[ad_1]

A brand new malware dubbed ‘ProxyShellMiner’ exploits the Microsoft Exchange ProxyShell vulnerabilities to deploy cryptocurrency miners all through a Windows area to generate revenue for the attackers.
ProxyShell is the identify of three Exchange vulnerabilities found and stuck by Microsoft in 2021. When chained collectively, the vulnerabilities enable unauthenticated, distant code execution, letting attackers take full management of the Exchange server and pivot to different elements of the group’s community.
In assaults seen by Morphisec, the menace actors exploit the ProxyShell flaws tracked as CVE-2021-34473 and CVE-2021-34523 to achieve preliminary entry to the group’s community.
Next, the menace actors drop a .NET malware payload into the NETLOGON folder of the area controller to make sure that all gadgets on the community run the malware.
For the malware to activate, it requires a command line parameter that additionally dubs as a password for the XMRig miner part.
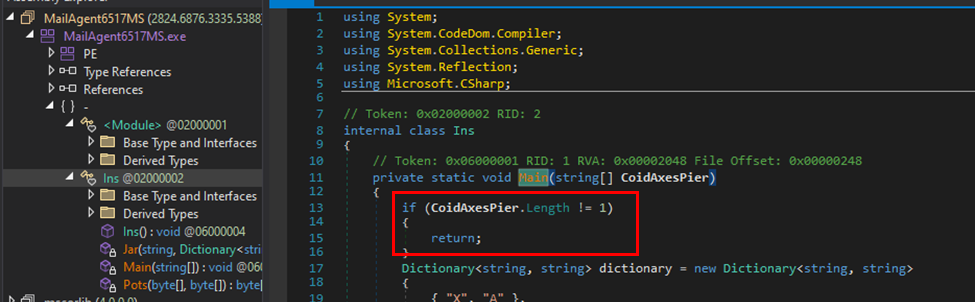
“ProxyShellMiner makes use of an embedded dictionary, an XOR decryption algorithm, and an XOR key downloaded from a distant server,” describes the Morphisec report.
“Then, it makes use of a C# compiler CSC.exe with “InReminiscence” compile parameters to execute the subsequent embedded code modules.”
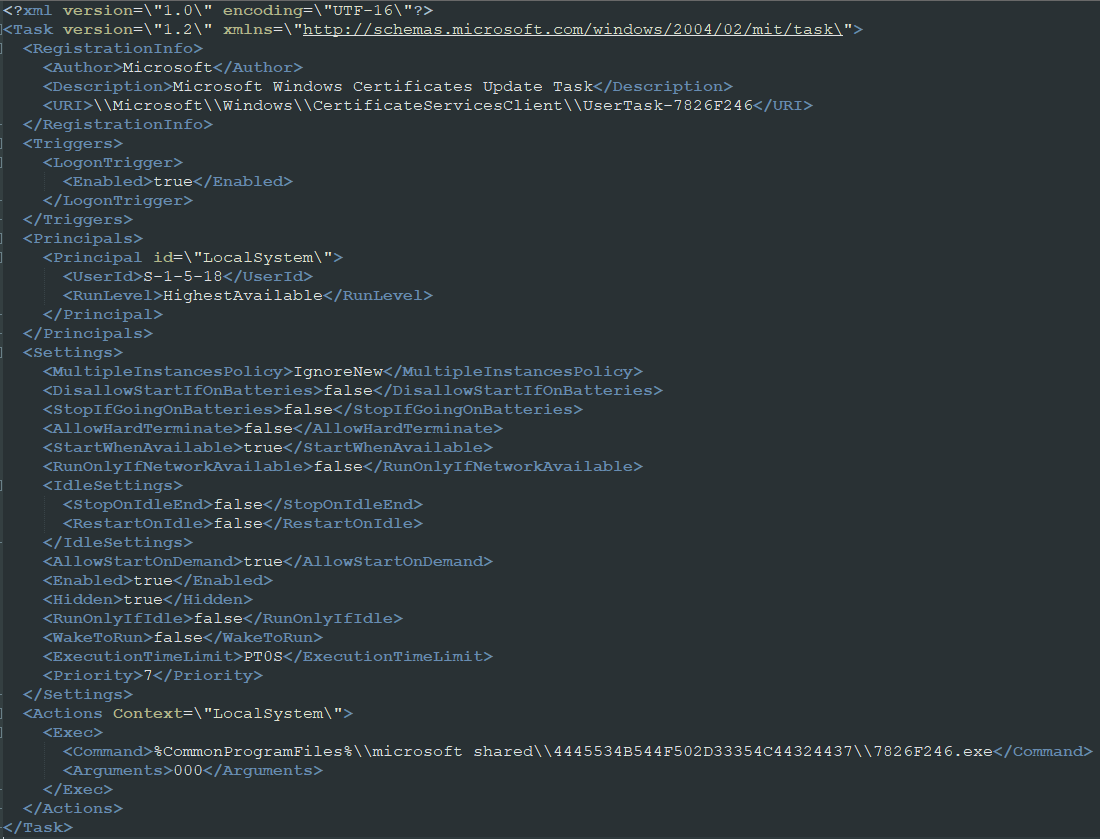
In the subsequent part, the malware downloads a file named “DC_DLL” and performs .NET reflection to extract arguments for the duty scheduler, XML, and the XMRig key. The DLL file is utilized for the decryption of extra recordsdata.
