[ad_1]
This submit was co-authored by Dan Russ, Associate Director, and Sacha Abinader, Managing Director from Accenture.
The yr 2022 was a notable one within the historical past of our local weather—it stood because the fifth warmest yr ever recorded1. An enhance in excessive climate situations, from devastating droughts and wildfires to relentless floods and warmth waves, made their presence felt greater than ever earlier than—and 2023 appears poised to shatter nonetheless extra data. These unnerving circumstances exhibit the ever-growing impression of local weather change that we’ve come to expertise because the planet continues to heat.
Microsoft’s sustainability journey
At Microsoft, our method to mitigating the local weather disaster is rooted in each addressing the sustainability of our personal operations and in empowering our clients and companions of their journey to net-zero emissions. In 2020, Microsoft set out with a sturdy dedication: to be a carbon-negative, water constructive, and zero-waste firm, whereas defending ecosystems, all by the yr 2030. Three years later, Microsoft stays steadfast in its resolve. As a part of these efforts, Microsoft has launched Microsoft Cloud for Sustainability, a complete suite of enterprise-grade sustainability administration instruments aimed toward supporting companies of their transition to net-zero.
Moreover, our contribution to a number of world sustainability initiatives has the purpose of benefiting each particular person and group on this planet. Microsoft has accelerated the provision of progressive local weather applied sciences by our Climate Innovation Fund and is working exhausting to strengthen our local weather coverage agenda. Microsoft’s give attention to sustainability-related efforts types the backdrop for the subject tackled on this weblog submit: our partnership with Accenture on the appliance of AI applied sciences towards fixing the difficult drawback of methane emissions detection, quantification, and remediation within the power trade.
“We are excited to partner with Accenture to deliver methane emissions management capabilities. This combines Accenture’s deep domain knowledge together with Microsoft’s cloud platform and expertise in building AI solutions for industry problems. The result is a solution that solves real business problems and that also makes a positive climate impact.”—Matt Kerner, CVP Microsoft Cloud for Industry, Microsoft.
Why is methane vital?
Methane is roughly 85 occasions stronger than carbon dioxide (CO2) at trapping warmth within the ambiance over a 20-year interval. It is the second most plentiful anthropogenic greenhouse gasoline after CO2, accounting for about 20 % of worldwide emissions.
The world oil and gasoline trade is likely one of the main sources of methane emissions. These emissions happen throughout the complete oil and gasoline worth chain, from manufacturing and processing to transmission, storage, and distribution. The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that it’s technically potential to keep away from round 75 % of as we speak’s methane emissions from world oil and gasoline operations. These statistics drive dwelling the significance of addressing this crucial subject.
Microsoft’s funding in Project Astra
Microsoft has signed on to the Project Astra initiative—along with main power firms, public sector organizations, and tutorial establishments—in a coordinated effort to exhibit a novel method to detecting and measuring methane emissions from oil and gasoline manufacturing websites.
Project Astra entails an progressive sensor community that harnesses advances in methane-sensing applied sciences, information sharing, and information analytics to supply near-continuous emissions monitoring of methane throughout oil and gasoline services. Once operational, this type of good digital community would enable producers and regulators to pinpoint methane releases for well timed remediation.
Accenture and Microsoft—The way forward for methane administration
Attaining the purpose of net-zero methane emissions is turning into more and more potential. The applied sciences wanted to mitigate emissions are maturing quickly, and digital platforms are being developed to combine complicated elements. As referenced in Accenture’s current methane thought management piece, “More than hot air with methane emissions”. What is required now could be a shift—from a reactive paradigm to a preventative one—the place the crucial subject of leak detection and remediation is remodeled into leak prevention by leveraging superior applied sciences.
Accenture’s particular capabilities and toolkit
To date, the power trade’s method to methane administration has been fragmented and comprised of a bunch of expensive monitoring instruments and gear which have been siloed throughout numerous operational entities. These siloed options have made it troublesome for power firms to precisely analyze emissions information, at scale, and remediate these issues rapidly.
