[ad_1]
The menace actor behind the Fodcha distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) botnet has resurfaced with new capabilities, researchers reveal.
This contains adjustments to its communication protocol and the flexibility to extort cryptocurrency funds in alternate for stopping the DDoS assault in opposition to a goal, Qihoo 360’s Network Security Research Lab mentioned in a report printed final week.
Fodcha first got here to mild earlier this April, with the malware propagating by way of recognized vulnerabilities in Android and IoT units in addition to weak Telnet or SSH passwords.
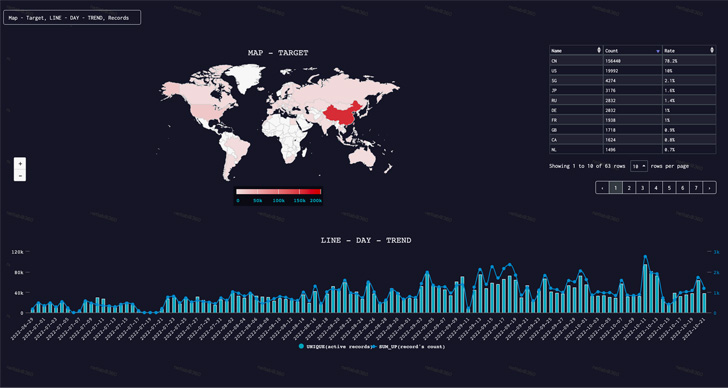
The cybersecurity firm mentioned that Fodcha has developed right into a large-scale botnet with over 60,000 lively nodes and 40 command-and-control (C2) domains that may “simply generate greater than 1 Tbps visitors.”
Peak exercise is alleged to have occurred on October 11, 2022, when the malware focused 1,396 units in a single day.
The prime international locations singled out by the botnet since late June 2022 contains China, the U.S., Singapore, Japan, Russia, Germany, France, the U.Ok., Canada, and the Netherlands.
Some of the outstanding targets vary from healthcare organizations and regulation enforcement businesses to a widely known cloud service supplier that was assaulted with visitors exceeding 1 Tbps.
Fodcha’s evolution has additionally been accompanied by new stealth options that encrypt communications with the C2 server and embed ransom calls for, making it a stronger menace.
“Fodcha reuses a variety of Mirai’s assault code, and helps a complete of 17 assault strategies,” the cybersecurity firm famous.
The findings come as new analysis from Lumen Black Lotus Labs identified the rising abuse of the Connectionless Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (CLDAP) to enlarge the dimensions of DDoS assaults.
To that finish, as many as 12,142 open CLDAP reflectors have been recognized, most of that are distributed within the U.S. and Brazil, and to a lesser extent in Germany, India, and Mexico.
In one occasion, a CLDAP service related to an unnamed regional retail enterprise in North America has been noticed directing “problematic quantities of visitors” in direction of a variety of targets for greater than 9 months, emitting as much as 7.8 Gbps of CLDAP visitors.