A second downloader establishes persistence on the contaminated system by making a scheduled activity that’s configured to run upon the person’s login. Finally, the second loader is downloaded from a distant useful resource, together with 4 different recordsdata.
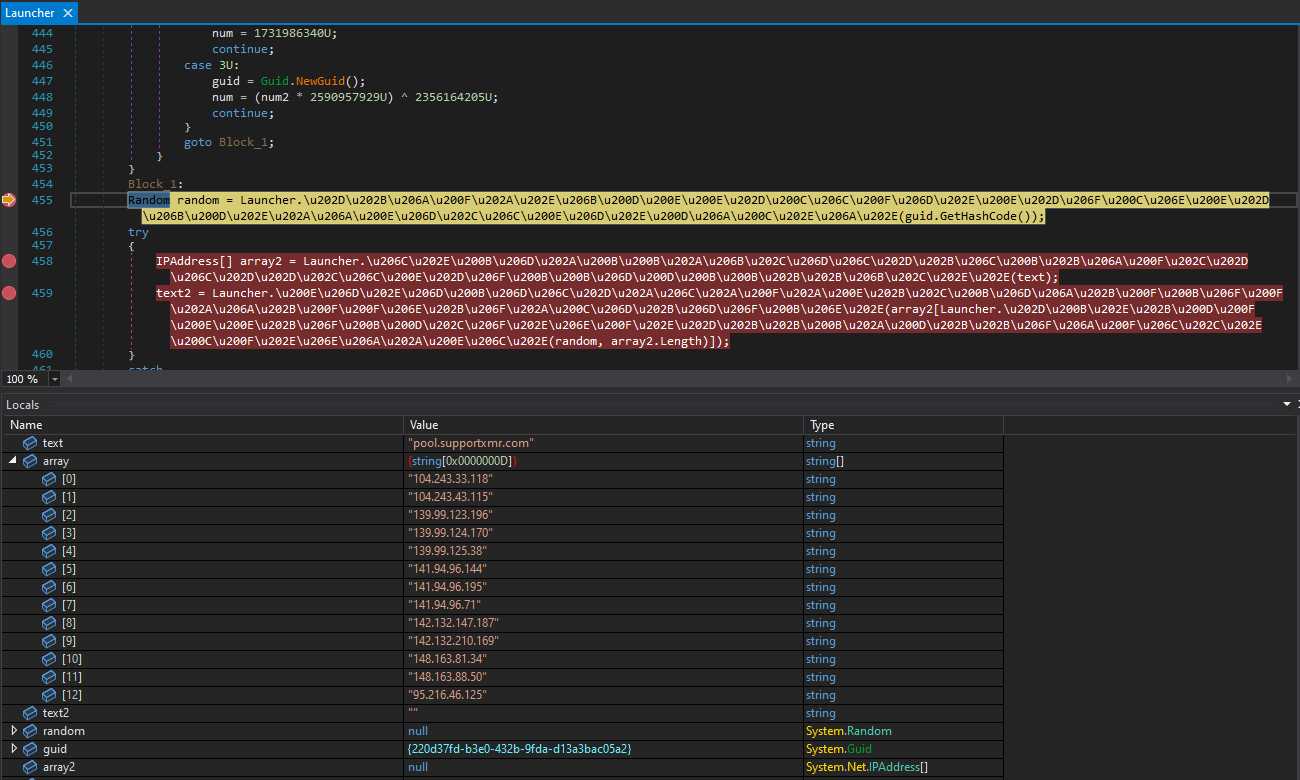
That file decides which browser of these put in on the compromised system might be used for injecting the miner into its reminiscence area, utilizing a way generally known as “course of hollowing.” After that, it picks a random mining pool from a hardcoded checklist, and the mining exercise begins.
