[ad_1]

Cybercriminals are abusing Microsoft’s Trusted Signing platform to code-sign malware executables with short-lived three-day certificates.
Threat actors have lengthy wanted code-signing certificates as they can be utilized to signal malware to seem like they’re from a legit firm.
Signed malware additionally has the benefit of doubtless bypassing safety filters that will usually block unsigned executables, or a minimum of deal with them with much less suspicion.
The holy grail for risk actors is to acquire Extended Validation (EV) code-signing certificates, as they robotically achieve elevated belief from many cybersecurity applications as a result of extra rigorous verification course of. Even extra vital, EV certificates are believed to achieve a status enhance in SmartScreen, serving to to bypass alerts that will usually be displayed for unknown information.
However, EV code-singing certificates could be tough to acquire, requiring them to be stolen from different corporations or for risk actors to arrange faux companies and spend hundreds of {dollars} to buy one. Furthermore, as soon as the certificates is utilized in a malware marketing campaign, it’s often revoked, making it unusable for future assaults.
Abusing Microsoft Trusted Signing service
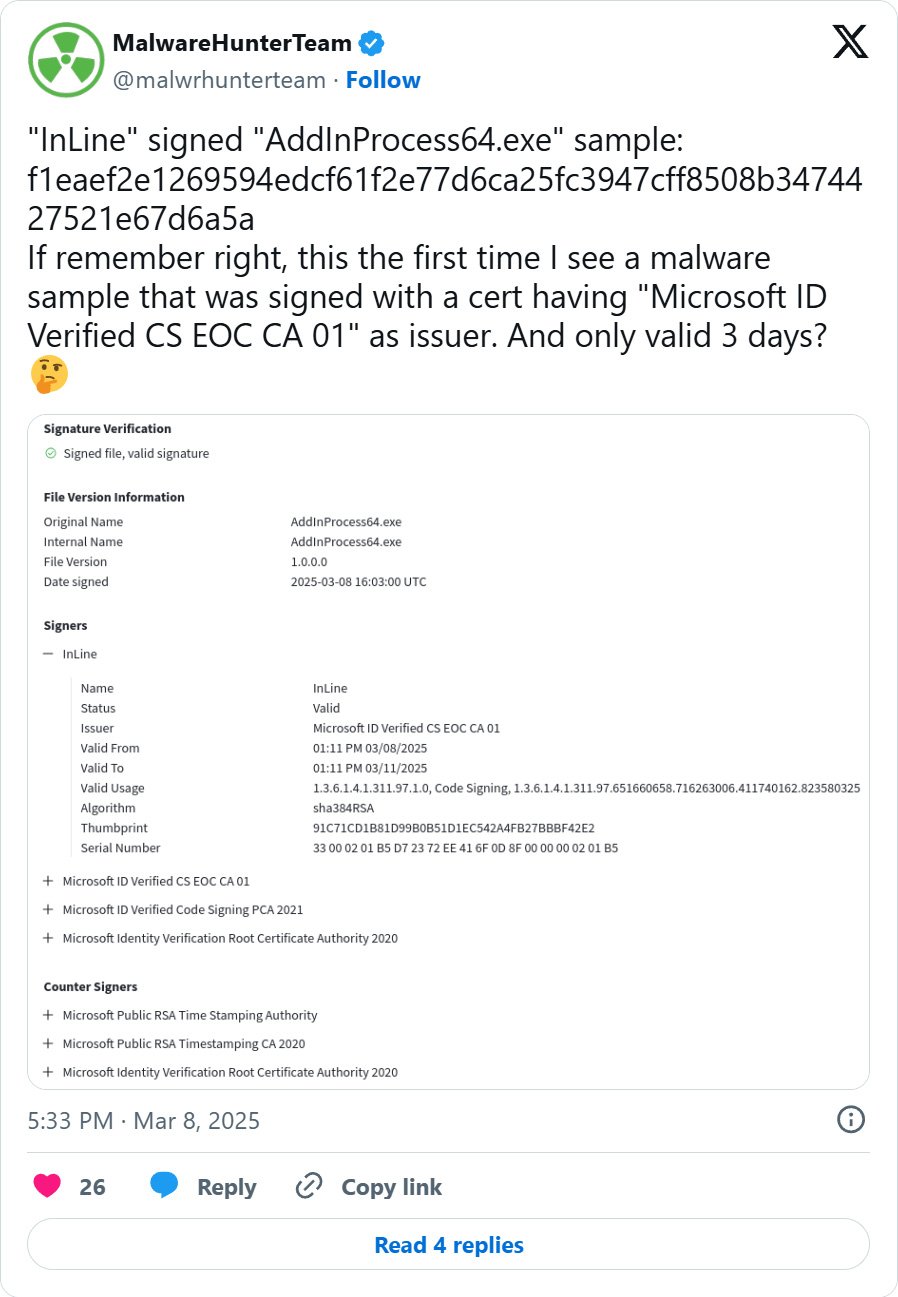
Recently, cybersecurity researchers have seen risk actors using the Microsoft Trusted Signing service to signal their malware with short-lived, three-day code-signing certificates.
