[ad_1]
To the neophyte, power coaching is simple: choose up a weight, put it down, get robust.
Spend a couple of weeks or months on the web or chatting up your new fit-buddies, and also you come to appreciate there’s a complete lot of science, artwork, and jargon behind the obvious simplicity: compound workouts; plyometrics; supination; RPE; 1RM; ATG.
To assist you determine what the gymnasium bros and health nerds are yapping about, we’ve put collectively a cheat-sheet of weightlifting phrases that breaks all of it down for you.
So subsequent time somebody recommends that you simply “Try to PR on the final pyramid set of your compound movements the final mesocycle before deload,” you’ll know what they’re speaking about.
FORM/MOVEMENT
Ass to grass
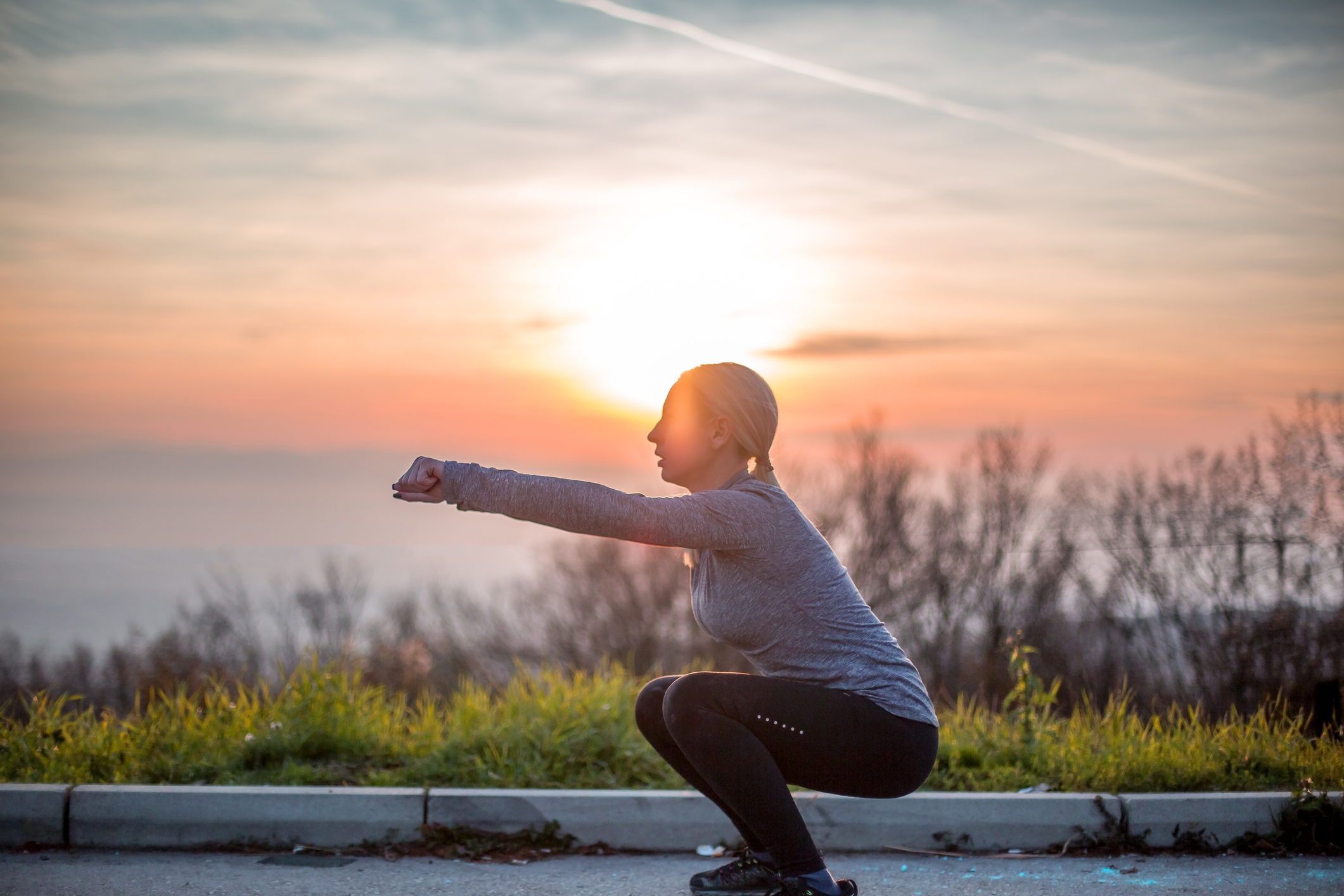

A motion carried out in squat variations whereby the knees and hips flex totally, and the glutes are shut as potential to the ground. Often abbreviated as ATG.
