Multiple menace actors have been noticed opportunistically weaponizing a now-patched important safety vulnerability impacting a number of Zoho ManageEngine merchandise since January 20, 2023.
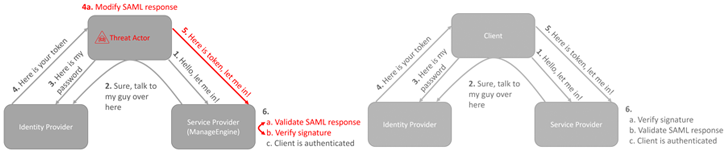
Tracked as CVE-2022-47966 (CVSS rating: 9.8), the distant code execution flaw permits a whole takeover of the prone programs by unauthenticated attackers.
As many as 24 completely different merchandise, together with Access Manager Plus, ADManager Plus, ADSelfService Plus, Password Manager Pro, Remote Access Plus, and Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM), are affected by the difficulty.
The shortcoming “permits unauthenticated distant code execution resulting from utilization of an outdated third-party dependency for XML signature validation, Apache Santuario,” Bitdefender’s Martin Zugec stated in a technical advisory shared with The Hacker News.
According to the Romanian cybersecurity agency, the exploitation efforts are stated to have commenced the day after penetration testing agency Horizon3.ai launched a proof-of-concept (PoC) final month.
A majority of the assault victims are situated in Australia, Canada, Italy, Mexico, the Netherlands, Nigeria, Ukraine, the U.Ok., and the U.S.
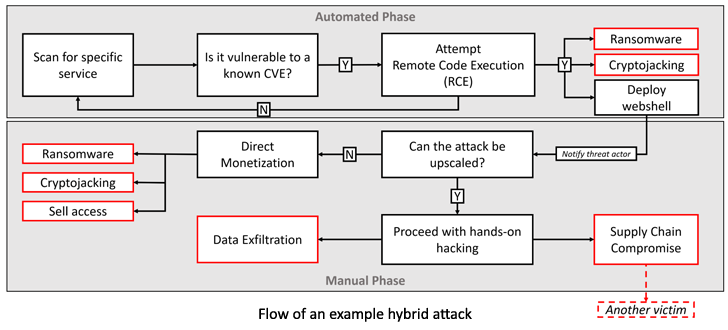
The primary goal of the assaults detected so far revolves round deploying instruments on susceptible hosts reminiscent of Netcat and Cobalt Strike Beacon.
Some intrusions have leveraged the preliminary entry to put in AnyDesk software program for distant entry, whereas a number of others have tried to put in a Windows model of a ransomware pressure referred to as Buhti.
What’s extra, there’s proof of a focused espionage operation, with the menace actors abusing the ManageEngine flaw to deploy malware able to executing next-stage payloads.
“This vulnerability is one other clear reminder of the significance of preserving programs updated with the most recent safety patches whereas additionally using sturdy perimeter protection,” Zugec stated.
“Attackers need not scour for brand spanking new exploits or novel strategies once they know that many organizations are susceptible to older exploits due, partially, to the dearth of correct patch administration and danger administration.”