
[ad_2]
