[ad_1]
The Hype, The Science, and What Healthy People Should Know About CGMs.
Why CGMs Took Off within the “Wellness” World
Continuous glucose displays (CGMs) have exploded in reputation because of influencers, wellness startups, and biohacking apps. CGMs for non-diabetics are sometimes marketed because the next-gen Fitbit to your metabolism—claiming to unlock personalised diet, fat-burning potential, and real-time suggestions to optimize your food regimen.
But right here’s the factor: CGMs had been developed for folks with diabetes, the place monitoring blood sugar is actually life-saving. If you don’t have diabetes, does slapping one in your arm provide any actual advantages—or simply extra information than you want?
What “Normal” Blood Glucose Actually Looks Like
Normal fasting glucose ranges vary between 3.9-5.6 mmol/L or 70-100 mg/dL. After meals, reaching 7.8 mmol/L (140 mg/dL) is regular, as your physique releases insulin to shuttle the glucose into the cells. 2 hours after consuming, blood glucose must be right down to below 7.8 mmol/L or 140 mg/dL
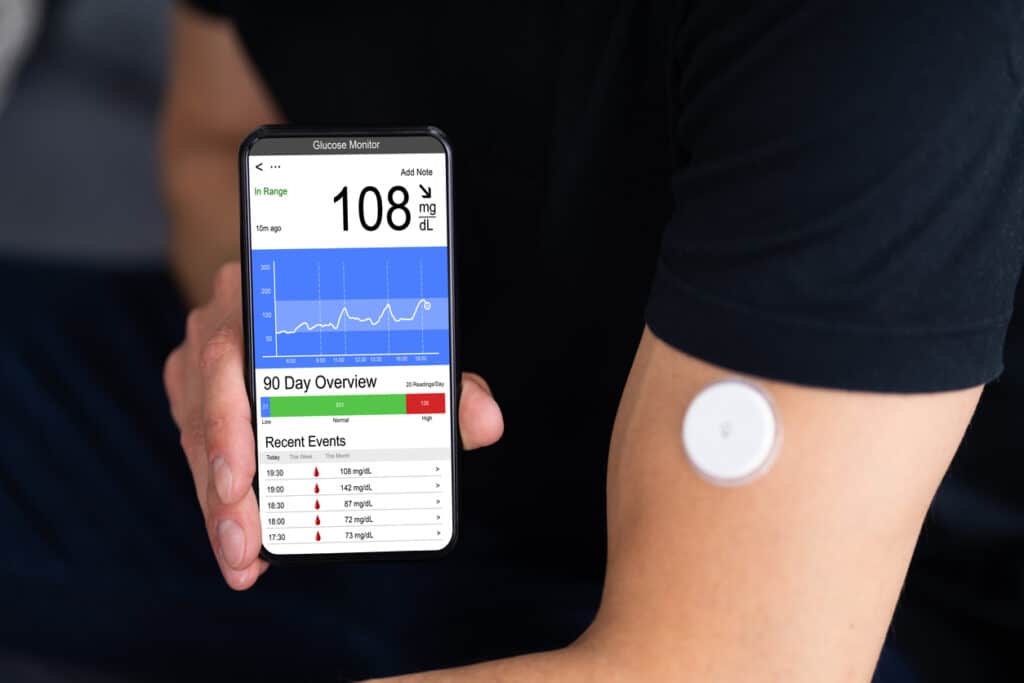

An enormous research known as CGMap (n > 7,000 wholesome adults aged 40–70) gave an in depth take a look at typical glucose ranges in folks with out diabetes:
- Average 24-hour glucose: ~5.5 mmol/L (99 mg/dL)
- Time spent ≥7.8 mmol/L (140 mg/dL): lower than 3% of the day (about 20 minutes)
- Overnight lows <3.9 mmol/L (70 mg/dL): uncommon
So sure—glucose spikes do occur, particularly after consuming. But these are regular and anticipated. In folks with wholesome metabolic operate, your pancreas rapidly clears that sugar and brings your ranges again to baseline.
