[ad_1]
Suspected North Korean nation-state actors focused a journalist in South Korea with a malware-laced Android app as a part of a social engineering marketing campaign.
The findings come from South Korea-based non-profit Interlab, which coined the brand new malware RambleOn.
The malicious functionalities embrace the “capability to learn and leak goal’s contact listing, SMS, voice name content material, location and others from the time of compromise on the goal,” Interlab risk researcher Ovi Liber mentioned in a report revealed this week.
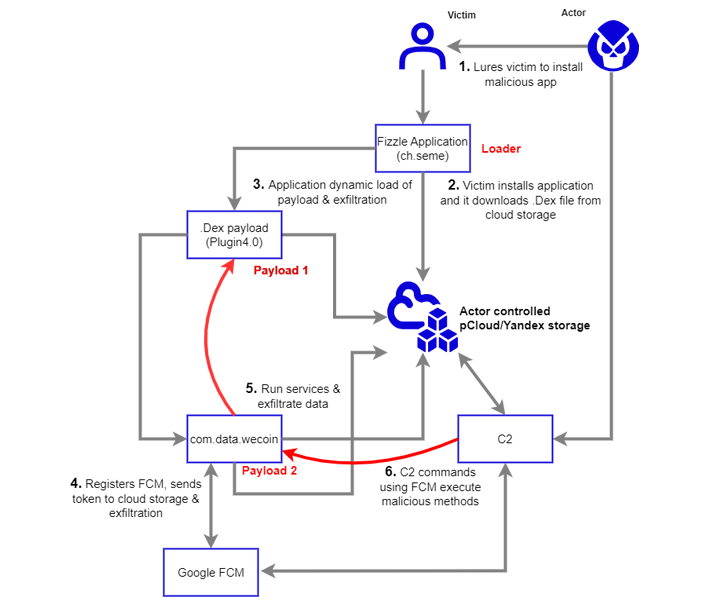
The spyware and adware camouflages as a safe chat app known as Fizzle (ch.seme), however in actuality, acts as a conduit to ship a next-stage payload hosted on pCloud and Yandex.
The chat app is alleged to have been despatched as an Android Package (APK) file over WeChat to the focused journalist on December 7, 2022, underneath the pretext of wanting to debate a delicate subject.
The major goal of RambleOn is to operate as a loader for an additional APK file (com.information.WeCoin) whereas additionally requesting for intrusive permissions to gather recordsdata, entry name logs, intercept SMS messages, report audio, and site information.
The secondary payload, for its half, is designed to supply another channel for accessing the contaminated Android machine utilizing Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) as a command-and-control (C2) mechanism.
Interlab mentioned it recognized overlaps within the FCM performance between RambleOn and FastFire, a bit of Android spyware and adware that was attributed to Kimsuky by South Korean cybersecurity firm S2W final 12 months.
“The victimology of this occasion suits very carefully with the modus operandi of teams similar to APT37 and Kimsuky,” Liber mentioned, mentioning the previous’s use of pCloud and Yandex storage for payload supply and command-and-control.
[ad_2]