[ad_1]
In a latest examine printed within the BMC Medicine journal, researchers in Sweden explored the affiliation between above-optimal maternal gestational weight acquire (GWG) and the chance of neurodevelopmental problems similar to mental incapacity, autism spectrum dysfunction (ASD), and attention-deficit/hyperactivity dysfunction (ADHD) in offspring.
 Rates of maternal weight acquire over the course of being pregnant and offspring danger of neurodevelopmental problems. Image Credit: Hazal Ak / Shutterstock
Rates of maternal weight acquire over the course of being pregnant and offspring danger of neurodevelopmental problems. Image Credit: Hazal Ak / Shutterstock
Background
Neurodevelopmental problems are extremely prevalent, and the social help necessities all through the affected person’s life considerably burden their households. The three most prevalent neurodevelopmental problems —ASD, ADHD, and mental incapacity — usually current collectively in kids.
Furthermore, whereas de novo and inherited mutations have each been related to these neurodevelopmental problems, different environmental, organic, and social elements are additionally thought to contribute to their etiology.
Although earlier research have explored the affiliation between maternal GWG past the optimum vary and the elevated danger of neurodevelopmental problems, it has been tough to separate the consequences of above-optimal GWG and gestational period on the opposed outcomes associated to neurodevelopmental problems. This is as a result of these research didn’t take into account the size of the being pregnant as a determinant issue.
Since the expansion of the purposeful and structural components of the fetal mind is a sequential course of and the vulnerability to exterior elements similar to vitamin and environmental stressors varies throughout trimesters, it’s vital to evaluate the hyperlink between trimester-specific GWG and the chance of neurodevelopmental problems.
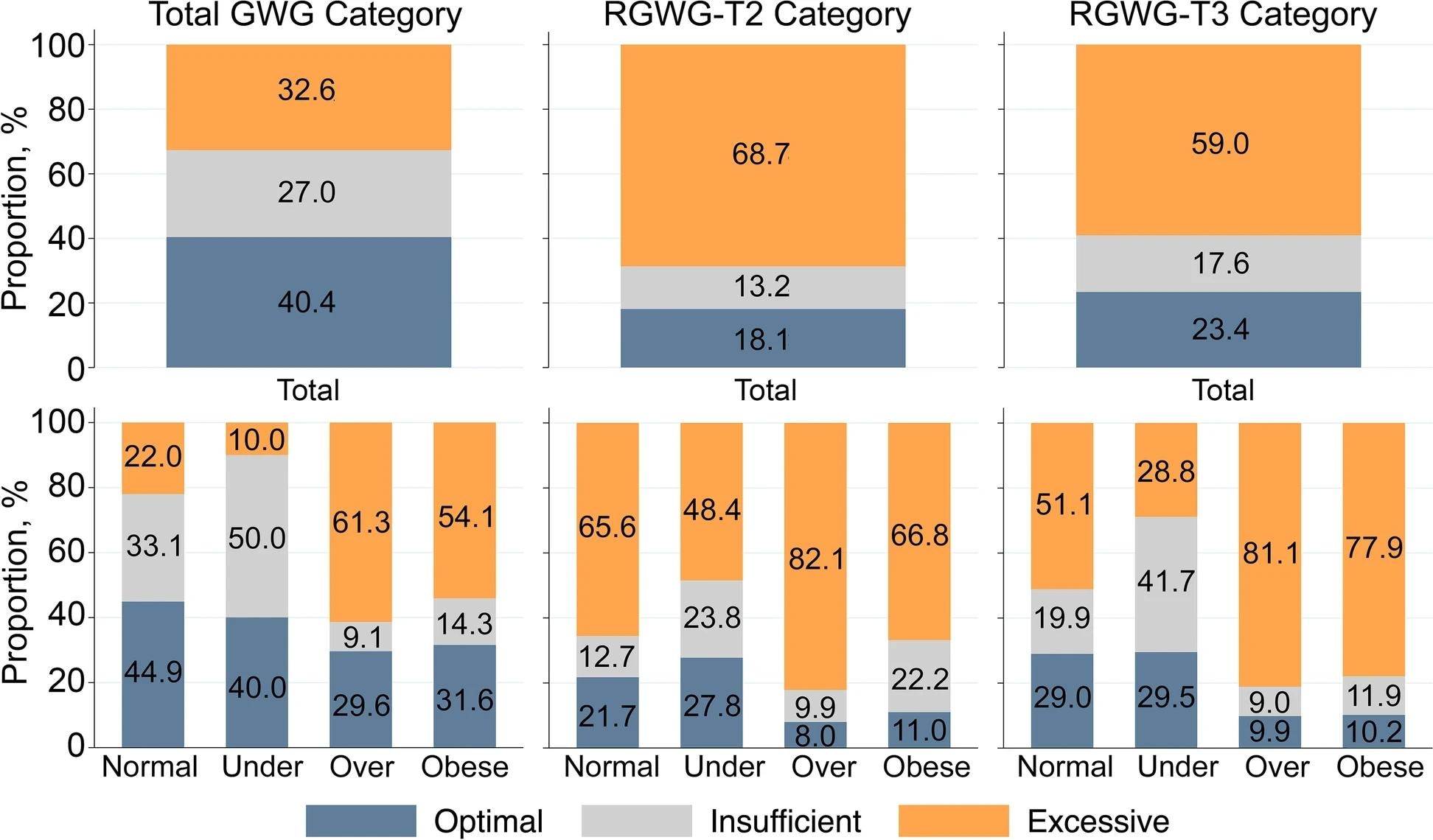 Distributions of complete GWG (kg), RGWG-T2, and RGWG-T3 classes in line with the IOM pointers
Distributions of complete GWG (kg), RGWG-T2, and RGWG-T3 classes in line with the IOM pointers
About the examine
In the current examine, the researchers carried out a cohort examine among the many Swedish inhabitants to guage the chance of neurodevelopmental problems in line with the z-scores for GWG and the speed of weight acquire over the last two trimesters of the being pregnant.
They used information from Stockholm’s document system for antenatal care and data on outcomes, exposures, and covariates from regional and nationwide well being and administrative registries. Children born between January 2007 and December 2010 for whom the info on maternal GWG measurements have been obtainable have been included within the examine.
All neurodevelopmental dysfunction diagnoses have been thought of for the first evaluation, together with one or a number of diagnoses of ADHD, mental incapacity, and ASD. For the secondary evaluation, the researchers solely included mixtures of mutually unique outcomes similar to solely ADHD or ASD, ADHD with ASD however no mental incapacity.