Compound motion
An train that includes important motion of two or extra main joints. Examples embrace squats, lunges, deadlifts, pull-ups, and presses of every kind.
Concentric motion
A kind of muscle contraction during which a working muscle goes from a lengthened to a shortened place. In power coaching, it’s the a part of the transfer at which the load (or your body weight) strikes upward, as within the ‘pushing’ portion of an overhead press.
Eccentric motion
A kind of muscle contraction during which a working muscle goes from a shortened to a lengthened place. In power coaching, it’s the a part of the transfer at which the load (or your body weight) strikes downward, as within the ‘lowering’ portion of an overhead press.
Flexion
A motion during which a joint goes from an open to a closed or bent place, as in a biceps curl or sit-up.
Extension
A motion during which a joint goes from a closed to an open or lengthened place, as in a triceps extension or a deadlift.
Functional motion
A motion, train, or drill that resembles, or helps to enhance, actions often encountered in on a regular basis life. For occasion, carrying groceries or hoisting baggage into an overhead bin.
Grip power
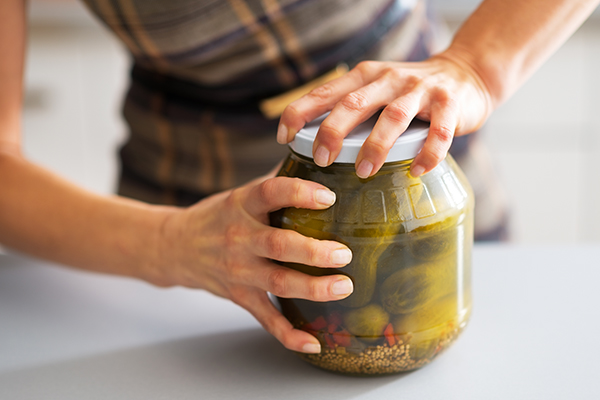

The capability to know, maintain, pinch, carry, and cling from objects of assorted shapes, sizes, and weights utilizing primarily the power of your fingers and palms.
Grip power is a element of many various gymnasium actions, together with farmer’s carries, rows, deadlifts, pull-downs, pull-ups, and, to a lesser extent, presses, and is taken into account an indicator of common well being and a dependable predictor of longevity.
Hip hinge
A motion during which each hip joints flex (bend) whereas the backbone stays braced and inflexible. A Romanian deadlift is an instance, as is the set-up place for the standing row.
Isolation actions
Exercises that contain important motion of only one main joint. Examples embrace lateral raises, triceps extensions, and biceps curls.
Isometric train
An train that locations rigidity on a number of muscle teams, however requires minimal motion at any main joint. Examples embrace the wall sit and the plank.
Lengthening
The act of extending, stress-free, or releasing a muscle or muscle group. In the ahead bend stretch, for instance, the hamstring muscle group on the backs of the thighs lengthens as you fold ahead.
Shortening
The act of tensing or contracting a muscle or muscle group. In the curl train, for instance, the biceps muscular tissues of the higher arms shorten as you increase the load.
Lifting to failure
Performing an train till you’re unable to finish one other repetition.