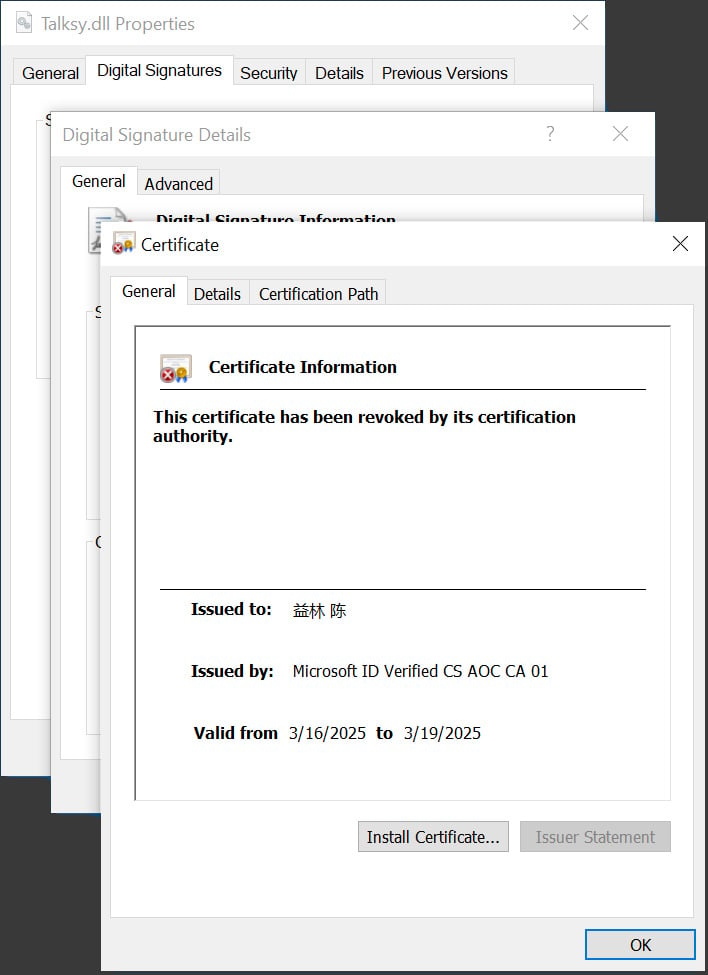
These malware samples are signed by “Microsoft ID Verified CS EOC CA 01” and the certificates is barely legitimate for 3 days. While the certificates expires three days after being issued, you will need to word that executables signed with it would nonetheless be thought-about legitimate till the issuer revokes the certificates.
Since then different researchers and BleepingComputer have discovered quite a few different samples utilized in ongoing malware campaigns, together with these utilized in a Crazy Evil Traffers crypto-theft marketing campaign [VirusTotal] and Lumma Stealer [VirusTotal] campaigns.
Source: BleepingComputer
The Microsoft Trusted Signing service launched in 2024 and is a cloud-based service that permits builders to simply have their applications signed by Microsoft.
“Trusted Signing is a full code signing service with an intuitive expertise for builders and IT professionals, backed by a Microsoft managed certification authority,” reads a Microsoft announcement for the service.
“The service helps each private and non-private belief signing situations and features a timestamping service.”
The platform has a $9.99 month-to-month subscription service designed to make it straightforward for builders to signal their executables, whereas additionally providing extra safety.
This elevated safety is completed by utilizing short-lived certificates that may simply be revoked within the occasion of abuse and by by no means issuing the certificates on to the builders, stopping them from being stolen within the occasion of a breach.
Microsoft additionally says certificates issued by way of the Trusted Signing service present an analogous SmartScreen status enhance to executables signed by its service.
“A Trusted Signing signature ensures that your utility is trusted by offering base status on sensible display screen, person mode belief on Windows, and integrity examine signature validation compliant,” reads an FAQ on the Trusted Signing website.
To shield towards abuse, Microsoft is at the moment solely permitting certificates to be issued below an organization title if they’ve been in enterprise for 3 years.
However, people can join and get authorized extra simply if they’re okay with the certificates being issued below their title.
A less complicated path
A cybersecurity researcher and developer referred to as ‘Squiblydoo,’ who has been monitoring malware campaigns abusing certificates for years, instructed BleepingComputer that they consider risk actors are switching to Microsoft’s service out of comfort.
“I believe there are just a few causes for the change. For a very long time, utilizing EV certificates has been the usual, however Microsoft has introduced adjustments to EV certificates,” Squiblydoo instructed BleepingComputer.
“However, the adjustments to EV certificates actually aren’t clear to anybody: not certificates suppliers, not attackers. However, resulting from these potential adjustments and lack of readability, simply having a code-signing certificates could also be ample for attacker wants.”
“In this regard, the verification course of for Microsoft’s certificates is considerably simpler than the verification course of for EV certificates: as a result of ambiguity over EV certificates, it is smart to make use of the Microsoft certificates.”
BleepingComputer contacted Microsoft in regards to the abuse and was instructed that the corporate makes use of risk intelligence monitoring to seek out and revoke certificates as they’re discovered.
“We use energetic risk intelligence monitoring to continually search for any misuse or abuse of our signing service,” Microsoft instructed BleepingComputer.
“When we detect threats we instantly mitigate with actions similar to broad certificates revocation and account suspension. The malware samples you shared are detected by our antimalware merchandise and we’ve got already taken motion to revoke the certificates and forestall additional account abuse.”
[ad_2]