[ad_1]
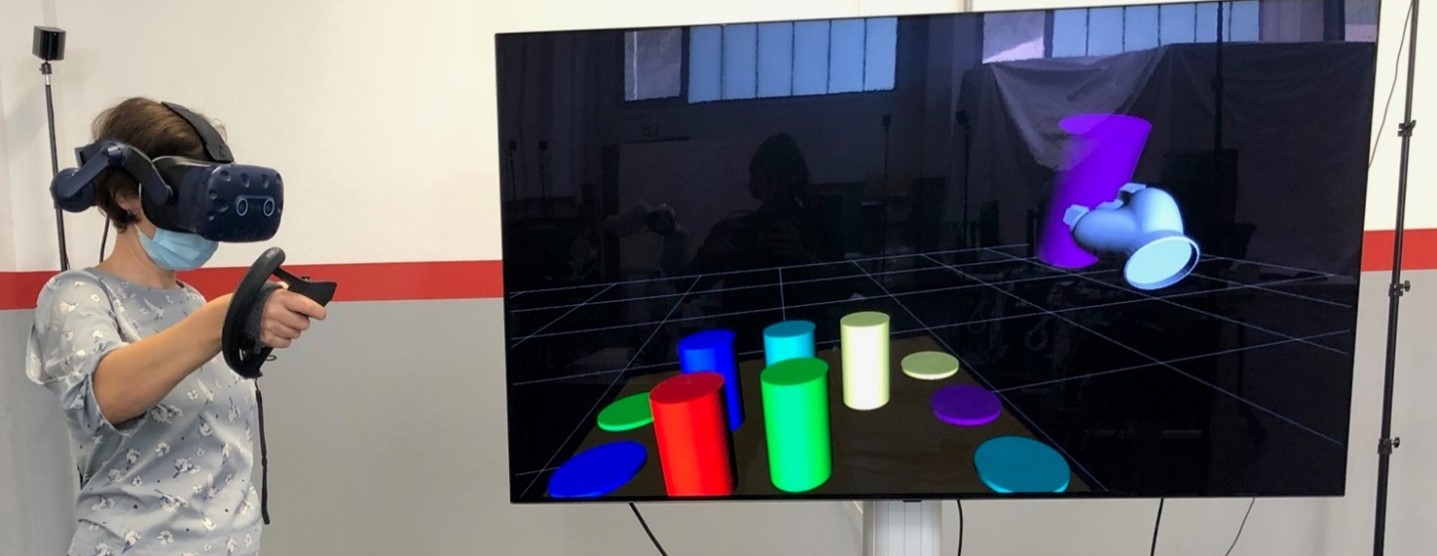

Teleoperation is among the longest-standing software fields in robotics. While full autonomy continues to be work in progress, the likelihood to remotely function a robotic has already opened situations the place people can act in dangerous environments with out endangering their very own security, comparable to when defusing explosives or decommissioning nuclear waste. It additionally permits one to be current and act even at nice distance: underwater, in house, or inside a affected person miles away from the surgeon. These are all essential functions, the place expert and certified operators management the robotic after receiving particular coaching to study to make use of the system safely.
Teleoperation for everybody?
The latest pandemic has but made much more obvious the necessity for immersive telepresence and distant motion additionally for non-expert customers: not solely might teleoperated robots take vitals or deliver medication to infectious sufferers, however we might help our aged dwelling distant with chores like transferring heavy stuff, or cooking, for instance. Also, quite a few bodily jobs might be executed from residence.
The latest ANA-Xprize finals have proven how far teleoperation can go (see this spectacular video of the profitable workforce), however in such conditions each the perceptual and management load lie solely on the operator. This might be fairly taxing on a cognitive stage: each notion and motion are mediated, by cameras and robotic arms respectively, decreasing the consumer’s state of affairs consciousness and pure eye-hand coordination. While robotic sensing capabilities and actuators have undergone related technological progress, the interface with the consumer nonetheless lacks intuitive options facilitating the operator’s job (Rea & Seo, 2022).
Human and robotic becoming a member of forces
Shared management has gained reputation lately, as an method championing human-machine cooperation: low-level motor management is carried out by the robotic, whereas the human is targeted on high-level motion planning. To obtain such a mix, the robotic system nonetheless wants a well timed approach to infer the operator intention, in order to consequently help with the execution. Usually, motor intentions are inferred by monitoring arm actions or movement management instructions (if the robotic is operated by way of a joystick), however particularly throughout object manipulation the hand is tightly following data collected by the gaze. In the final a long time, rising proof in eye-hand coordination research has proven that gaze reliably anticipates the hand motion goal (Hayhoe et al., 2012), offering an early cue about human intention.
