[ad_1]

Multiple proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits for a crucial Jenkins vulnerability permitting unauthenticated attackers to learn arbitrary information have been made publicly out there, with some researchers reporting attackers actively exploiting the failings in assaults.
Jenkins is an open-source automation server extensively utilized in software program improvement, significantly for Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD).
It performs a crucial function in automating numerous components of the software program improvement course of, like constructing, testing, and deploying functions. It helps over a thousand integration plugins and is utilized by organizations of all sizes, together with giant enterprises.
SonarSupply researchers found two flaws in Jenkins that might allow assaults to entry knowledge in weak servers and execute arbitrary CLI instructions below sure circumstances.
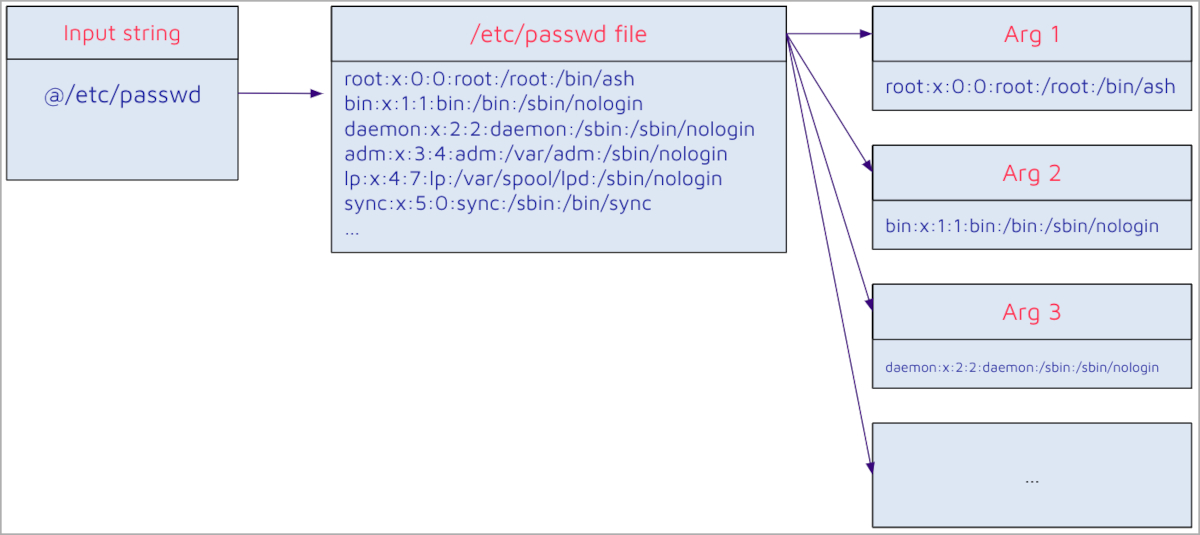
The first flaw, rated crucial, is CVE-2024-23897, permitting unauthenticated attackers with ‘general/learn’ permission to learn knowledge from arbitrary information on the Jenkins server.
Attackers with out this permission can nonetheless learn the primary few strains of information, with the quantity relying on the out there CLI instructions.
The flaw stems from the default conduct of the args4j command parser in Jenkins, which routinely expands file contents into command arguments when an argument begins with the “@” character, permitting unauthorized studying of arbitrary information on the Jenkins controller file system.
Sonar defined that exploitation of the actual flaw may result in admin privilege escalation and arbitrary distant code execution. This step, nonetheless, is dependent upon sure circumstances that have to be met, that are completely different for every assault variant.
The second flaw, tracked as CVE-2024-23898, is a cross-site WebSocket hijacking challenge the place attackers may execute arbitrary CLI instructions by tricking a person into clicking a malicious hyperlink.
This danger that arises from this bug needs to be mitigated by present protecting insurance policies in internet browsers, nevertheless it persists because of the lack of common enforcement of those insurance policies.
SonarSupply reported the failings to the Jenkins safety crew on November 13, 2023, and helped confirm the fixes within the following months.
On January 24, 2024, Jenkins launched fixes for the 2 flaws with variations 2.442 and LTS 2.426.3, and printed an advisory that shares numerous assault eventualities and exploitation pathways, in addition to repair descriptions and potential workarounds for these unable to use the safety updates.
Exploits out there
With considerable details about the Jenkins flaws now out there, many researchers reproduced a number of the assault eventualities and created working PoC exploits printed on GitHub.
The PoCs are for CVE-2024-23897, which provides attackers distant code execution on unpatched Jenkins servers.
Many of those PoCs have already been validated, so attackers scanning for uncovered servers can seize the scripts and take a look at them out with minimal or no modification.
Some researchers report that their Jenkins honeypots have already caught exercise within the wild, suggesting that hackers have began exploiting the vulnerabilities.
[ad_2]