The examined exposures comprised complete GWG and the speed of GWG for the second and third trimesters of the being pregnant. The evaluation was additionally carried out utilizing the “inadequate,” “optimum,” and “extreme” classes for the speed of GWG for every physique mass index group. Potential confounding covariates included start yr, intercourse of the kid, family revenue, paternal and maternal area of start, maternal age, mom’s schooling degree, interpregnancy interval, psychiatric historical past of the mom, and smoking conduct.
Results
The outcomes indicated that larger than optimum complete GWG was related to a 19% enhance within the danger of any neurodevelopmental dysfunction, whereas decrease than optimum GWG elevated the chance of neurodevelopmental problems by 12%.
Furthermore, the speed of GWG was additionally related to the chance of neurodevelopmental problems, with a slower GWG charge throughout the second trimester growing the chance of neurodevelopmental problems by 9%, however a better charge of GWG within the second trimester not being related to neurodevelopmental dysfunction danger.
In distinction, whereas a slower charge of GWG was not linked to neurodevelopmental dysfunction danger within the third trimester, a better charge of GWG was related to a 28% enhance within the danger of neurodevelopmental dysfunction diagnoses.
In the secondary evaluation utilizing categorized charges of GWG within the final two trimesters, the outcomes reported {that a} low GWG charge within the second trimester mixed with an extreme charge of GWG within the third trimester considerably elevated the chance of mental incapacity and ADHD within the offspring.
The authors additionally mentioned believable mechanisms for linking extreme GWG and fetal neurodevelopment, such because the downstream affect of maternal and fetal adipose tissue accumulation.
Increased adiposity within the mom and fetus is regarded as linked to dysregulations of the pro-inflammatory cytokine, insulin, leptin, and glucose signaling, elevated oxidative stress, and dysregulated signaling associated to dopamine and serotonin. In distinction, inadequate GWG may lead to a vitamin deficit atmosphere, which has detrimental results on the fetus’s mind growth.
Conclusions
Overall, the outcomes supplied proof that maternal GWG beneath and above the optimum vary have been related to an elevated danger of neurodevelopmental problems within the offspring. The outcomes additionally indicated that the speed of GWG was additionally an vital think about figuring out neurodevelopmental dysfunction danger.
Insufficient GWG charge throughout the second trimester coupled with a fast charge of GWG within the third trimester was linked to the very best danger of neurodevelopmental problems, particularly ADHD and mental incapacity.
These findings urged that the speed of maternal GWG may probably be used as a marker to estimate the chance of neurodevelopmental problems within the fetus.
[ad_2]
