[ad_1]
An unofficial patch has been made accessible for an actively exploited safety flaw in Microsoft Windows that makes it potential for recordsdata signed with malformed signatures to sneak previous Mark-of-the-Web (MotW) protections.
The repair, launched by 0patch, arrives weeks after HP Wolf Security disclosed a Magniber ransomware marketing campaign that targets customers with pretend safety updates which make use of a JavaScript file to proliferate the file-encrypting malware.
While recordsdata downloaded from the web in Windows are tagged with a MotW flag to forestall unauthorized actions, it has since been discovered that corrupt Authenticode signatures can be utilized to permit the execution of arbitrary executables with none SmartScreen warning.
Authenticode is a Microsoft code-signing know-how that authenticates the identification of the writer of a selected piece of software program and verifies whether or not the software program was tampered with after it was signed and printed.
“The [JavaScript] file truly has the MotW however nonetheless executes and not using a warning when opened,” HP Wolf Security researcher Patrick Schläpfer famous.
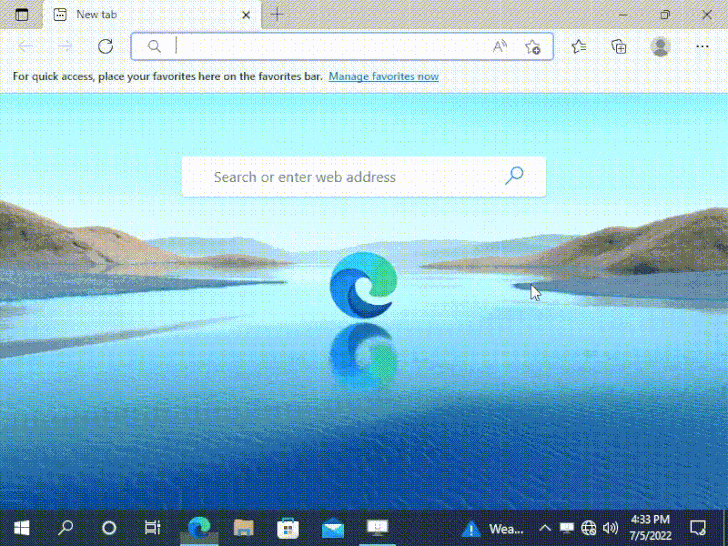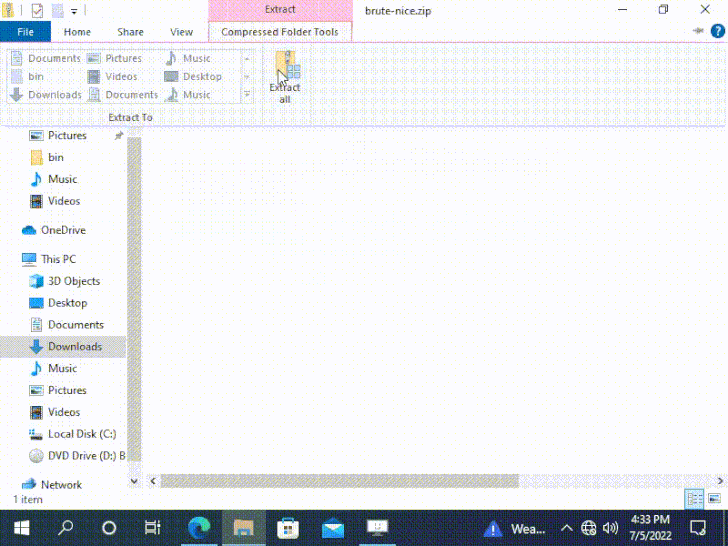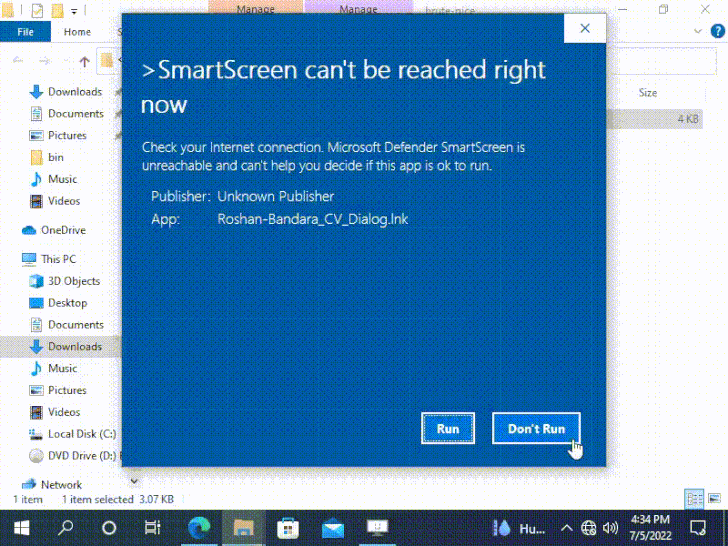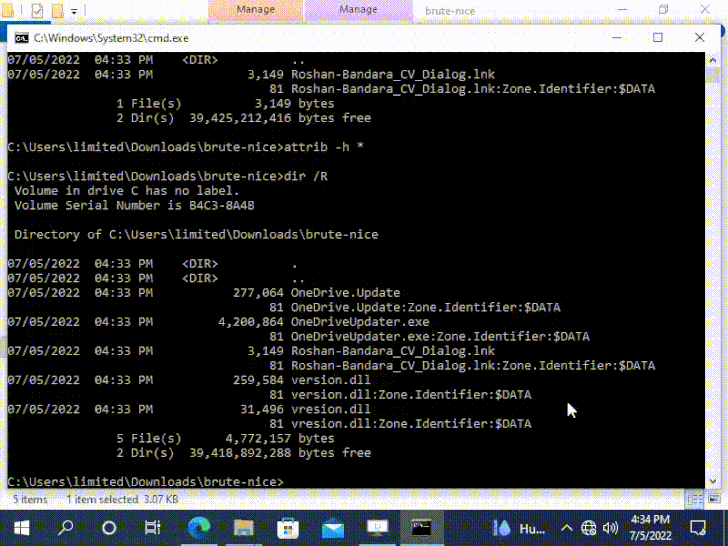 |
| Source: Will Dormann Twitter |
“If the file has this malformed Authenticode signature, the SmartScreen and/or file-open warning dialog shall be skipped,” safety researcher Will Dormann defined.
Now in response to 0patch co-founder Mitja Kolsek, the zero-day bug is the results of SmartScreen returning an exception when parsing the malformed signature, which is incorrectly interpreted as a choice to run this system quite than set off a warning.
Fixes for the flaw additionally come lower than two weeks after unofficial patches had been shipped for one more zero-day MotW bypass flaw that got here to gentle in July and has since come underneath lively assault, per safety researcher Kevin Beaumont.
The vulnerability, found by Dormann, pertains to how Windows fails to set the MotW identifier to recordsdata extracted from particularly crafted .ZIP recordsdata.
“Attackers due to this fact understandably desire their malicious recordsdata not being marked with MOTW; this vulnerability permits them to create a ZIP archive such that extracted malicious recordsdata won’t be marked,” Kolsek stated.