What has been missing is a single, inexpensive platform that may combine these elements into an efficient methane emissions mitigation instrument. These elements embody enhanced detection and measurement capabilities, machine studying for higher decision-making, and modified working procedures and gear that make “net-zero methane” occur quicker. These platforms are being developed now and might accommodate all kinds of expertise options that can kind the digital core mandatory to realize a aggressive benefit.
Accenture has created a Methane Emissions Monitoring Platform (MEMP) that facilitates the combination of a number of information streams and embeds key methane insights into enterprise operations to drive motion (see Figure 1 under).
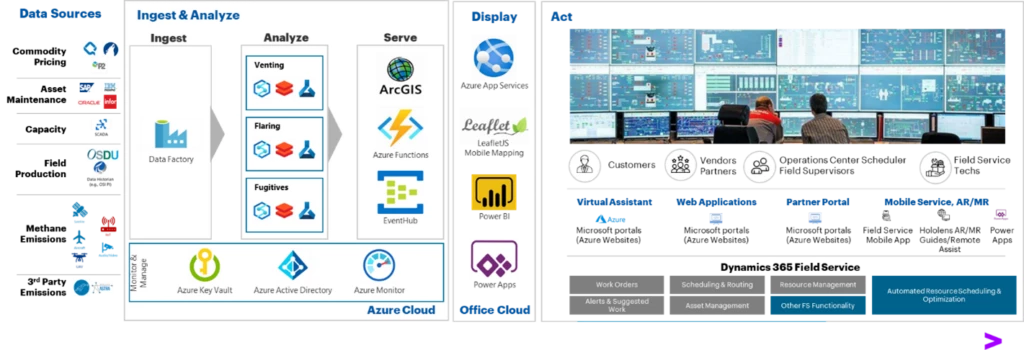
Figure 1: Accenture’s Methane Emissions Monitoring Platform (MEMP).
The cloud-based platform, which runs on Microsoft Azure, permits power firms to each measure baseline methane emissions in close to real-time and detect leaks utilizing satellites, fastened wing plane, and floor stage sensing applied sciences. It is designed to combine a number of information sources to optimize venting, flaring, and fugitive emissions. Figure 2 under illustrates the aspirational end-to-end course of incorporating Microsoft applied sciences. MEMP additionally facilitates connectivity with back-end methods liable for work order creation and administration, together with the scheduling and dispatching of area crews to remediate particular emission occasions.
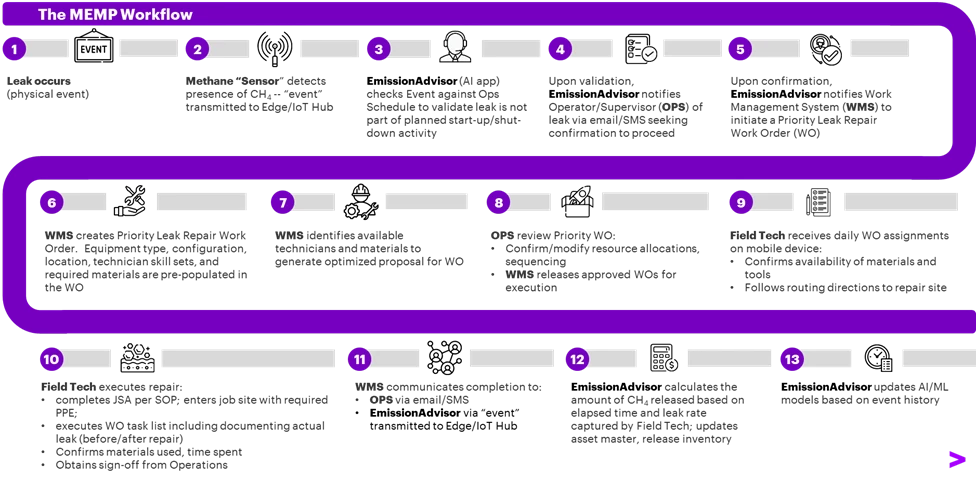
Figure 2: The Methane Emissions Monitoring Platform Workflow (aspirational).
Microsoft’s AI instruments powering Accenture’s Methane Emissions Monitoring Platform
Microsoft has supplied a lot of Azure-based AI instruments for tackling methane emissions, together with instruments that assist sensor placement optimization, digital twin for methane Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, anomaly (leak) detection, and emission supply attribution and quantification. These instruments, when built-in with Accenture’s MEMP, enable customers to observe alerts in close to real-time by a user-friendly interface, as proven in Figure 3.
