[ad_1]
A set of 38 safety vulnerabilities has been uncovered in wi-fi industrial web of issues (IIoT) units from 4 completely different distributors that would pose a major assault floor for menace actors seeking to exploit operational know-how (OT) environments.
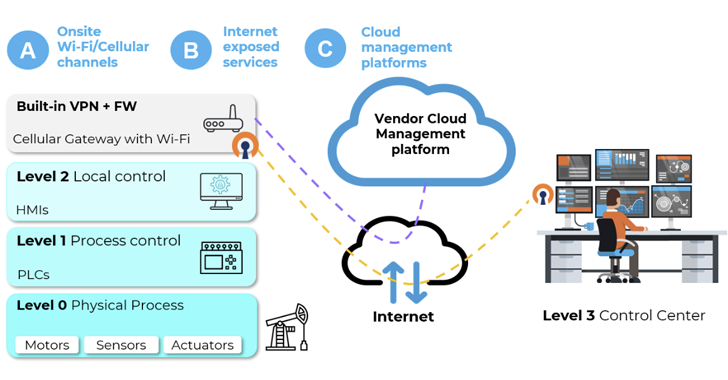
“Threat actors can exploit vulnerabilities in Wireless IIoT units to realize preliminary entry to inside OT networks,” Israeli industrial cybersecurity firm Otorio stated. “They can use these vulnerabilities to bypass safety layers and infiltrate goal networks, placing essential infrastructure in danger or interrupting manufacturing.”
The flaws, in a nutshell, provide a distant entry level for assault, enabling unauthenticated adversaries to realize a foothold and subsequently use it as leverage to unfold to different hosts, thereby inflicting vital injury.
Some of the recognized shortcomings could possibly be chained to present an exterior actor direct entry to hundreds of inside OT networks over the web, safety researcher Roni Gavrilov stated.
Of the 38 defects, three have an effect on ETIC Telecom’s Remote Access Server (RAS) – CVE-2022-3703, CVE-2022-41607, and CVE-2022-40981 – and could possibly be abused to fully seize management of prone units.
Five different vulnerabilities concern InHand Networks InRouter 302 and InRouter 615 that, if exploited, may end in command injection, data disclosure, and code execution.
Specifically, it entails making the most of points within the “Device Manager” cloud platform, which allows operators to carry out distant actions like configuration adjustments and firmware upgrades, to compromise each cloud-managed InRouter gadget with root privileges.
Also recognized are two weaknesses in Sierra Wireless AirLink Router (CVE-2022-46649 and CVE-2022-46650) that would enable a lack of delicate data and distant code execution. The remaining flaws are nonetheless beneath accountable disclosure.
The findings underscore how OT networks could possibly be put in danger by making IIoT units instantly accessible on the web, successfully making a “single level of failure” that may bypass all safety protections.
Alternatively, native attackers can break into industrial Wi-Fi entry factors and mobile gateways by concentrating on on-site Wi-Fi or mobile channels, resulting in adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) situations with hostile potential impression.
The assaults can vary from concentrating on weak encryption schemes to coexistence assaults geared toward combo chips used broadly in digital units.
To pull this off, menace actors can make the most of platforms like WiGLE – a database of various wi-fi hotspots worldwide – to determine high-value industrial environments, bodily find them, and exploit the entry factors from shut proximity, Otorio famous.
As countermeasures, it is really useful to disable insecure encryption schemes, conceal Wi-Fi community names, disable unused cloud administration providers, and take steps to forestall units from being publicly accessible.
“The low complexity of exploit, mixed with the broad potential impression, makes wi-fi IIoT units and their cloud-based administration platforms an attractive goal for attackers seeking to breach industrial environments,” the corporate stated.
The improvement additionally comes as Otorio disclosed particulars of two high-severity flaws in Siemens Automation License Manager (CVE-2022-43513 and CVE-2022-43514) that could possibly be mixed to realize distant code execution and privilege escalation. The bugs had been patched by Siemens in January 2023.
[ad_2]