Nvidia says it has discovered a approach pace up a computation-limited step within the chipmaking course of so it occurs 40 occasions as quick as right now’s normal. Called inverse lithography, it’s a key software to permit chipmakers to print nanometer-scale options utilizing mild with an extended wavelength than the scale of these options. Inverse lithography’s use has been restricted by the huge dimension of the wanted computation. Nvidia’s reply, cuLitho, is a set of algorithms designed to be used with GPUs, that turns what has been two weeks of labor into an in a single day job.
The expertise “will allow fabs to increase throughput, reduce their carbon footprint, and set the foundations for 2-nanometer [manufacturing processes] and beyond,” stated Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang on the Nvidia GTC developer on Tuesday.
Leading logic chip foundry TSMC will likely be qualifying cuLitho’s use in manufacturing beginning in June, stated Huang. Design automation software program agency Synopsys plans to combine software program, too, and lithography tools maker ASML plans to assist cuLitho in its merchandise as nicely.
Photolithography is principally step one within the chipmaking course of. It includes bouncing mild off of a sample referred to as a photomask to challenge the types of transistor buildings and interconnects onto the wafer. (More mature expertise makes use of transmissive photomasks as a substitute of reflective ones, however the thought is similar.) It takes 98 photomasks to make an H100 GPU, Jensen stated. The options projected from the photomask are smaller than the wavelength of sunshine used—193 nanometers for the comparatively giant options and 13.5 nanometers for the finer bits. So, with out the help of tips and design guidelines collectively referred to as optical proximity correction, you’d solely get a blurry mess projected on the wafer. With optical proximity correction, the designs on the photomask solely vaguely resemble the sample of sunshine on the chip.
With the necessity for finer and finer options, the corrected shapes on the photomask have change into an increasing number of elaborate and tough to give you. It can be significantly better to begin with the sample you need on the wafer after which calculate what sample on the photomask would produce them. Such a scheme is named inverse lithography. Simple because it sounds, it’s fairly tough to compute, typically taking weeks to compile.
In reality, it’s such a slog that it’s typically reserved to be used on just a few essential layers of modern chips or simply notably thorny bits of them, in response to knowledge from the E-Beam Initiative, which periodically surveys the business.
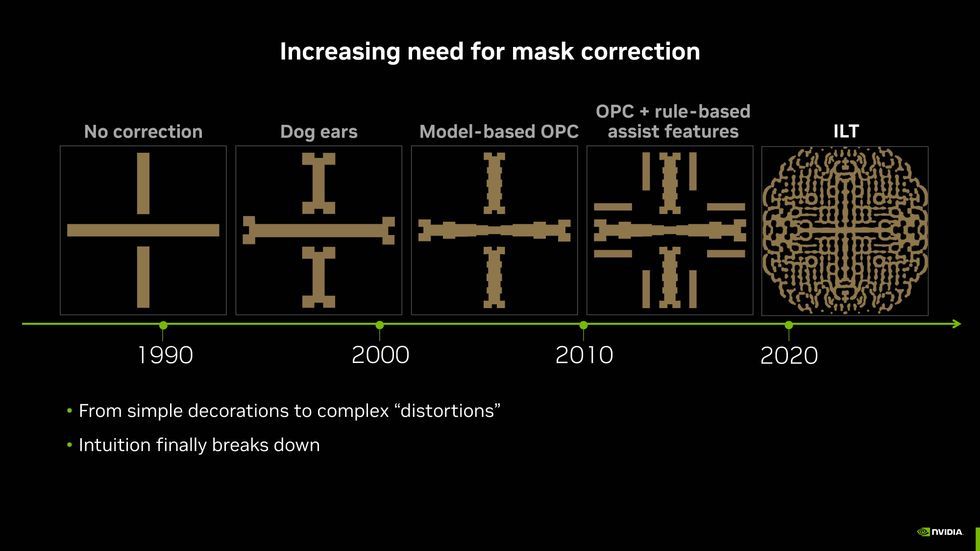 As chipmaking required finer and finer options, engineers needed to produce an increasing number of advanced designs to challenge these options onto the silicon. Inverse lithography (ILT) is the newest growth.Nvidia
As chipmaking required finer and finer options, engineers needed to produce an increasing number of advanced designs to challenge these options onto the silicon. Inverse lithography (ILT) is the newest growth.Nvidia
The lengthy computation time for lithography slows the event and enchancment of chip expertise Even a change to the thickness of a fabric can result in the necessity for a brand new set of photomasks, notes Vivek Okay. Singh, vp within the superior expertise group engaged on silicon manufacturing at Nvidia. Computing masks “has been a long pole in chip development,” he says. “If inverse lithography technology were sped up 40 times, would more companies use it on more layers? Surely.”
Part of the computation is a picture downside that’s a pure match for GPUs, says Singh. But at most, that may solely reduce the computation time in half. The relaxation shouldn’t be really easy to make parallel. But over the previous 4 years, with growth companions together with TSMC, Nvidia engineers have give you a group of algorithms for making the remaining work parallel and have packaged it as a software program library to be used with GPUs.
According to Nvidia, utilizing the cuLitho lets 500 Nvidia DGX H100 computer systems do the work of 40,000 CPU techniques. It can produce 3 to five occasions as many photomasks per day, drawing solely 5 megawatts as a substitute of 35 MW.
What’s extra, it could ship higher outcomes, in response to Singh. cuLitho produces in any other case onerous to calculate curvy polygons on the masks that end in a larger depth of focus for the sample forged onto the wafer. That depth of focus ought to result in much less variation throughout the wafer and due to this fact a greater yield of working chips per wafer, he says. In future, it additionally might imply fewer photomasks are wanted, as a result of what should now be accomplished utilizing a double sample would possibly work with just one utilizing inverse lithography.
Nvidia shouldn’t be the primary to look to GPUs to speed up inverse lithography expertise. Silicon Valley-based D2S introduced a GPU-based pc customized constructed for the issue in 2019. IEEE Spectrum reached out to D2S for remark, however the firm didn’t reply earlier than press time.
From Your Site Articles
Related Articles Around the Web