[ad_1]

Research crew : Maxence LEVEZIEL, Wissem HAOUAS, Michaël GAUTHIER, Guillaume J. LAURENT, Redwan DAHMOUCHE.
By Redwan Dahmouche
Speed and precision are two main points in robotics and in Industry of the Future (also referred to as Industry 4.0). Within this framework, RoMoCo analysis crew of AS2M division at FEMTO-ST Institute has developed MiGriBot, a miniature robotic in a position to carry out 720 pick-and-place operations of sub-millimeter objects per minute. The outcomes of this analysis work have been printed in Science Robotics.
These performances are made potential due to its structure, that enables it to grip and manipulate micro-objects barely seen to the bare eye (from 40 micrometers to a number of hundred micrometers). In truth, the place different microrobots have a inflexible end-effector, MiGriBot is predicated on a precept with an articulated finish. This articulated finish permits to drive a microgripper with none wire or embedded actuator. The second benefit of this robotic is that every one its levels of mobility, together with those from the microgripper on the articulated finish, are operated from the bottom of the robotic, making its cellular elements very light-weight. Finally, its robotic construction occupies a floor of solely 20x20mm2. This degree of compactness is achieved through the use of Silicon for the inflexible components, a polymer (Polydimethylsiloxane – PDMS) as versatile joints and piezoelectric actuators geared up with place sensors. MiGriBot is subsequently lighter, extra compact and sooner than current robotic micro-manipulators.
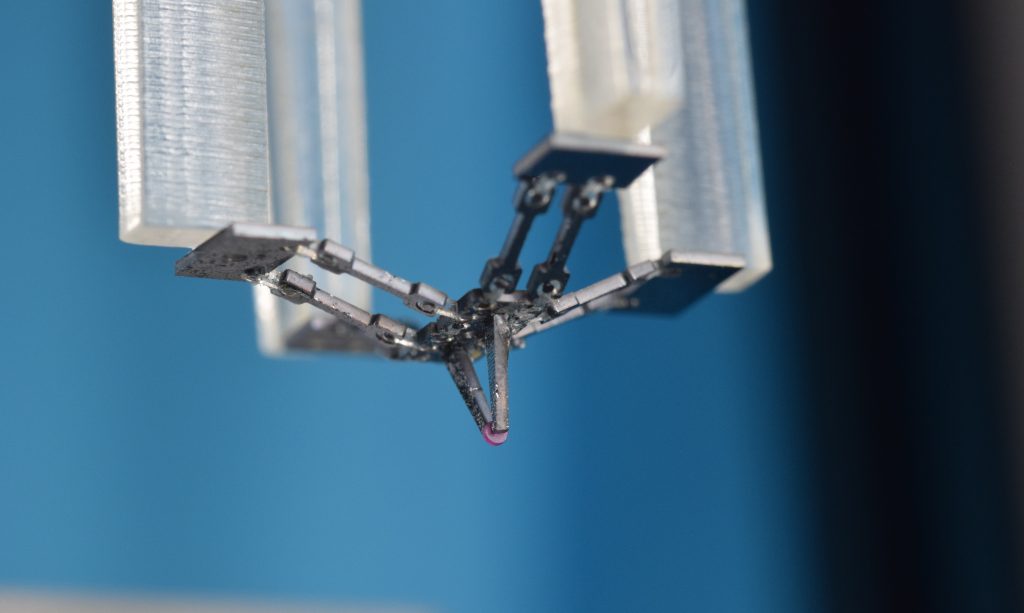

MiGriBot holding a cylindrical ruby with a diameter of 700µm and a thickness of 200µm.
While the quickest industrial pick-and-place robots don’t exceed 250 cycles per minute, the mix of all of the options of this robotic: mushy joints, small footprint, built-in gripping, light-weight construction and closed-loop management of the quick actuators permits MiGriBot to succeed in 720 pick-and-place operations per minute with about one micrometer accuracy. In the blink of an eye fixed, MiGRiBot could have manipulated 5 micro-objects, which implies that it’ll have approached, grabbed, moved and launched an object 5 occasions successively.
This robotic will likely be used to assemble Micro-Electro-Mechanical and Optical Systems (MEMS/MOEMS) used within the electronics business, the place the manufacturing throughput is more and more excessive. Thanks to its velocity and compactness, greater than 2000 robots might be positioned in 1m2 to carry out multiple million operations per second. Increasing work charges will enhance the productiveness and competitiveness of producers, which can encourage the relocation of manufacturing to Europe, America and nations with excessive labor prices. Applications in watch business, medical instrumentation, aerospace, and different fields are additionally potential.
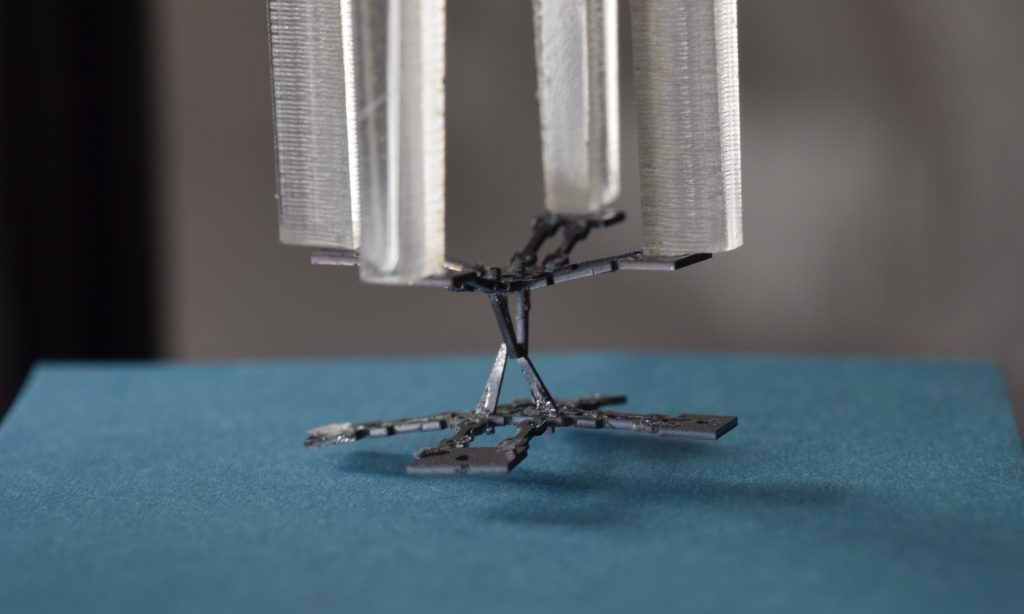
MiGriBot holding one other parallel construction exhibiting the capability of the microrobot to control heavy objects.
This work was funded by the ANR MiniSoRo venture (ANR-19-CE10-0004) and by Grand Besançon Métropole.
Research crew: Maxence LEVEZIEL, Wissem HAOUAS, Michaël GAUTHIER, Guillaume J. LAURENT, Redwan DAHMOUCHE (affiliate professor at université de Franche-Comté, venture chief and head of the analysis crew: redwan.dahmouche@univ-fcomte.fr).
tags: c-Research-Innovation, Manipulation
FEMTO-ST Institute
consists by the Université de Franche-Comté (UFC), the Ecole Nationale Supérieure de Mécanique et Microtechniques (ENSMM) and the Université de Technologie Belfort-Montbéliard (UTBM) and Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS).

FEMTO-ST Institute
consists by the Université de Franche-Comté (UFC), the Ecole Nationale Supérieure de Mécanique et Microtechniques (ENSMM) and the Université de Technologie Belfort-Montbéliard (UTBM) and Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS).
