[ad_1]
Organizations in East Asia are being focused by a possible Chinese-speaking actor dubbed DragonSpark whereas using unusual ways to go previous safety layers.
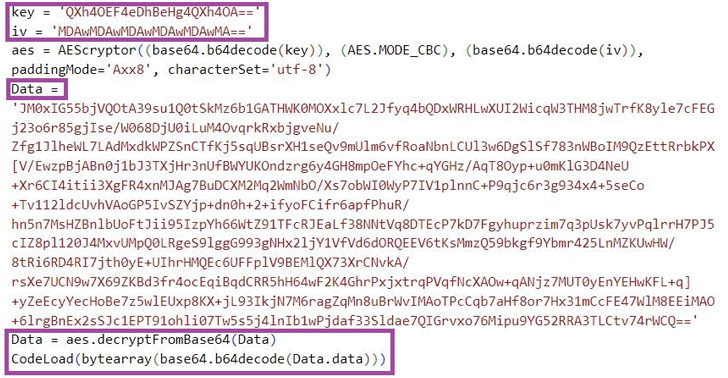
“The assaults are characterised by means of the little identified open supply SparkRAT and malware that makes an attempt to evade detection by Golang supply code interpretation,” SentinelOne stated in an evaluation revealed in the present day.
A putting side of the intrusions is the constant use of SparkRAT to conduct a wide range of actions, together with stealing info, acquiring management of an contaminated host, or operating extra PowerShell directions.
The risk actor’s finish targets stay unknown as but, though espionage or cybercrime is prone to be the motive. DragonSpark’s ties to China stem from the usage of the China Chopper net shell to deploy malware – a extensively used assault pathway amongst Chinese risk actors.
Furthermore, not solely do the open supply instruments used within the cyber assaults originate from builders or corporations with hyperlinks to China, the instructure for staging the payloads are situated in Taiwan, Hong Kong, China, and Singapore, a few of which belong to reputable companies.
The command-and-control (C2) servers, however, are located in Hong Kong and the U.S., the cybersecurity agency stated.
Initial entry avenues entail compromising internet-exposed net servers and MySQL database servers to drop the China Chopper net shell. The foothold is then leveraged to hold out lateral motion, privilege escalation, and malware deployment utilizing open supply instruments like SharpToken, BadPotato, and GotoHTTP.
Also delivered to the hosts are customized malware able to executing arbitrary code and SparkRAT, a cross-platform distant entry trojan that may run system instructions, manipulate recordsdata and processes, and siphon info of curiosity.
Another malware of be aware is the Golang-based m6699.exe, which interprets at runtime the supply code contained inside it in order to fly underneath the radar and launch a shellcode loader that is engineered to contact the C2 server for fetching and executing the next-stage shellcode.
“Chinese-speaking risk actors are identified to ceaselessly use open supply software program in malicious campaigns,” the researchers concluded.
“Since SparkRAT is a multi-platform and feature-rich software, and is commonly up to date with new options, we estimate that the RAT will stay enticing to cybercriminals and different risk actors sooner or later.”