[ad_1]
Responding to a current surge in AI-generated bot accounts, LinkedIn is rolling out new options that it hopes will assist customers make extra knowledgeable selections about with whom they select to attach. Many LinkedIn profiles now show a creation date, and the corporate is increasing its area validation providing, which permits customers to publicly affirm that they will reply to emails on the area of their acknowledged present employer.
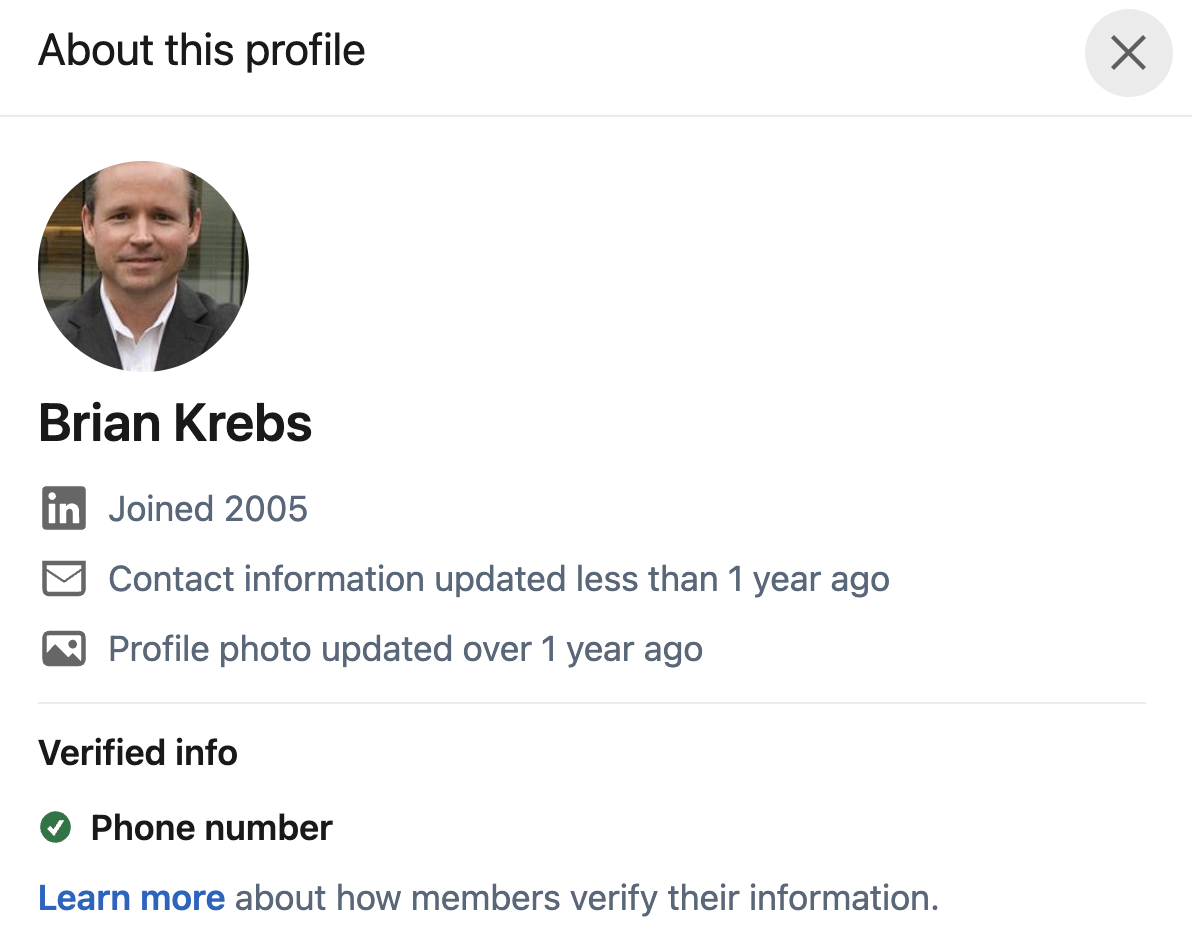
LinkedIn’s new “About This Profile” part — which is seen by clicking the “More” button on the prime of a profile — contains the 12 months the account was created, the final time the profile data was up to date, and a sign of how and whether or not an account has been verified.
LinkedIn additionally stated it’s including a warning to some LinkedIn messages that embrace high-risk content material, or that attempt to entice the person into taking the dialog to a different platform (like WeChat).
“We may warn you about messages that ask you to take the conversation to another platform because that can be a sign of a scam,” the corporate stated in a weblog put up. “These warnings will also give you the choice to report the content without letting the sender know.”
In late September 2022, KrebsOnSecurity warned about the proliferation of faux LinkedIn profiles for Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) roles at among the world’s largest companies. A follow-up story on Oct. 5 confirmed how the phony profile downside has affected nearly all govt roles at companies, and the way these faux profiles are creating an identification disaster for the companies networking web site and the businesses that depend on it to rent and display potential staff.
Reporting right here final month additionally tracked a large drop in profiles claiming to work at a number of main expertise corporations, as LinkedIn apparently took motion towards a whole bunch of 1000’s of inauthentic accounts that falsely claimed roles at these corporations.
For instance, on October 10, 2022, there have been 576,562 LinkedIn accounts that listed their present employer as Apple Inc. The subsequent day, half of these profiles now not existed. At across the identical time, the variety of LinkedIn profiles claiming present roles at Amazon fell from roughly 1.25 million to 838,601 in simply sooner or later, a 33 % drop.
For no matter purpose, nearly all of the phony LinkedIn profiles reviewed by this creator have been younger ladies with profile images that seem to have been generated by synthetic intelligence (AI) instruments.
“We’re seeing rapid advances in AI-based synthetic image generation technology and we’ve created a deep learning model to better catch profiles made with this technology,” LinkedIn’s Oscar Rodriguez wrote. “AI-based image generators can create an unlimited number of unique, high-quality profile photos that do not correspond to real people.”
It stays unclear who or what’s behind the current proliferation of faux govt profiles on LinkedIn, however seemingly they’re from a mix of scams. Cybersecurity agency Mandiant (not too long ago acquired by Google) advised Bloomberg that hackers working for the North Korean authorities have been copying resumes and profiles from main job itemizing platforms LinkedIn and Indeed, as a part of an elaborate scheme to land jobs at cryptocurrency companies.
Identity thieves have been recognized to masquerade on LinkedIn as job recruiters, gathering private and monetary data from individuals who fall for employment scams.
Also, faux profiles additionally could also be tied to so-called “pig butchering” scams, whereby persons are lured by flirtatious strangers on-line into investing in cryptocurrency buying and selling platforms that finally seize any funds when victims attempt to money out.
[ad_2]