Gaze and movement options to estimate intentions
In a contribution offered at IROS 2022 final month (Belardinelli et al., 2022), we launched an intention estimation mannequin that depends on each gaze and movement options. We collected pick-and-place sequences in a digital setting, the place individuals might function two robotic grippers to know objects on a cluttered desk. Motion controllers have been used to trace arm motions and to know objects by button press. Eye actions have been tracked by the eye-tracker embedded within the digital actuality headset.
Gaze options have been computed by defining a Gaussian distribution centered on the gaze place and taking for every object the probability for it to be the goal of visible consideration, which was given by the cumulative distribution collected by the article bounding field. For the movement options, the hand pose and velocity have been used to estimate the hand’s present trajectory which was in comparison with an estimated optimum trajectory to every object. The normalized similarity between the 2 trajectories outlined the probability of every object to be the goal of the present motion.
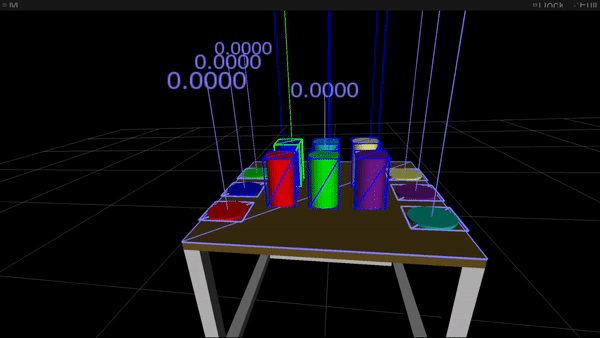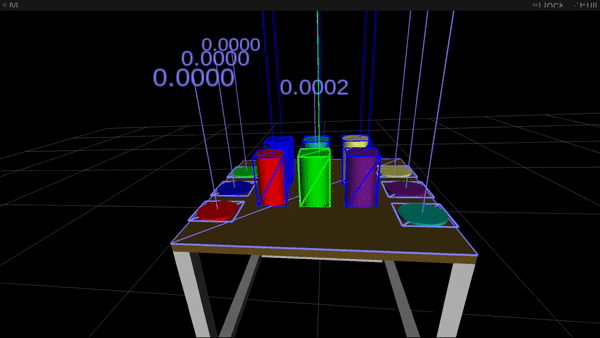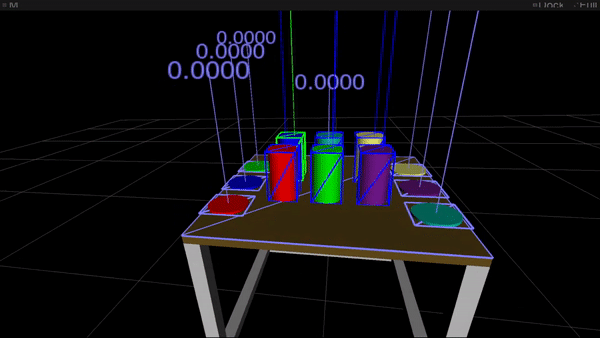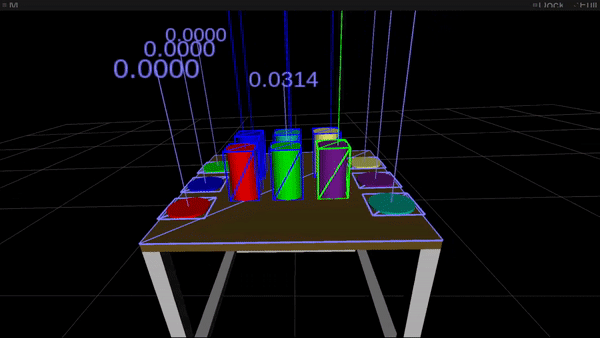
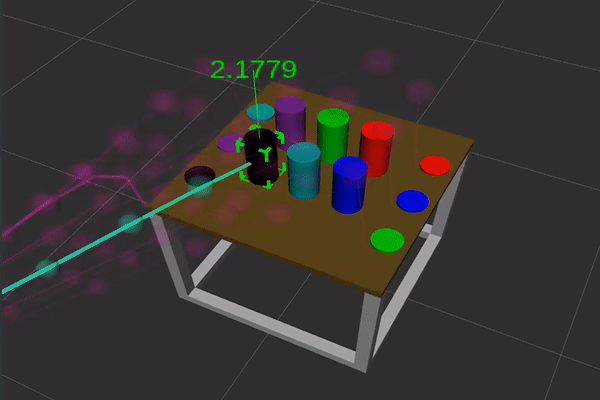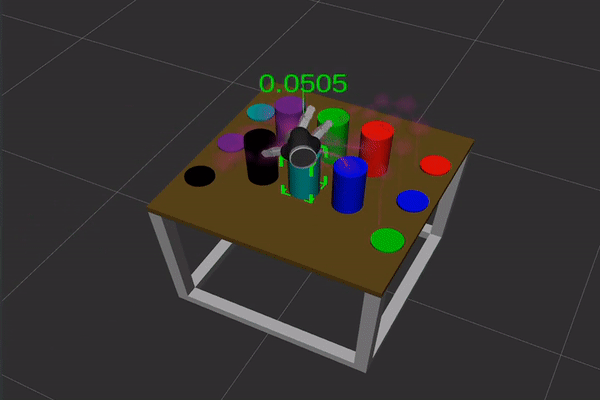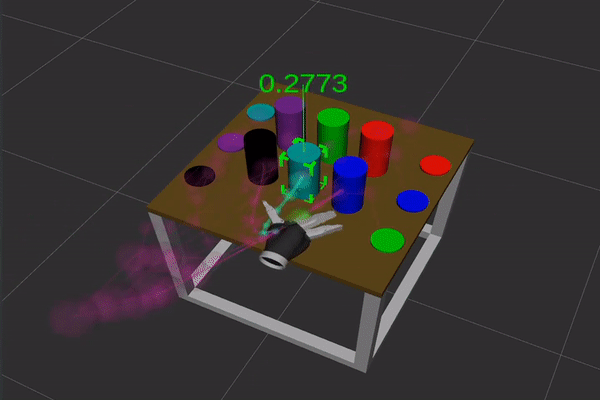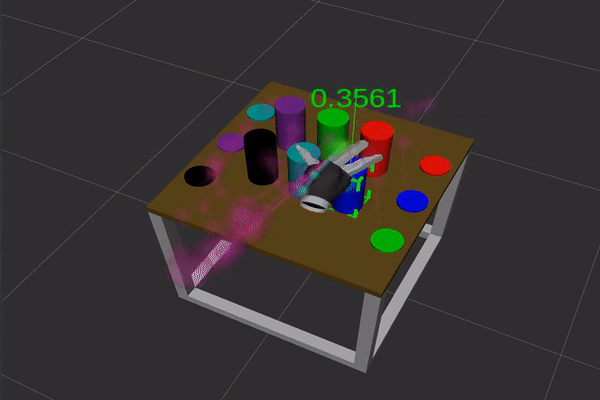 Figure 1: Gaze options (high) and movement options (backside) used for intention estimation. In each movies the article highlighted in inexperienced is the most probably goal of visible consideration and of hand motion, respectively.
