[ad_1]
Clinical trials have detailed research protocols and are registered on ClinicalTrials.gov. What stage of particulars are wanted for real-world information (RWD) analyses that purpose to estimate remedy results? In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) requires registration of many research protocols utilizing a template for observational post-authorization security research (PASS) performed by advertising authorization holders. Other efforts embody ISPE’s pointers for good pharmacoepidemiology observe (GPP) part on protocol improvement, National Evaluation System for well being Technology (NEST) protocol steerage, and the Structured Template and Reporting Tool for Real World Evidence (STaRT-RWE).
The International Society for Pharmacoepidemiology (ISPE) and the International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research (ISPOR) convened a joint activity power to supply requirements for RWD protocols. They developed the HARmonized Protocol Template to Enhance Reproducibility (HARPER). The Table under compares HARPER towards PASS, GPP, NEST and STaRT-RWE.
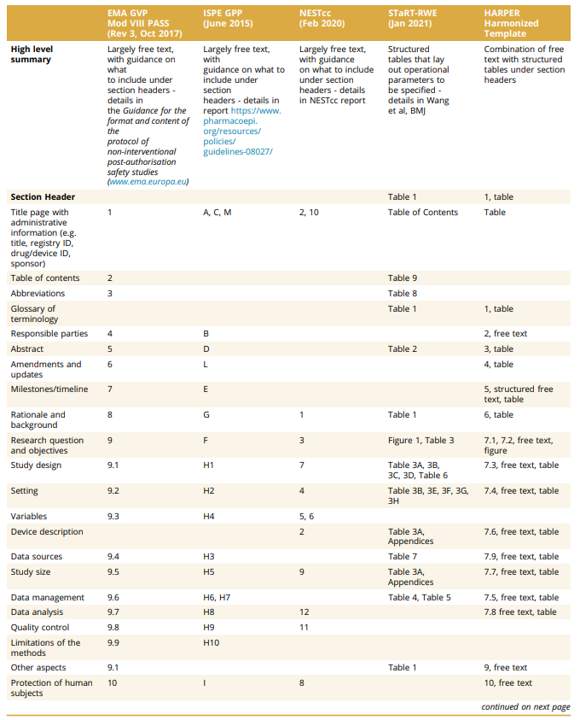

The authors properly observe a couple of limitations of HARPER.
- Structured vs. Flexibility. HARPER’s structured method enhances readability for stakeholders and consistency throughout research. However, some advanced research designs could also be utterly cheap, however might not match throughout the HARPER construction. Many of the sections, nevertheless, include free textual content sections.
- Minimum, not most transparency. HARPER doesn’t cowl each facet of transparency over the lifecycle of a analysis research, which can contain sharing of protocol, code, information, in addition to outcomes. Thus, HARPER ought to be seen because the minimal necessities for research protocol transparency.
- Data evolution. As information assortment evolves and new strategies are developed, HARPER’s method might have to adapt over time.
The full HARPER Table of Contents is listed under.
- 1. Title Page
- 2. Abstract
- 3. Amendments and updates
- 4. Timeline
- Table 1 Milestones and Timeline
- 5. Rationale and background
- 6. Research query and aims
- Table 2 Primary and secondary analysis questions and goal
- 7. Research strategies
- 7.1. Study design
- 7.2. Study design diagram
- 7.3. Setting
- 7.3.1 Context and rationale for definition of time 0 (and different major time anchors) for entry to the research inhabitants
- Table 3 Operational Definition of Time 0 (index date) and different major time anchors
- 7.3.2 Context and rationale for research inclusion standards:
- Table 4. Operational Definitions of Inclusion Criteria
- 7.3.3 Context and rationale for research exclusion standards
- Table 5. Operational Definitions of Exclusion Criteria
- 7.3.1 Context and rationale for definition of time 0 (and different major time anchors) for entry to the research inhabitants
- 7.4. Variables
- 7.4.1 Context and rationale for publicity(s) of curiosity
- Table 6. Operational Definitions of Exposure
- 7.4.2 Context and rationale for final result(s) of curiosity
- Table 7. Operational Definitions of Outcome
- 7.4.3 Context and rationale for observe up
- Table 8. Operational Definitions of Follow-Up
- 7.4.4 Context and rationale for covariates (confounding variables and impact modifiers, e.g. danger elements, comorbidities, comedications)
- Table 9. Operational Definitions of Covariates
- 7.4.1 Context and rationale for publicity(s) of curiosity
- 7.5. Data evaluation
- 7.5.1 Context and rationale for evaluation plan
- Table 10. Primary, secondary, and subgroup evaluation specification
- Table 11. Sensitivity analyses – rationale, strengths and limitations
- 7.5.1 Context and rationale for evaluation plan
- 7.6. Data sources
- 7.6.1 Context and rationale for information sources
- Table 12. Metadata about information sources and software program
- 7.6.1 Context and rationale for information sources
- 7.7. Data administration
- 7.8. Quality management
- 7.9. Study measurement and feasibility
- Table 13. Power and pattern measurement
- 8. Limitation of the strategies
- 9. Protection of human topics
- 10. Reporting of opposed occasions
- 11. References
- 12. Appendices
You can learn extra particulars on the HARPER method right here and on the Open Science Foundation right here.
[ad_2]
