[ad_1]
Multiple vulnerabilities have been disclosed in Checkmk IT Infrastructure monitoring software program that may very well be chained collectively by an unauthenticated, distant attacker to completely take over affected servers.
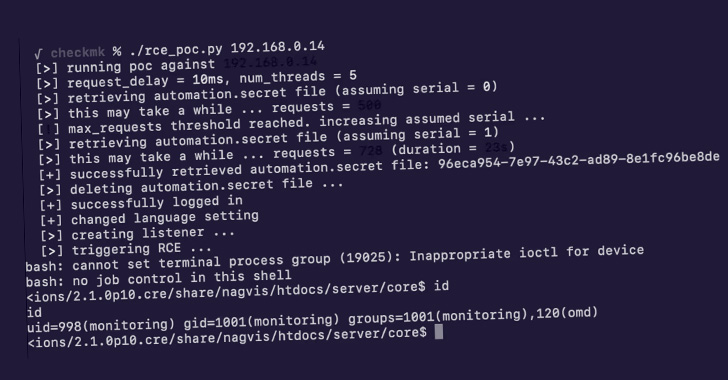
“These vulnerabilities may be chained collectively by an unauthenticated, distant attacker to realize code execution on the server working Checkmk model 2.1.0p10 and decrease,” SonarSource researcher Stefan Schiller stated in a technical evaluation.
Checkmk’s open supply version of the monitoring device is predicated on Nagios Core and gives integrations with NagVis for the visualization and technology of topological maps of infrastructures, servers, ports, and processes.
According to its Munich-based developer tribe29 GmbH, its Enterprise and Raw editions are utilized by over 2,000 prospects, together with Airbus, Adobe, NASA, Siemens, Vodafone, and others.
The 4 vulnerabilities, which encompass two Critical and two Medium severity bugs, are as follows –
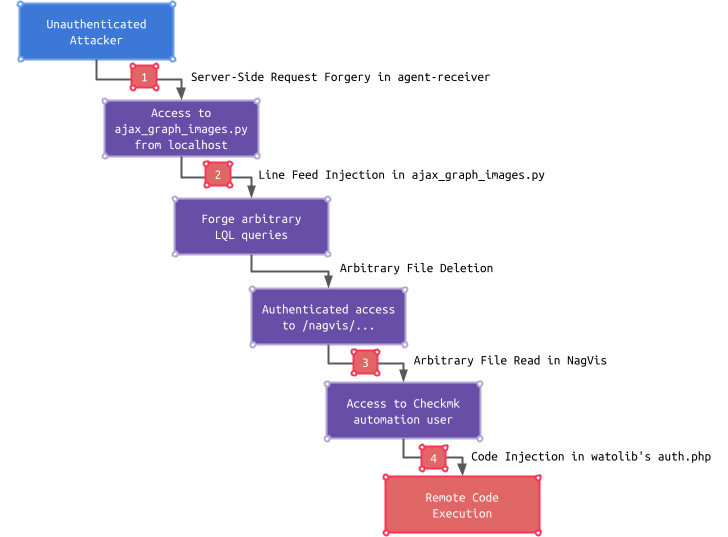
While these shortcomings on their very own have a restricted affect, an adversary can chain the problems, beginning with the SSRF flaw to entry an endpoint solely reachable from localhost, utilizing it to bypass authentication and browse a configuration file, in the end getting access to the Checkmk GUI.
“This entry can additional be changed into distant code execution by exploiting a Code Injection vulnerability in a Checkmk GUI subcomponent referred to as watolib, which generates a file named auth.php required for the NagVis integration,” Schiller defined.
Following accountable disclosure on August 22, 2022, the 4 vulnerabilities have been patched in Checkmk model 2.1.0p12 launched on September 15, 2022.
The findings observe the invention of a number of flaws in different monitoring options like Zabbix and Icinga because the begin of the 12 months, which might have been exploited to compromise the servers by working arbitrary code.
[ad_2]