[ad_1]
The password supervisor service LastPass is now forcing a few of its customers to select longer grasp passwords. LastPass says the modifications are wanted to make sure all clients are protected by their newest safety enhancements. But critics say the transfer is little greater than a public relations stunt that can do nothing to assist numerous early adopters whose password vaults have been uncovered in a 2022 breach at LastPass.
LastPass despatched this notification to customers earlier this week.
LastPass instructed clients this week they might be compelled to replace their grasp password if it was lower than 12 characters. LastPass formally instituted this modification again in 2018, however some undisclosed variety of the corporate’s earlier clients have been by no means required to extend the size of their grasp passwords.
This is critical as a result of in November 2022, LastPass disclosed a breach during which hackers stole password vaults containing each encrypted and plaintext information for greater than 25 million customers.
Since then, a gradual trickle of six-figure cryptocurrency heists concentrating on security-conscious individuals all through the tech trade has led some safety consultants to conclude that crooks probably have succeeded at cracking open a few of the stolen LastPass vaults.
KrebsOnSecurity final month interviewed a sufferer who lately noticed greater than three million {dollars} value of cryptocurrency siphoned from his account. That consumer signed up with LastPass practically a decade in the past, saved their cryptocurrency seed phrase there, and but by no means modified his grasp password — which was simply eight characters. Nor was he ever compelled to enhance his grasp password.
That story cited analysis from Adblock Plus creator Wladimir Palant, who stated LastPass did not improve many older, unique clients to safer encryption protections that have been provided to newer clients over time.
For instance, one other vital default setting in LastPass is the variety of “iterations,” or what number of instances your grasp password is run via the corporate’s encryption routines. The extra iterations, the longer it takes an offline attacker to crack your grasp password.
Palant stated that for a lot of older LastPass customers, the preliminary default setting for iterations was anyplace from “1” to “500.” By 2013, new LastPass clients got 5,000 iterations by default. In February 2018, LastPass modified the default to 100,100 iterations. And very lately, it upped that once more to 600,000. Still, Palant and others impacted by the 2022 breach at LastPass say their account safety settings have been by no means forcibly upgraded.
Palant referred to as this newest motion by LastPass a PR stunt.
“They sent this message to everyone, whether they have a weak master password or not – this way they can again blame the users for not respecting their policies,” Palant stated. “But I just logged in with my weak password, and I am not forced to change it. Sending emails is cheap, but they once again didn’t implement any technical measures to enforce this policy change.”
Either method, Palant stated, the modifications received’t assist individuals affected by the 2022 breach.
“These people need to change all their passwords, something that LastPass still won’t recommend,” Palant stated. “But it will somewhat help with the breaches to come.”
LastPass CEO Karim Toubba stated altering grasp password size (and even the grasp password itself) will not be designed to deal with already stolen vaults which are offline.
“This is meant to better protect customers’ online vaults and encourage them to bring their accounts up to the 2018 LastPass standard default setting of a 12-character minimum (but could opt out from),” Toubba stated in an emailed assertion. “We know that some customers may have chosen convenience over security and utilized less complex master passwords despite encouragement to use our (or others) password generator to do otherwise.”
A primary performance of LastPass is that it’ll decide and bear in mind prolonged, complicated passwords for every of your web sites or on-line companies. To mechanically populate the suitable credentials at any web site going ahead, you merely authenticate to LastPass utilizing your grasp password.
LastPass has all the time emphasised that for those who lose this grasp password, that’s too dangerous as a result of they don’t retailer it and their encryption is so robust that even they will’t make it easier to get well it.
But consultants say all bets are off when cybercrooks can get their palms on the encrypted vault information itself — versus having to work together with LastPass by way of its web site. These so-called “offline” assaults permit the dangerous guys to conduct limitless and unfettered “brute force” password cracking makes an attempt in opposition to the encrypted information utilizing highly effective computer systems that may every strive thousands and thousands of password guesses per second.
A chart on Palant’s weblog put up gives an concept of how rising password iterations dramatically will increase the prices and time wanted by the attackers to crack somebody’s grasp password. Palant stated it could take a single high-powered graphics card a couple of 12 months to crack a password of common complexity with 500 iterations, and about 10 years to crack the identical password run via 5,000 iterations.
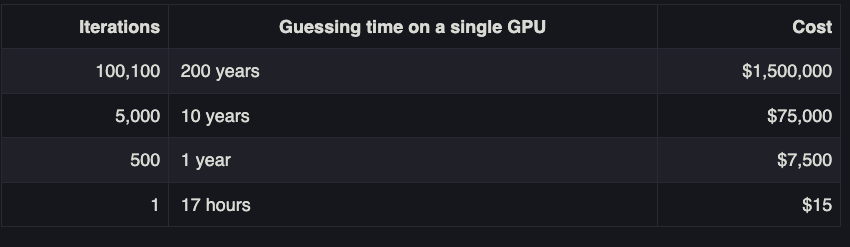
Image: palant.data
However, these numbers radically come down when a decided adversary additionally has different large-scale computational belongings at their disposal, akin to a bitcoin mining operation that may coordinate the password-cracking exercise throughout a number of highly effective methods concurrently.
Meaning, LastPass customers whose vaults have been by no means upgraded to increased iterations and whose grasp passwords have been weak (lower than 12 characters) probably have been a main goal of distributed password-cracking assaults ever because the LastPass consumer vaults have been stolen late final 12 months.
Asked why some LastPass customers have been left behind on older safety minimums, Toubba stated a “small percentage” of consumers had corrupted objects of their password vaults that prevented these accounts from correctly upgrading to the brand new necessities and settings.
“We have been able to determine that a small percentage of customers have items in their vaults that are corrupt and when we previously utilized automated scripts designed to re-encrypt vaults when the master password or iteration count is changed, they did not complete,” Toubba stated. “These errors were not originally apparent as part of these efforts and, as we have discovered them, we have been working to be able to remedy this and finish the re-encryption.”
Nicholas Weaver, a researcher at University of California, Berkeley’s International Computer Science Institute (ICSI) and lecturer at UC Davis, stated LastPass made an enormous mistake years in the past by not force-upgrading the iteration depend for present customers.
“And now this is blaming the users — ‘you should have used a longer passphrase’ — not them for having weak defaults that were never upgraded for existing users,” Weaver stated. “LastPass in my book is one step above snake-oil. I used to be, ‘Pick whichever password manager you want,’ but now I am very much, ‘Pick any password manager but LastPass.’”
Asked why LastPass isn’t recommending that customers change all the passwords secured by the encrypted grasp password that was stolen when the corporate bought hacked final 12 months, Toubba stated it’s as a result of “the data demonstrates that the majority of our customers follow our recommendations (or greater), and the probability of successfully brute forcing vault encryption is greatly reduced accordingly.”
“We’ve been telling customers since December of 2022 that they should be following recommended guidelines,” Toubba continued. “And if they haven’t followed the guidelines we recommended that they change their downstream passwords.”
[ad_2]
