[ad_1]
According to Accenture, greater than one-third of cyberattacks are geared toward small companies, however solely 14% of them are ready to defend themselves.1 Cyberattacks may depart many small and midsize enterprises (SMEs) reeling from monetary and productiveness losses, operation disruptions, extortion funds, settlement prices, and regulatory fines.
Given this backdrop, specialists say it’s time to plan for when, not if. Clear backup and catastrophe restoration plans—specializing in IT infrastructure, information, and functions—to execute restoration processes after a catastrophe are important in each enterprise’s enterprise continuity technique. This report explores what catastrophe restoration planning entails and the way SMEs can implement it in at present’s fast-evolving cyber panorama.
The following are the report’s key findings:
- Cyberattacks have grown extra frequent and complicated, and SMEs are within the firing line. The information tells a worrying story. With the pandemic, together with geopolitical elements, inflicting shifts in how we stay and work, the case for catastrophe restoration planning has by no means been extra pressing.
According to 1 cross-industry examine, midsize corporations had been nearly 500% extra prone to be focused by the top of 2021 than two years in the past.2 Experts say synthetic intelligence–primarily based assaults are rising. Ransomware-as-a-service and, in some circumstances, deepfakes are additionally growing, though most SMEs change into victims due to human error.
- A well-built catastrophe restoration plan can considerably reduce and even get rid of downtime. Disaster restoration plans are a key element of enterprise continuity plans. While enterprise continuity focuses on total technique, together with insurance policies and procedures for restoration following an incident, catastrophe restoration focuses on IT infrastructure, information, and functions.
- A well-crafted catastrophe restoration plan contains clear definitions of restoration time goal (RTO) and restoration level goal (RPO).3,4 Having such a plan is essential for safeguarding information and functions towards malware and ransomware assaults and will considerably reduce and even get rid of downtime.

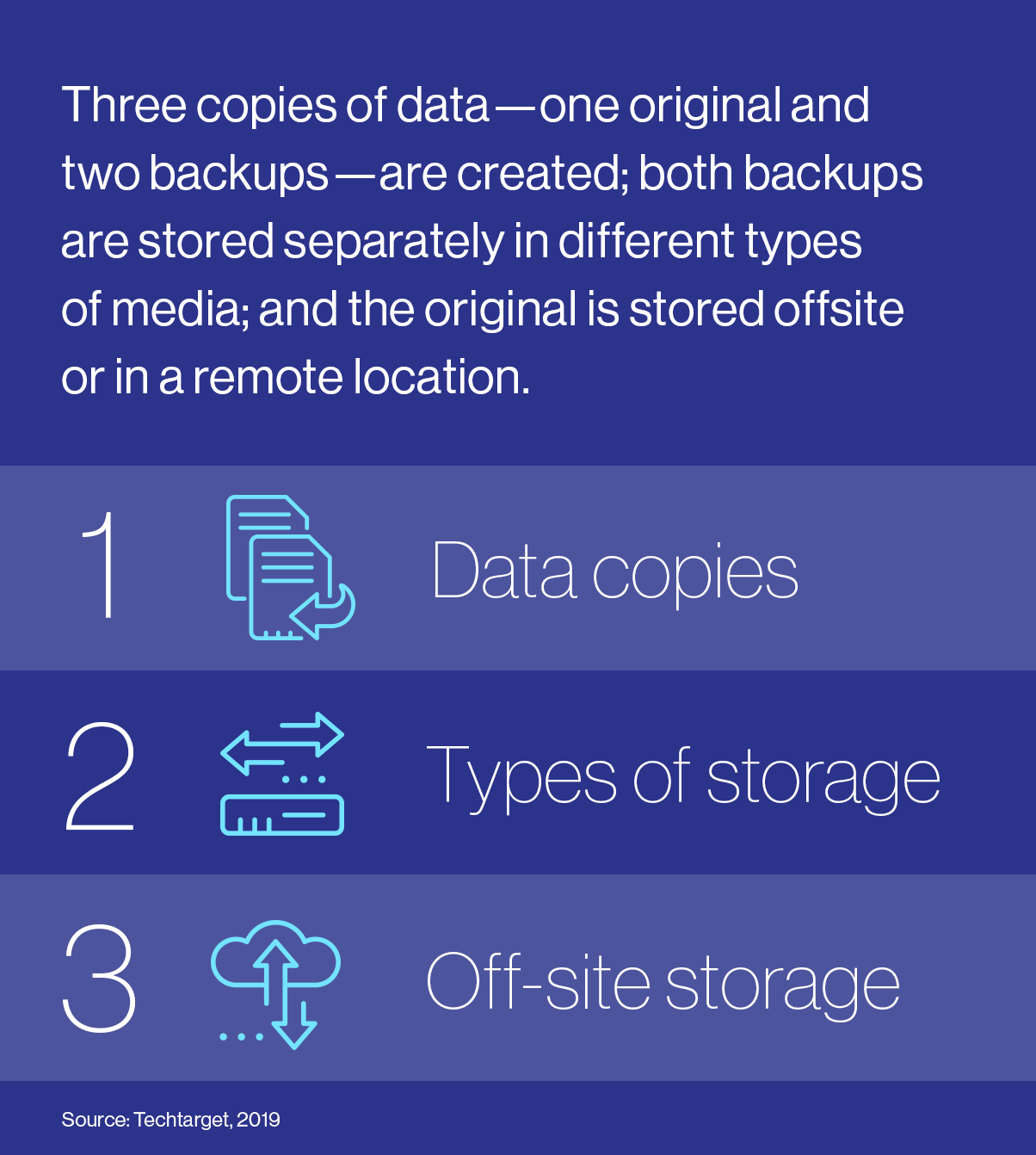
- Backups and replication of knowledge are important for catastrophe restoration. With cybercriminals spending over 200 days in corporations’ methods earlier than being noticed5 and corrupting backups, SMEs have to retailer their information in a number of codecs on completely different methods or look towards an information replication answer to make sure near-instantaneous restoration. While the longstanding 3-2-1 strategy6 is endorsed by cybersecurity specialists, some organizations are looking for better safety with the 3-3-2 approach7, which incorporates an additional disconnected and inaccessible (“air-gapped”) copy.
- An unexamined catastrophe restoration plan may carry enterprises again to sq. one. Disaster restoration plans are primarily pointless with out common apply runs—and the way typically this apply ought to be accomplished is determined by how briskly a company is rising or adopting new applied sciences. Experts say such plans ought to be up to date and examined at the least yearly, and ideally each quarter.
This content material was produced by Insights, the customized content material arm of MIT Technology Review. It was not written by MIT Technology Review’s editorial employees.