Figure 1: Gaze options (high) and movement options (backside) used for intention estimation. In each movies the article highlighted in inexperienced is the most probably goal of visible consideration and of hand motion, respectively.
These options together with the binary greedy state have been used to coach two Gaussian Hidden Markov Models, one on choose and one on place sequences. For 12 totally different intentions (selecting of 6 totally different objects and inserting at 6 totally different places) the overall accuracy (F1 rating) was above 80%, even for occluded objects. Importantly, for each actions already 0.5 seconds earlier than the top of the motion a prediction with over 90% accuracy was accessible for at the least 70% of the observations. This would enable for an helping plan to be instantiated and executed by the robotic.
We additionally performed an ablation examine to find out the contribution of various function mixtures. While the fashions with gaze, movement, and greedy options carried out higher within the cross validation, the advance with respect to solely gaze and greedy state was minimal. Even when checking obstacles close by at first, the truth is, the gaze was already on the goal earlier than the hand trajectory grew to become sufficiently discriminative.
We additionally ascertained that our fashions might generalize from one hand to the opposite (when fed the corresponding hand movement options), therefore the identical fashions might be used to concurrently estimate every hand intention. By feeding every hand prediction to a easy rule-based framework, primary bimanual intentions may be acknowledged. So, for instance, reaching for an object with the left hand whereas the precise hand goes to put the identical object on the left hand is taken into account a bimanual handover.