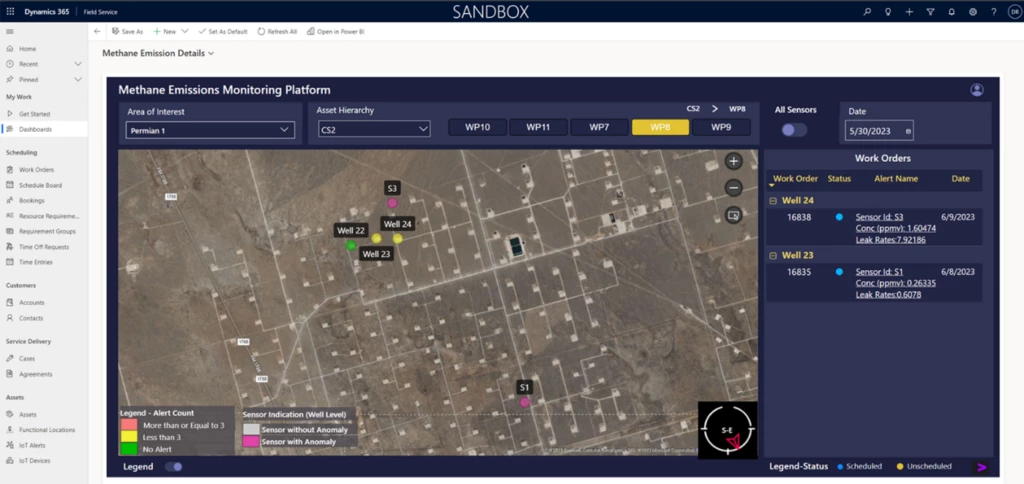
Figure 3: MEMP Landing Page visualizing wells, IoT sensors, and Work Orders.
“Microsoft has developed differentiated AI capabilities for methane leak detection and remediation, and is excited to partner with Accenture in integrating these features onto their Methane Emissions Monitoring Platform, to deliver value to energy companies by empowering them in their path to net-zero emissions”—Merav Davidson, VP, Industry AI, Microsoft.
Methane IoT sensor placement optimization
Placing sensors in strategic areas to make sure most potential protection of the sector and well timed detection of methane leaks is step one in the direction of constructing a dependable end-to-end IoT-based detection and quantification answer. Microsoft’s answer for sensor placement makes use of geospatial, meteorological, and historic leak fee information and an atmospheric dispersion mannequin to mannequin methane plumes from sources inside the space of curiosity and procure a consolidated view of emissions. It then selects the most effective areas for sensors utilizing both a mathematical programming optimization methodology, a grasping approximation methodology, or an empirical downwind methodology that considers the dominant wind course, topic to price constraints.
In addition, Microsoft offers a validation module to judge the efficiency of any candidate sensor placement technique. Operators can consider the marginal features supplied by using further sensors within the community, by sensitivity evaluation as proven in Figure 4 under.
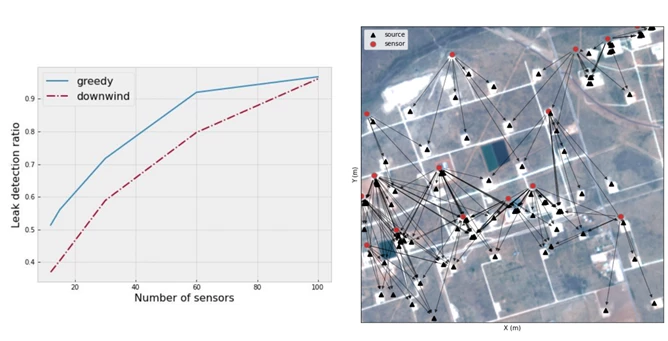
Figure 4: Left: Increase in leak protection with a lot of sensors. By rising the variety of sensors which might be accessible for deployment, the leak detection ratio (i.e., the fraction of detected leaks by deployed sensors) will increase. Right: Source protection for 15 sensors. The arrows map every sensor (crimson circles) to the sources (black triangles) that it detects.
