[ad_1]
Because knowledge might be saved and archived, categorised and delicate info—which can must be protected longer than a decade, or extra—must be protected with quantum-resistant algorithms. The 4 algorithms chosen by NIST symbolize an early milestone within the growth of the post-quantum encryption commonplace.
“Cryptographic protocols that are deployed today can still be in use in 10 years, in 20 years, in 30 years,” says Daniel Gottesman, a professor of theoretical pc science on the University of Maryland and a quantum computing guide at Keysight Technologies, a U.S.-based supplier of design, emulation, and take a look at tools for electronics. “If you send messages today, if they’re still going to be relevant in that time, then you need to worry about security against quantum computers of the future.”
Yet, quantum computing’s promise goes far past unlocking decades-old secrets and techniques.
Quantum computing affords the attractive promise of problem-solving talents and computing energy far exceeding in the present day’s strongest supercomputers. Google has constructed a quantum AI campus with the purpose of making a “useful, error-corrected quantum computer” by 2029. IBM expanded its quantum efforts with the purpose of making a 4,000-qubit quantum pc by 2025.
These extra refined platforms will enable a higher breadth of functions—comparable to chemical simulation and machine studying—and supply extra momentum to the long-term growth of quantum pc techniques. According to analyst agency International Data Corporation (IDC), the worldwide quantum computing market will develop 51% yearly, as measured in spending, from $412 million in 2020 to $8.6 billion in 2027.
“Companies building quantum hardware and software services now have several platforms already used by niche customers in the financial and defense spaces,” says John Blyler, industrial options supervisor, wireline communications, at Keysight Technologies. “And new applications are being identified, such as the simulation of molecules that may result in new life-saving drugs that cure various diseases.”

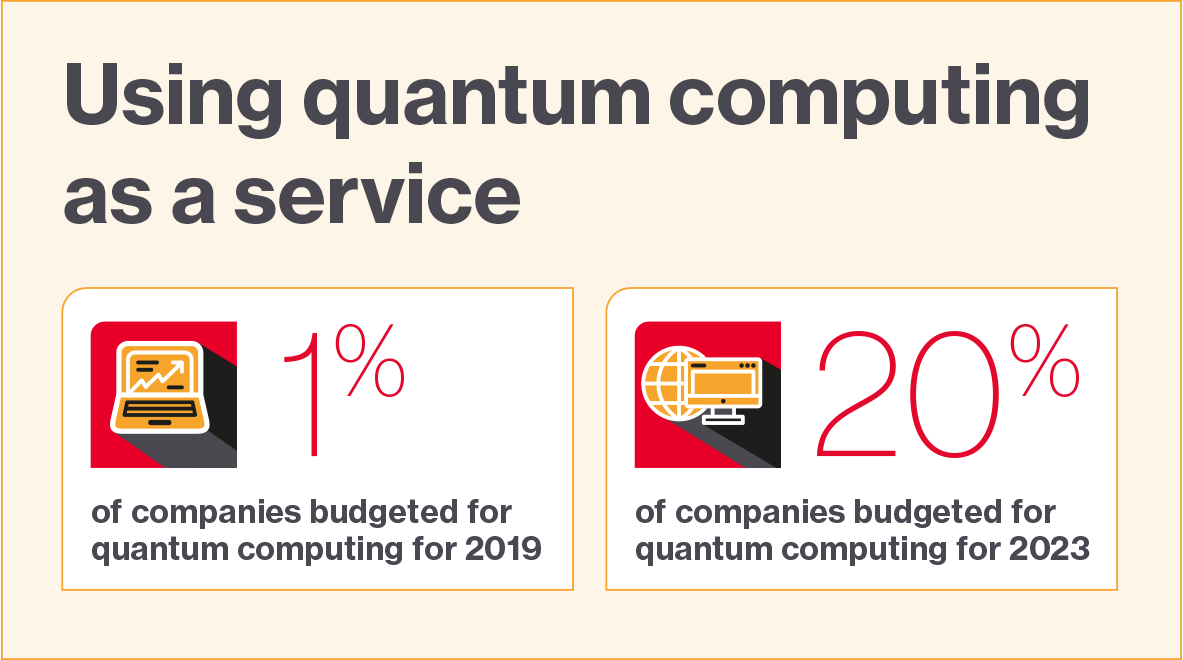
Companies that develop functions for the near-future quantum computer systems will derive a variety of advantages and lead the market due to their quantum benefit, says Chad Rigetti, former CEO of Rigetti Computing, an organization that gives quantum computing as a service. Quantum computing as a service, or QCaaS, permits prospects to have entry to a quantum pc by a cloud service that sometimes integrates with workloads based mostly on classical computing. The result’s a hybrid system that may be optimized for the precise downside: Most of the software program will run on classical computer systems, whereas quantum algorithms and simulations can run on quantum techniques.
While a lot of the dialogue of quantum computing has targeted on the dangers to privateness and encrypted info, the far higher threat in the present day is failing to plan for the ways in which quantum computing can have an effect on an organization’s enterprise.
This content material was produced by Insights, the customized content material arm of MIT Technology Review. It was not written by MIT Technology Review’s editorial workers.
