[ad_1]
In the evolving world of robotics, a groundbreaking collaboration between Princeton University and Google stands out. Engineers from these prestigious establishments have developed an revolutionary methodology that teaches robots an important talent: recognizing after they need assistance and how one can ask for it. This growth marks a major leap ahead in robotics, bridging the hole between autonomous functioning and human-robot interplay.
The journey in direction of extra clever and unbiased robots has at all times been hindered by one vital problem: the complexity and ambiguity of human language. Unlike the binary readability of pc codes, human language is riddled with nuances and subtleties, making it a labyrinth for robots. For occasion, a command so simple as “pick up the bowl” can turn into a posh activity when a number of bowls are current. Robots, outfitted to sense their surroundings and reply to language, usually discover themselves at a crossroads when confronted with such linguistic uncertainties.
Quantifying Uncertainty
Addressing this problem, the Princeton and Google crew has launched a novel strategy that quantifies the ‘fuzziness’ of human language. This approach basically measures the extent of uncertainty in language instructions and makes use of this metric to information robotic actions. In conditions the place a command may result in a number of interpretations, the robotic can now gauge the extent of uncertainty and resolve when to hunt additional clarification. For occasion, in an surroundings with a number of bowls, a better diploma of uncertainty would immediate the robotic to ask which bowl to select up, thereby avoiding potential errors or inefficiencies.
This strategy not solely empowers robots with a greater understanding of language but additionally enhances their security and effectivity in activity execution. By integrating massive language fashions (LLMs) like these behind ChatGPT, the researchers have taken a major step in aligning robotic actions extra carefully with human expectations and wishes.
Role of Large Language Models
The integration of LLMs performs a pivotal position on this new strategy. LLMs are instrumental in processing and decoding human language. In this context, they’re used to judge and measure the uncertainty current in language instructions given to robots.
However, the reliance on LLMs is not with out its challenges. As identified by the analysis crew, outputs from LLMs can typically be unreliable.
Anirudha Majumdar, an assistant professor at Princeton, emphasizes the significance of this steadiness:
“Blindly following plans generated by an LLM could cause robots to act in an unsafe or untrustworthy manner, and so we need our LLM-based robots to know when they don’t know.”
This highlights the need for a nuanced strategy, the place LLMs are used as instruments for steering quite than infallible decision-makers.
Practical Application and Testing
The practicality of this methodology has been examined in varied situations, illustrating its versatility and effectiveness. One such check concerned a robotic arm, tasked with sorting toy meals objects into totally different classes. This easy setup demonstrated the robotic’s capacity to navigate duties with clear-cut selections successfully.
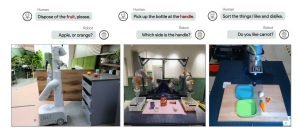
Image: Princeton University
The complexity elevated considerably in one other experiment that includes a robotic arm mounted on a wheeled platform in an workplace kitchen. Here, the robotic confronted real-world challenges like figuring out the proper merchandise to put in a microwave when offered with a number of choices.
Through these checks, the robots efficiently demonstrated their capacity to make use of the quantified uncertainty to make selections or search clarification, thereby validating the sensible utility of this methodology.
Future Implications and Research
Looking forward, the implications of this analysis prolong far past the present functions. The crew, led by Majumdar and graduate pupil Allen Ren, is exploring how this strategy might be utilized to extra advanced issues in robotic notion and AI. This consists of situations the place robots want to mix imaginative and prescient and language info to make selections, additional closing the hole between robotic understanding and human interplay.
The ongoing analysis goals to not solely improve the flexibility of robots to carry out duties with increased accuracy but additionally to navigate the world with an understanding akin to human cognition. This analysis might pave the best way for robots that aren’t solely extra environment friendly and safer but additionally extra in tune with the nuanced calls for of human environments.
You can discover the printed analysis right here.
[ad_2]