End-to-end information pipeline for methane IoT sensors
To obtain steady monitoring of methane emissions from oil and gasoline property, Microsoft has applied an end-to-end answer pipeline the place streaming information from IoT Hub is ingested right into a Bronze Delta Lake desk leveraging Structured Streaming on Spark. Sensor information cleansing, aggregation, and transformation to algorithm information mannequin are finished and the resultant information is saved in a Silver Delta Lake desk in a format that’s optimized for downstream AI duties.
Methane leak detection is carried out utilizing uni- and multi-variate anomaly detection fashions for improved reliability. Once a leak has been detected, its severity can be computed, and the emission supply attribution and quantification algorithm then identifies the probably supply of the leak and quantifies the leak fee.
This occasion data is shipped to the Accenture Work Order Prioritization module to set off acceptable alerts primarily based on the severity of the leak to allow well timed remediation of fugitive or venting emissions. The quantified leaks will also be recorded and reported utilizing instruments such because the Microsoft Sustainability Manager app. The particular person elements of this end-to-end pipeline are described within the sections under and illustrated in Figure 5.
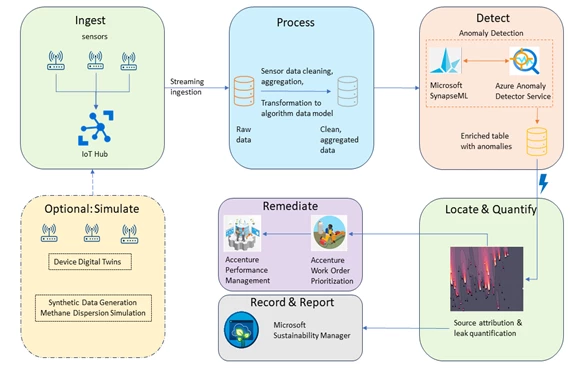
Figure 5: End-to-end IoT information pipeline that runs on Microsoft Azure demonstrating methane leak detection, quantification, and remediation capabilities.
Digital twin for methane IoT sensors
Data streaming from IoT sensors deployed within the area must be orchestrated and reliably handed to the processing and AI execution pipeline. Microsoft’s answer creates a digital twin for each sensor. The digital twin includes a sensor simulation module that’s leveraged in several levels of the methane answer pipeline. The simulator is used to check the end-to-end pipeline earlier than area deployment, reconstruct and analyze anomalous occasions by what-if eventualities and allow the supply attribution and leak quantification module by a simulation-based, inverse modeling method.
Anomaly (leak) detection
A methane leak at a supply may manifest as an uncommon rise within the methane focus detected at close by sensor areas that require well timed mitigation. The first step in the direction of figuring out such an occasion is to set off an alert by the anomaly detection system. A severity rating is computed for every anomaly to assist prioritize alerts. Microsoft offers the next two strategies for time sequence anomaly detection, leveraging Microsoft’s open-source SynapseML library, which is constructed on the Apache Spark distributed computing framework and simplifies the creation of massively scalable machine studying pipelines:
- Univariate anomaly detection: Based on a single variable, for instance, methane focus.
- Multivariate anomaly detection: Used in eventualities the place a number of variables, together with methane focus, wind velocity, wind course, temperature, relative humidity, and atmospheric stress, are used to detect an anomaly.
Post-processing steps are applied to reliably flag true anomalous occasions in order that remedial actions may be taken in a well timed method whereas decreasing false positives to keep away from pointless and costly area journeys for personnel. Figure 6 under illustrates this characteristic in Accenture’s MEMP: the ‘hover field” over Sensor 6 paperwork a complete of seven alerts leading to simply two work orders being created.
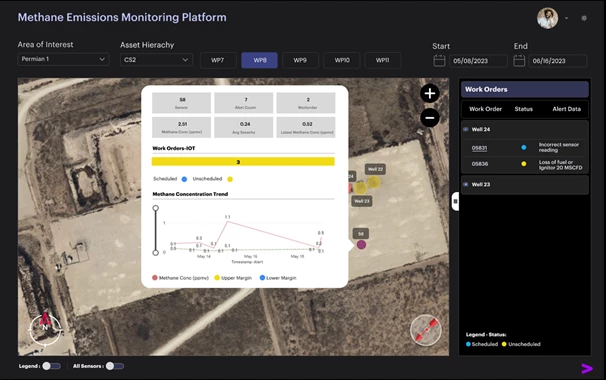
Figure 6: MEMP dashboard visualizing alerts and ensuing work orders for Sensor 6.