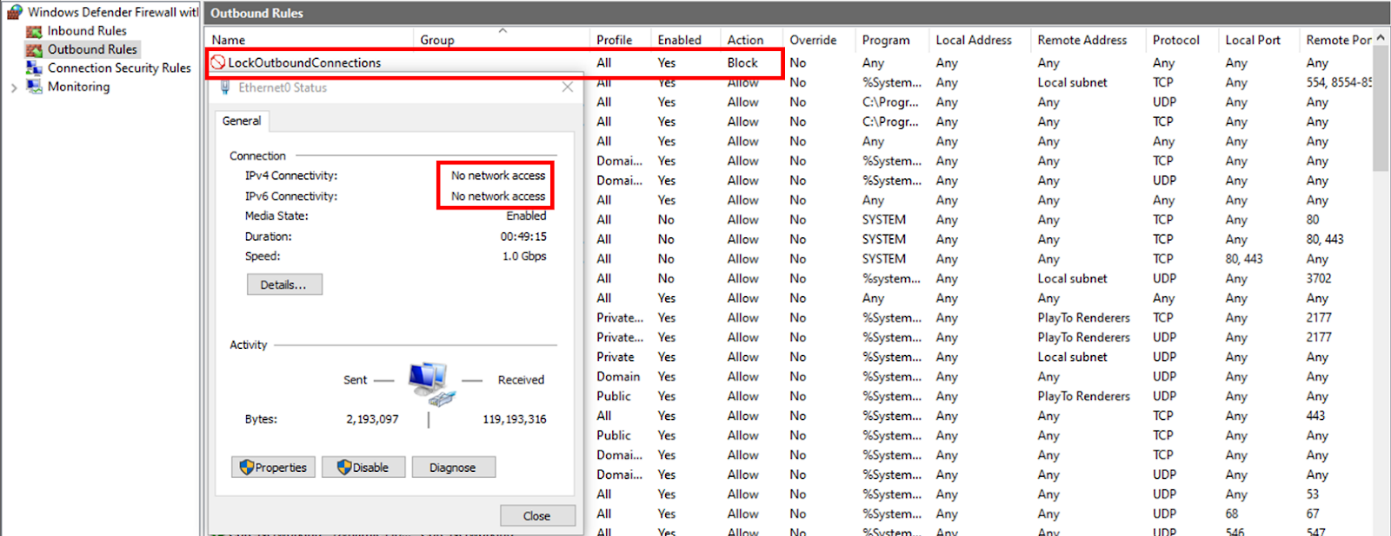
The closing step within the assault chain is to create a firewall rule that blocks all outgoing visitors, which applies to all Windows Firewall profiles.
The objective of that is to make it much less probably for defenders to detect an infection markers or obtain any alerts a couple of potential compromise from the breached system.
To evade safety instruments that monitor course of runtime conduct, the malware waits a minimum of 30 seconds after the browser’s hollowing earlier than creating the firewall rule. Possibly, the miner continues to speak with its mining pool by way of a backdoor that is not monitored by safety instruments.
Morphisec warns that the influence of the malware goes past inflicting service outages, degrading server efficiency, and overheating computer systems.
Once the attackers have gained a foothold within the community, they will do something from backdoor deployment to code execution.
To tackle the chance of ProxyShellMiner infections, Morphisec advises all admins to use out there safety updates and use complete and multi-faceted menace detection and protection methods.
[ad_2]