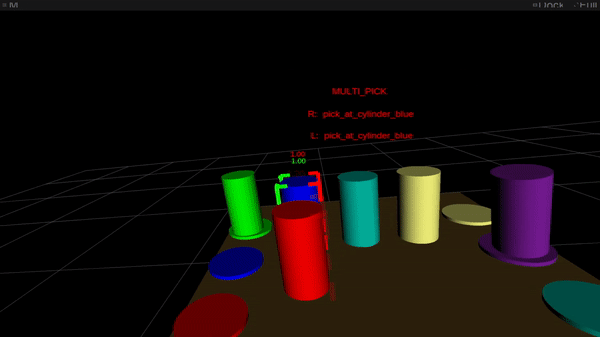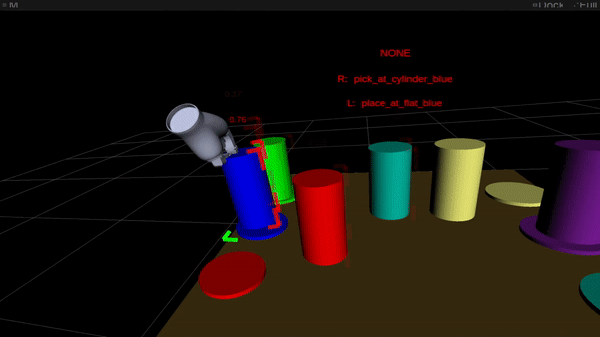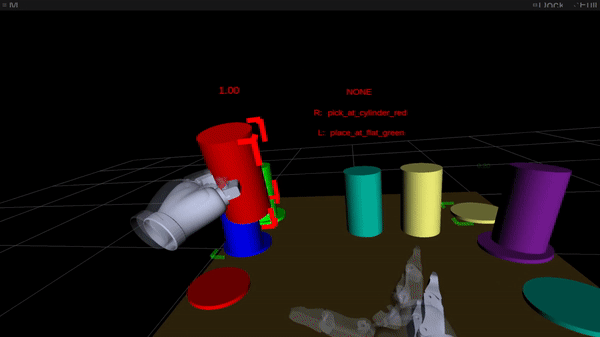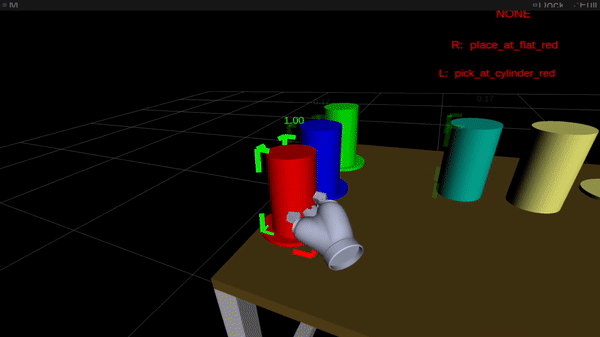 Figure 2: Online intention estimation: the pink body denotes the present right-hand intention prediction, the inexperienced body the left-hand prediction. Above the scene, the bimanual intention is proven in capital letters.
Figure 2: Online intention estimation: the pink body denotes the present right-hand intention prediction, the inexperienced body the left-hand prediction. Above the scene, the bimanual intention is proven in capital letters.
Such an intention estimation mannequin might assist an operator to execute such manipulations with out specializing in choosing the parameters for the precise motor execution of the choose and place, one thing we don’t normally do consciously in pure eye-hand coordination, since we automated such cognitive processes. For instance, as soon as a greedy intention is estimated with sufficient confidence, the robotic might autonomously choose one of the best grasp and greedy place and execute the grasp, relieving the operator of fastidiously monitoring a grasp with out tactile suggestions and presumably with inaccurate depth estimation.
Further, even when in our setup movement options weren’t decisive for early intention prediction, they could play a bigger function in additional complicated settings and when extending the spectrum of bimanual manipulations.
Combined with appropriate shared management insurance policies and suggestions visualizations, such programs might additionally allow untrained operators to regulate robotic manipulators transparently and successfully for longer instances, enhancing the overall psychological workload of distant operation.
References
Belardinelli, A., Kondapally, A. R., Ruiken, D., Tanneberg, D., & Watabe, T. (2022). Intention estimation from gaze and movement options for human-robot shared-control object manipulation. 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2022.
Hayhoe, M. M., McKinney, T., Chajka, Okay., & Pelz, J. B. (2012). Predictive eye actions in pure imaginative and prescient. Experimental mind analysis, 217(1), 125-136.
Rea, D. J., & Seo, S. H. (2022). Still Not Solved: A Call for Renewed Focus on User-Centered Teleoperation Interfaces. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 9.

Anna Belardinelli
is Principal Scientist on the Honda Research Institute Europe.
AIhub
is a non-profit devoted to connecting the AI group to the general public by offering free, high-quality data in AI.

AIhub
is a non-profit devoted to connecting the AI group to the general public by offering free, high-quality data in AI.
[ad_2]
