[ad_1]
Thanks to the broad collection of out there health trackers and smartwatches, it’s by no means been simpler to trace and file your coronary heart fee. But how helpful is that data?
Very, it seems. First of all, it’s doable to calculate energy burned by coronary heart fee.
So, should you’ve ever puzzled concerning the effectiveness of a selected health class or wished to check the depth of 1 sort of exercise to a different, your coronary heart fee generally is a helpful clue.
Monitoring your coronary heart fee in actual time may enable you keep inside your goal coronary heart fee zone and supply beneficial insights into your progress and general health degree.
So don’t ignore that little heart-shaped graphic on the display screen of your wearable — use it.
How to Calculate Calories Burned by Heart Rate
Only an train physiologist with entry to a lab can present a scientifically correct measurement of what number of energy you’ve burned throughout a exercise.
But, with some primary math expertise, it’s doable to get an estimate. To calculate energy burned by coronary heart fee, you’ll want:
- The period of your exercise
- Your common coronary heart fee for that exercise
- Some primary private data
- A calculator
Below are two formulation primarily based on organic intercourse:
Male: [(-55.0969 + (0.6309 x HR) + (0.1988 x W) + (0.2017 x A)] / 4.184) x 60 x T
Female: [(-20.4022 + (0.4472 x HR) – (0.1263 x W) + (0.074 x A)] / 4.184) x 60 x THR = Heart fee (in beats/minute)
W = Weight (in kilograms; 1 kg = 2.2 kilos)
A = Age (in years)
T = Exercise period time (in hours)
For instance, a 40-year-old girl weighing 68 kilograms (about 150 kilos) who averages 160 bpm throughout an hour-long exercise will burn about 653 energy.
“Generally speaking, the higher your heart rate, the more calories you will burn for a given amount of time,” says Todd Buckingham, Ph.D, an train physiologist at Mary Free Bed Sports Rehabilitation Performance Lab in Wyoming, Michigan. “For example, if running for 10 minutes, you will burn more calories if your heart rate is 180 beats per minute (bpm) than if it was 140 bpm.”
Buckingham describes this method as a “good, scientifically developed formula,” however notes that every one the individuals within the research that examined it have been bodily energetic and freed from any metabolic or cardiovascular ailments.
“This means that the equation accurately predicted actual energy expenditure extremely well for a wide range of active individuals and can therefore be generalized to other active individuals who regularly partake in physical activity,” he says. “Whether this equation is accurate for individuals who have some type of metabolic or cardiovascular disease or who have not engaged in prior physical activity remains unknown.”
What Heart Rate Zone Is Best for Losing Weight?
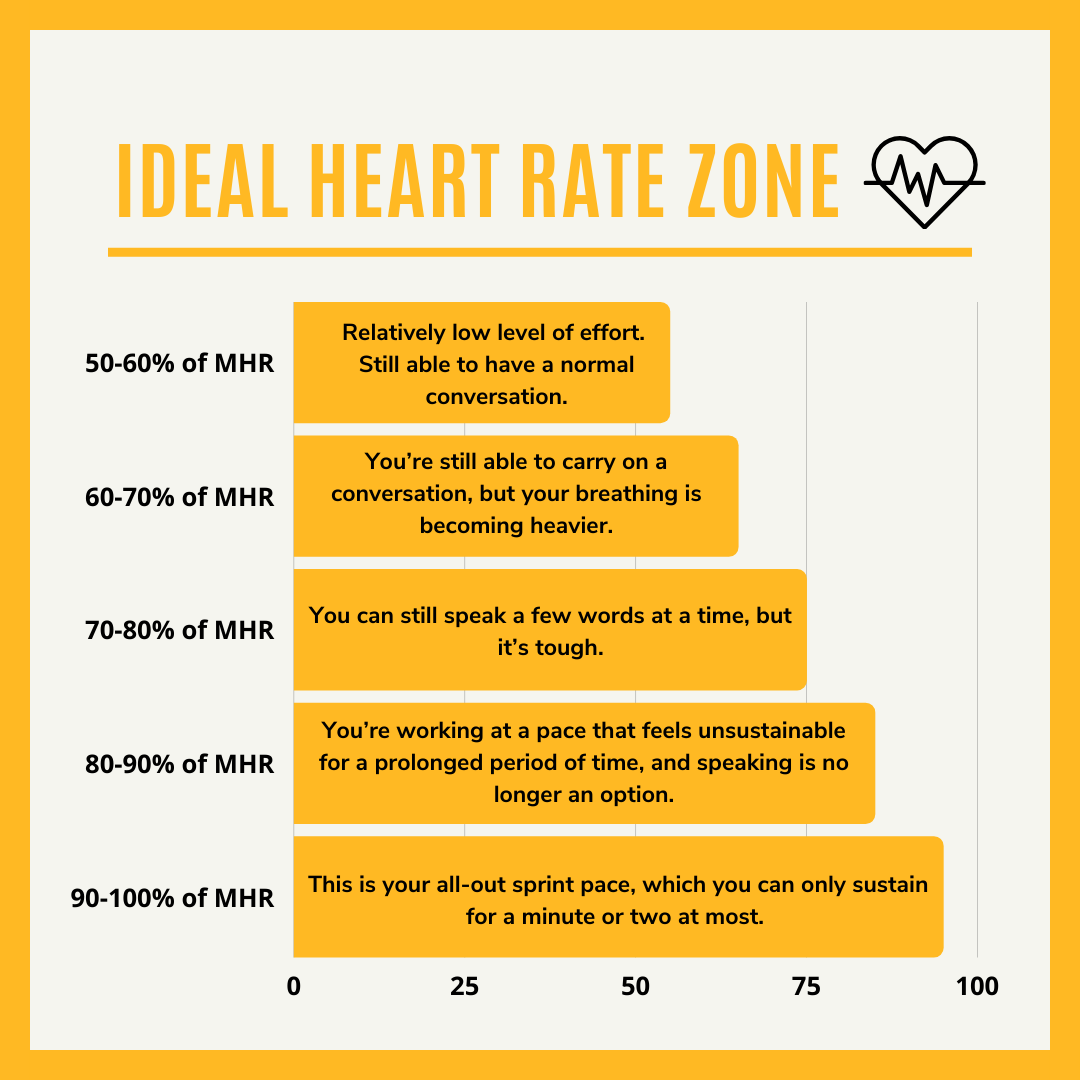