Technical failure refers to performing an train till you’re unable to finish one other full repetition with good type.
Absolute failure refers to performing the train till you possibly can not transfer the load in any respect, and often includes performing a number of partial repetitions — typically with the assistance of a coaching companion — till your muscular tissues are fully exhausted.
Supination

The act of turning your hand or foot upward or outward in order that the palm or sole is pointing up. In a dumbbell curl, supinating your hand as you increase the load leads to better rigidity in your biceps muscular tissues.
The time period additionally applies to the entire physique, when an train is carried out on one’s again (supine).
Pronation
The act of turning your hand or foot downward or inward in order that the palm or sole is pointing down. The time period additionally applies to the entire physique, when an train is carried out on one’s abdomen or going through down (inclined).
Time beneath rigidity (TUT)
The time taken to finish all phases of a strength-training train, typically expressed as a four-digit quantity, with every digit referring to the time taken to finish a particular portion of the motion.
So a pushup with a 4210 tempo could be a set of pushups during which you’re taking 4 seconds to decrease your self in the direction of the ground; two seconds holding the “down” place; one second to push your self again up, and nil seconds — no time — within the “up” place. Each rep of the pushup would give your chest, shoulders, and triceps seven complete seconds beneath rigidity.
WORKOUT DESIGN
Active restoration
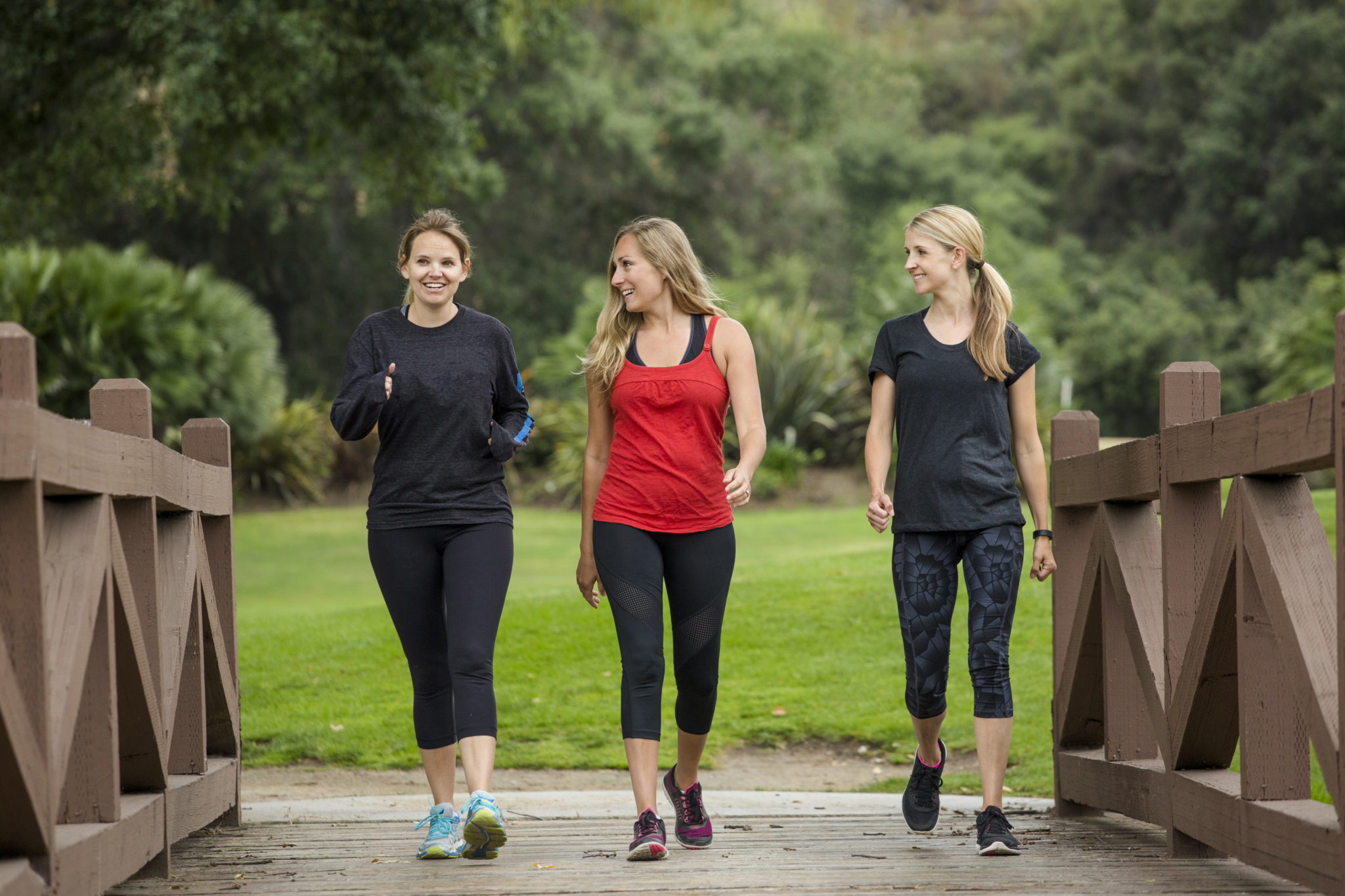

Light, straightforward motion carried out on non-exercise days — or between or after coaching classes on exercise days — meant to stimulate circulation, relieve soreness, and improve restoration. Examples embrace foam rolling, straightforward swimming, strolling, stretching, dynamic warmups, and yoga.
Bulking
A coaching block targeted on constructing muscle mass, often involving heavy, compound workouts, further protein and energy, and a give attention to relaxation exterior the gymnasium.
Calisthenics
Repetitive workouts involving body weight solely. Examples embrace push-ups, squats, leaping jacks, and sit-ups.
Cutting
