[ad_1]

One of the important components for widespread robotics adoption, particularly within the inspection and upkeep space, is the regulatory panorama. Regulatory and authorized points must be addressed to ascertain efficient robotics deployment authorized frameworks. Common objectives of boosting the widespread adoption of robotics can solely be achieved by creating networks between the robotics neighborhood and regulators.
On the twenty third of March, Maarit Sandelin, Peter Voorhans and Dr Carlos Cuevas Garcia have been invited by Robotics4EU and RIMA community to debate how cooperation amongst regulators and the robotics neighborhood may be fostered and what are essentially the most urgent authorized challenges for the inspection & upkeep software space of robotics.
Maarit Sandelin and Peter Voorhans from Robotic Innovation Department in SPRINT Robotics have opened the workshop with the query of why robotics are necessary in inspection and upkeep? Speakers highlighted three fundamental points: security, effectivity and prices. Firstly, robotic options enable for decreasing the fatalities and dangers of accidents within the environments of heights, confined areas or under-water. Secondly, the preparation work for inspection and upkeep (shutting down the services, clearing and cleansing the areas, air sampling, getting the permits) isn’t required for inspection and upkeep finished by a robotic. The forms – making use of and ready for permits – is diminished as nicely.
However, the combination of robots faces obstacles in two fundamental dimensions: variations in cross-border requirements and acceptance of robotics by inspectors. Speaking of regulatory challenges, Peter Voorhans recognized the principle issues:
- The regulatory framework for acceptance in robotics is disastrous on the world stage
- Robotic inspections usually are not at all times allowed based mostly on rules or interpretation of the regulation
- A special interpretation of rules causes points for service and technical suppliers
To transfer additional with the combination of robots into Inspection and upkeep, the Europe-wide acceptance and laws of robots are wanted. First, the acceptance of robotics (for instance, distant visible methods) by notified our bodies can be a giant step additional. Also, the coaching of inspectors ought to contain robotics coaching, so the inspectors would perceive the benefits and penalties of the combination of robotics and will advocate themselves for the uptake of robotics.
Different laws and rules throughout borders imply that in every nation, inspection needs to be carried out by native licensed inspectors. For instance, a Dutch firm is performing an in-service inspection in France. Due to variations in laws, an authorized inspector from the Netherlands isn’t allowed to carry out the distant visible inspection in France. A neighborhood notified physique must be concerned.
Leaving apart the nationwide & cross-border laws points, Peter Voornhans has drawn consideration to the company-level of insurance policies. As an instance, the inner insurance policies in DOW, chemical and plastics producer, outlined that individuals is not going to be allowed in confined areas ranging from 2025. This management place gave a robust incentive to introduce robotics and persuade inspectors to make use of them. The inner programme ensured the popularity and celebration of robotic use instances and greatest practices, making certain greater ranges of robotics acceptance general.
Dr Carlos Cuevas Garcia, a postdoctoral researcher on the Innovation, Society and Public Policy Research Group on the Munich Center for Technology in Society (MCTS), Technical University Munich, has shared his expertise in following the EU-funded initiatives for uptake of robotics in I&M. Dr Garcia has evaluated the coverage objectives and outcomes, following the cycle of the initiatives, as coverage devices.
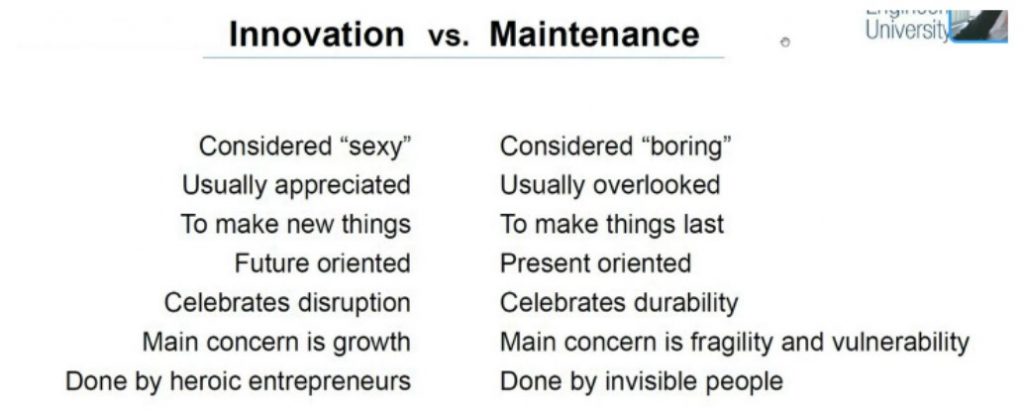
From the sociology of know-how perspective, robotics in I&M performs on the distinctive intersection of innovation and upkeep. Innovation is completed by heroic folks, entrepreneurs, it’s celebrated, and lined in information. Maintenance is completed by invisible folks, it’s normally neglected. However, such initiatives as RIMA, convey the 2 dimensions collectively. As innovation goals at enhancing upkeep, what can innovation be taught from upkeep? How can upkeep enhance innovation?