Emission supply attribution and quantification
Once deployed within the area, methane IoT sensors can solely measure compound alerts within the proximity of their location. For an space of curiosity that’s densely populated with potential emission sources, the problem is to establish the supply(s) of the emission occasion. Microsoft offers two approaches for figuring out the supply of a leak:
- Area of affect attribution mannequin: Given the sensor measurements and placement, an “area of influence” is computed for a sensor location at which a leak is detected, primarily based on the real-time wind course and asset geo-location. Then, the asset(s) that lie inside the computed “area of influence” are recognized as potential emissions sources for that flagged leak.
- Bayesian attribution mannequin: With this method, supply attribution is achieved by inversion of the methane dispersion mannequin. The Bayesian method includes two primary elements—a supply leak quantification mannequin and a probabilistic rating mannequin—and might account for uncertainties within the information stemming from measurement noise, statistical and systematic errors, and offers the almost certainly sources for a detected leak, the related confidence stage and leak fee magnitude.
Considering the excessive variety of sources, low variety of sensors, and the variability of the climate, this poses a fancy however extremely priceless inverse modeling drawback to unravel. Figure 7 offers perception relating to leaks and work orders for a specific nicely (Well 24). Specifically, diagrams present well-centric and sensor-centric assessments that attribute a leak to this nicely.
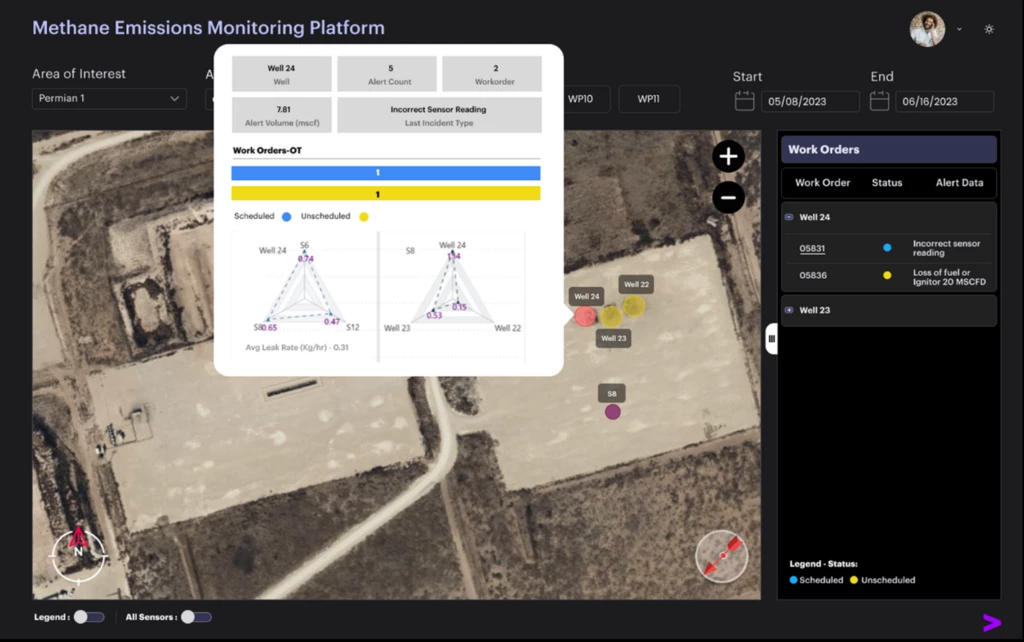
Figure 7: Leak Source Attribution for Well 24.
Further, Accenture’s Work Order Prioritization module utilizing Microsoft Dynamics 365 Field Service utility (Figure 8) permits Energy operators to provoke remediation measures below the Leak Detection and Remediation (LDAR) paradigm.