A coaching block targeted on dropping fats, often involving lowered energy, continued give attention to protein consumption and power coaching, and an emphasis on further low-intensity train exterior the gymnasium.
Deloading
A brief interval — often every week — of lowered quantity and depth in a strength-training program, often following every week or extra of high-intensity and high-volume coaching.
Density coaching
A coaching type targeted on finishing as many reps, units, and/or workouts as potential in a given time period. Example: performing as many rounds as potential of 10 reps every of push-ups and squats in 10 minutes.
Drop set
A set of a power coaching train carried out instantly after a number of medium to heavy units during which you drastically cut back the load used with a purpose to additional exhaust a muscle.
Dynamic stretching/warmup

Light warmup strikes, carried out with body weight solely, to extend core temperature, loosen joints, enhance circulation, and cut back harm. Examples embrace excessive kicks, leaping jacks, and strolling lunges.
Full-body coaching
A coaching block or program during which you’re employed all the key muscular tissues of the physique in every exercise.
Muscular endurance
The capability of a muscle to contract repeatedly beneath rigidity earlier than fatiguing.
One-rep max
The quantity of weight you’re able to lifting, for a single repetition at maximal depth, in a given strength-training train.
Overtraining
In power coaching (versus endurance coaching), understanding at a degree of quantity and/or depth from which you’re unable to get better from one exercise to the following.
Symptoms embrace elevated resting coronary heart price, lowered coronary heart price variability, lack of motivation, and hampered progress.
Periodization
An method to coaching which focuses on totally different targets — power, energy, endurance, restoration — in coaching blocks lasting 4 to 12 weeks, all through the coaching 12 months.
An instance is the Super Blocks idea, during which you’re employed out in three-week blocks, every targeted on a selected side of health, separated by one-week deloads (see above).
Power
The capability to precise power shortly. A 100-meter dash or an extended soar are assessments of energy. In physics, energy is expressed as drive x acceleration, so the stronger you’re and the quicker you progress the extra highly effective you’re.