No human trial has proven that these short-lived spikes in wholesome individuals are dangerous, or that they enhance the chance for illness.
Do CGMs Change Health Behaviours in Healthy People?
Let’s break down what current human trials have found.
🍽️ CGMs Don’t Change Diets Much
In a 2022 crossover research (PMID: 36279286), 15 wholesome adults ate two isocaloric diets—one excessive in refined carbs, one excessive in fiber—whereas sporting CGMs. Though the gadgets clearly detected larger spikes with the refined-carb meals, this didn’t result in long-term dietary modifications.
🏃 Exercise Doesn’t Shift Glucose within the Way You Might Expect
In a 2023 Canadian research (PMID: 37562361), 27 sedentary adults wore CGMs whereas doing 11 minutes of day by day vigorous calisthenics vs. sitting. The intervention group received fitter, however their glucose didn’t budge—imply glucose and glycemic variability remained unchanged.
🕐 TRE (Time-Restricted Eating) + CGMs = Minor Changes
A 2023 RCT (PMID: 37527388) studied chubby adults with out diabetes. Participants did time-restricted consuming (consuming 7am–3pm) with a calorie deficit, in comparison with a calorie deficit alone.
- The TRE group had barely smaller glucose spikes (~0.3 mmol/L decrease),
- But no change in weight reduction or imply glucose.
🧠 Most People Misinterpret CGM Data
In a 2023 survey of non-diabetic CGM customers (PMID: 37470511), most individuals mentioned they checked the info often—however few understood it. Some even eradicated wholesome carbs unnecessarily.
“CGM use outside of a clinical setting may lead to inappropriate dietary restrictions and increased food anxiety.” — Study authors
Bottom line: CGMs aren’t driving higher outcomes in people who find themselves already metabolically wholesome. They could even backfire.
Are Post-Meal Glucose Spikes Harmful?
No, and right here’s why:
- After you eat carbs, glucose naturally rises.
- Your pancreas releases insulin, which clears the sugar into your muscular tissues and liver.
- This whole course of is regular, non permanent, and not dangerous in wholesome folks.
The spike is a part of the system working appropriately, not failing.
Studies in wholesome folks present that transient post-meal glucose elevations (e.g. 120–140 mg/dL for an hour) are not related with irritation, oxidative stress, or long-term metabolic injury. Attempts to flatten these small rises usually result in excessive meals avoidance or nervousness—not higher well being.
The Case Against Wearing a CGM Without Diabetes
| Concern | What the Science Shows |
|---|---|
| Medicalizing regular biology | 97% of CGM readings in wholesome folks fall inside vary (CGMap information). Normal spikes don’t want “fixing.” |
| Inaccuracy | Even newer CGMs (like Dexcom G7 and Libre 3) present 9–14% error charges in comparison with lab glucose in wholesome folks. |
| Skin reactions | Adhesives could cause rashes or allergic reactions (PMID: 31794494). |
| Data obsession | People usually develop into overly centered on particular person readings. This can gasoline nervousness or orthorexia-like behaviors. |
CGMs For Non-Diabetics – Can They Help?
Possibly—however solely in very particular instances:
- Pre-diabetes screening in high-risk people (household historical past, PCOS, weight problems)
- Elite athletic efficiency, the place exact fueling may have an effect on endurance
- Clinical analysis settings finding out metabolic operate
But for most individuals, life-style elements (food regimen, sleep, train, stress) provide you with extra affect than micromanaging your glucose minute-by-minute.
Conclusion: You Probably Don’t Need a CGM
If you don’t have diabetes or a identified blood sugar dysfunction:
✅ Your physique handles glucose regulation by itself
✅ Small spikes after consuming are regular and innocent
❌ CGMs don’t meaningfully enhance well being outcomes in wholesome folks
❌ You may find yourself overcorrecting, over-restricting, or stressing out
Save your cash—and spend it on fiber-rich meals, motion you take pleasure in, and good sleep hygiene. The easy stuff nonetheless works greatest.
[ad_2]