Speaking of the coverage function on this intersection, Dr Garcia has offered the innovation coverage panorama from the instrument’s perspective.
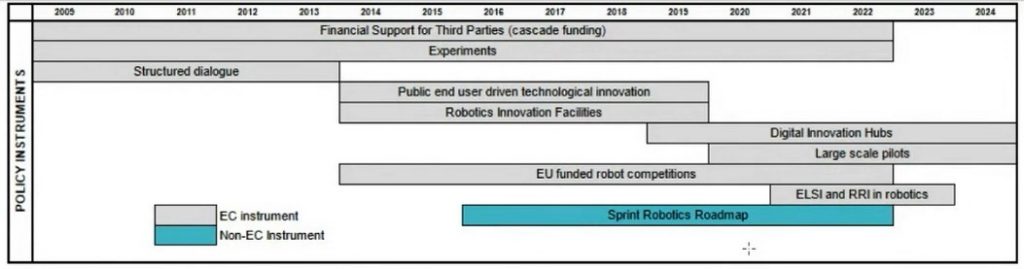
In order to enhance this panorama, he recognized two methods ahead:
- Examine the results of particular person coverage devices on the sphere of I&M robotics
- Examine the dynamics of completely different devices collectively, and the way they allow (and constrain!) the continuity of initiatives
The examination might be applied contemplating the vulnerabilities within the coverage devices. Drawing from the expertise in observing and analysing the EU-funded initiatives, as devices to attain coverage objectives, Carlos recognized a number of vulnerabilities:
- The confusion between the function of the “public end-user” and the function of the subcontractor. In the case of the noticed initiatives, the subcontractors’ enter was not formally concerned, though the upkeep is definitely finished by the subcontractor.
- The curiosity of the “public end-user” and subcontractor to buy or maintain funding the applied sciences of the answer after the undertaking was not enough
- The “public end-user” didn’t wish to immediately fund a know-how thought of dangerous for employees’ jobs.
- The specific coverage instrument noticed (Public finish user-Driven Technological Innovation) was too inflexible to reply to the complexities of the state of affairs, but too weak to supply additional instructions
.
Speaking of how to enhance the coverage course of, Carlos recognized that moreover technical progress (for instance, going past technological readiness stage from 2 to five), devices ought to think about different metrics of success, e.g.:
- How nicely do roboticists’ groups and maintainers work collectively?
- How do robots empower maintainers?
- How does the group co-create a imaginative and prescient of the entire inspection course of (service logistics, transporting, unloading, fixing robots, and so forth.)?
Dr Carlos concluded by suggesting a few coverage suggestions:
- We should discover the training trajectories of several types of stakeholders concerned in sequences of I&M robotics initiatives;
- We should discover ways to present upkeep to innovation networks and restore innovation coverage devices by higher figuring out their contradictions, fragilities and vulnerabilities;
- This requires shut and sturdy engagement between I&M specialists, roboticists, undertaking coordinators, policymakers, regulators, and sociologists of know-how.
Finally, the session was concluded with a panel dialogue thematizing earlier displays, and fascinating the viewers. As a ultimate conclusion, the specialists urged starting with industry-led insights to alter the paradigm of coverage framework on a bigger scale.
tags: c-Industrial-Automation
Robotics4EU
is a 3-year-long undertaking funded underneath the European Union’s Horizon 2020 analysis and innovation programme.

Robotics4EU
is a 3-year-long undertaking funded underneath the European Union’s Horizon 2020 analysis and innovation programme.