Heart fee zones are primarily based in your most coronary heart fee (MHR), or the quickest fee at which your coronary heart can beat. The hottest method for calculating MHR is: 220 minus age.
So, primarily based on this method, the MHR for a 40-year-old particular person is estimated to be about 180 bpm.
(Note that, whereas this method is straightforward to make use of, there are different, barely extra difficult formulation which are believed to be extra correct.)
Each coronary heart fee zone is decided by a share of your MHR:
- 50-60% of MHR: A comparatively low degree of effort. You can nonetheless keep on a dialog. (Think: warming up, cooling down, and energetic restoration.)
- 60-70% of MHR: You’re respiration heavier, however you may nonetheless communicate briefly sentences.
- 70-80% of MHR: Your coronary heart is thrashing sooner, respiration is labored, and it’s tougher to talk.
- 80-90% of MHR: Speaking is not an possibility.
- 90-100% of MHR: An all-out effort that you may maintain for less than very quick bursts (e.g., a dash).
Your splendid coronary heart fee zone is dependent upon your health targets, says Buckingham.
“If your goal is weight loss, you should try to keep your heart rate as high as possible for as long as possible [without increasing your risk of overtraining or injury],” he explains. “So, if you’re able to sustain a high heart rate for an extended period of time, you will get the most of your calorie burn.”
However, whether or not you’re a aggressive sprinter or marathon runner, you’ll want to regulate your method accordingly.
“If your goal is training for endurance, you need to be able to run for long durations,” Buckingham says. “Therefore, it’s important to incorporate a lot of long, steady state runs into your training where you keep your heart rate at about 70% of your maximum.”
For the sprinter, coronary heart fee monitoring is much less relevant to on a regular basis coaching. “When sprint training, it’s best just to run really fast and not pay attention to heart rate,” he says.
What Can You Learn From Your Heart Rate?
When tracked over time, your coronary heart fee will be an indicator of your general well being and progress towards attaining your health targets.
If you’re in keeping with train, you’ll seemingly discover that your coronary heart fee is decrease than once you first started understanding — each at relaxation and once you’re energetic.
“This shows that your body is becoming more efficient,” Buckingham says.
“Cardiac output is the amount of blood your heart pumps out each minute and is comprised of your heart rate and stroke volume (milliliters per beat). As you become more fit, your heart gets stronger and can pump more blood with each beat. Because your heart is now pumping more blood with each beat, it doesn’t have to beat as fast to maintain the same cardiac output,” he explains.
[ad_2]