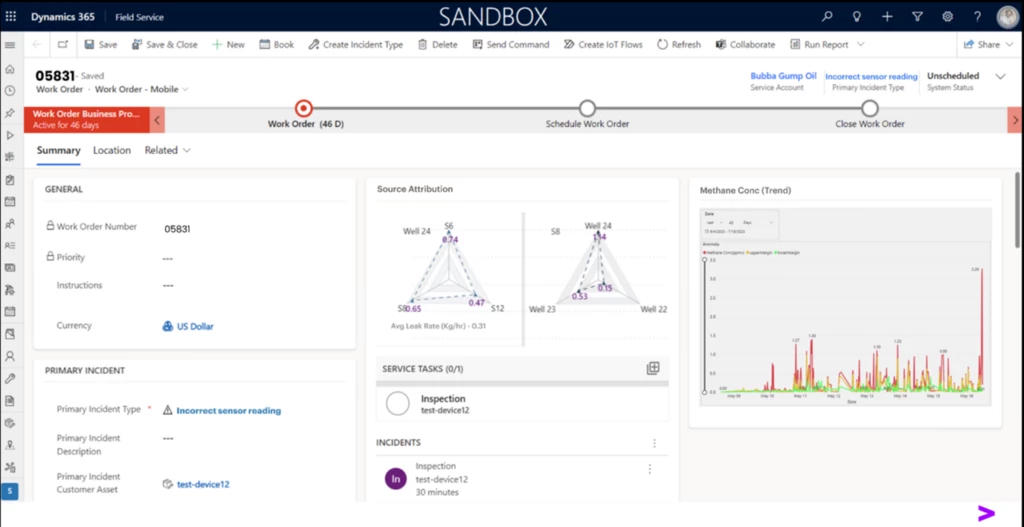
Figure 8: Dynamics 365 Work Order with emission supply attribution and CH4 focus development information embedded.
Looking forward
In partnership with Microsoft, Accenture is seeking to proceed refining MEMP, which is constructed on the superior AI and statistical fashions offered on this weblog. Future capabilities of MEMP look to maneuver from “detection and remediation” to “prediction and prevention” of emission occasions, together with enhanced occasion quantification and supply attribution.
Microsoft and Accenture will proceed to put money into superior capabilities with an eye fixed towards each:
- Integrating trade requirements platforms reminiscent of Azure Data Manager for Energy (ADME) and Open Footprint Forum to allow each publishing and consumption of emissions information.
- Leveraging Generative AI to simplify the consumer expertise.
Learn extra
Case research
Duke Energy is working with Accenture and Microsoft on the improvement of a brand new expertise platform designed to measure precise baseline methane emissions from pure gasoline distribution methods.
Accenture Methane Emissions Monitoring Platform
More data relating to Accenture’s MEMP may be present in “More than hot air with methane emissions”. Additional data relating to Accenture may be discovered on the Accenture homepage and on their power web page.
Microsoft Azure Data Manager for Energy
Azure Data Manager for Energy is an enterprise-grade, absolutely managed, OSDU Data Platform for the power trade that’s environment friendly, standardized, straightforward to deploy, and scalable for information administration—ingesting, aggregating, storing, looking, and retrieving information. The platform will present the dimensions, safety, privateness, and compliance anticipated by our enterprise clients. The platform gives out-of-the-box compatibility with main service firm purposes, which permits geoscientists to make use of domain-specific purposes on information contained in Azure Data Manager for Energy with ease.
Related publications and convention shows
Source Attribution and Emissions Quantification for Methane Leak Detection: A Non-Linear Bayesian Regression Approach. Mirco Milletari, Sara Malvar, Yagna Oruganti, Leonardo Nunes, Yazeed Alaudah, Anirudh Badam. The 8th International Online & Onsite Conference on Machine Learning, Optimization, and Data Science.
Surrogate Modeling for Methane Dispersion Simulations Using Fourier Neural Operator. Qie Zhang, Mirco Milletari, Yagna Oruganti, Philipp Witte. Presented on the NeurIPS 2022 Workshop on Tackling Climate Change with Machine Learning.
1https://climate.nasa.gov/news/3246/nasa-says-2022-fifth-warmest-year-on-record-warming-trend-continues/
[ad_2]