Plyometrics

Jumps, throws, and calisthenics strikes designed to develop athletic explosiveness and energy, and improve power.
PR (Personal report)
An particular person’s efficiency in a carry or different train that represents their greatest effort thus far. Examples in power coaching might embrace performing extra pull-ups in a row than you’ve ever carried out with out dropping from the bar, or lifting extra weight for a single repetition than you ever have in a deadlift.
Progressive overload
Systematically rising the reps, weight, and/or quantity of a power coaching program over time with a purpose to increase power, muscle mass, endurance, and different elements of health.
Pyramiding
A power coaching technique during which the load will increase incrementally in an train over a number of units whereas repetitions inversely lower, usually culminating in a single all-out set of 5 or fewer reps.
Reps
A single cycle of a strength-training motion, together with — if relevant — decreasing, lifting, and/or isometric holds.
Sets
A rep or group of reps of an train carried out in succession to extend some side of health. Usually expressed together with the rep rely of the train, as in, “Three sets of 10 reps,” or, merely, “3 x 10.”
Split coaching
As against full-body coaching (see above) a break up program focuses on totally different muscle teams or actions on totally different days of the week, or days inside a cycle of exercises.
Some examples embrace “push-pull” during which the lifter performs actions that contain pushing workouts on some days, and pulling workouts on others; “upper-lower,” during which the lifter works higher physique some days and decrease on others, and “body part splits,” during which the lifter works only one or two particular person muscle teams — say, arms or again or legs — every exercise.
Strength

The capability to exert drive to beat resistance. In physics, power is expressed as drive x distance — so the extra drive you possibly can exert, and farther you progress the resistance, the stronger you’re.
Super setting
Alternating units of a minimum of two workouts, again to again, often to save lots of time, or to extend the workload on a given muscle group.
Undulating periodization
A variation of the usual periodization (see above) mannequin during which you range the main target of the exercises throughout the identical coaching block with a purpose to cut back stress, and create a stimulus for broader adaptation.
So, as a substitute of specializing in endurance for 4 weeks, hypertrophy for 4 weeks, and power for 4 weeks, you would possibly carry out two endurance exercises, two hypertrophy exercises, and two power exercises every week for a six- or eight-week interval.
Volume
The complete quantity of labor carried out in a given exercise, week, or coaching block. Sometimes expressed as “weight lifted x sets x reps,” however usually brief handed as “number of working sets.”
METABOLISM/ENERGY/NUTRITION
Amino acids
The constructing blocks of dietary protein, which type the uncooked supplies for muscle- and tissue-building throughout the physique.
Anaerobic vs. cardio
In biology, cardio reactions are those who require oxygen, and anaerobic ones don’t. So, many trainers and exercisers discuss with endurance actions (operating, swimming, biking, and many others.) as cardio, and power and energy actions (power coaching, sprinting) as anaerobic.
In reality, few if any bodily actions are purely one or the opposite; most actions lie on a spectrum someplace between the 2 extremes.
ATP (Adenosine triphosphate)
The major gasoline that powers organic exercise within the physique. Energy in meals (carbohydrate, fats) is transformed by metabolism into this power to carry out work.
Broscience
Scientifically unproven coaching and dietary recommendation, usually delivered by individuals with few if any authentic credentials, in individual or on social media.
EPOC (Excess post-exercise oxygen consumption)
The tendency for the physique to proceed burning power above your baseline metabolic price after the conclusion of a exercise.
EPOC is considerably larger after high-intensity actions like sprints and circuit coaching than lower-intensity ones, however, opposite to some older analysis, not a serious contributor to caloric burn or fats loss.
Hypertrophy
Lactate
An often-misunderstood and mischaracterized gasoline supply for muscle contraction, produced and burned throughout extended high-intensity power or endurance coaching.
RPE (Rate of perceived exertion)
A subjective scale, expressed as a quantity from six to twenty or one to 10, of how arduous an individual is working relative to their maximal capability.
ANATOMY
Biceps
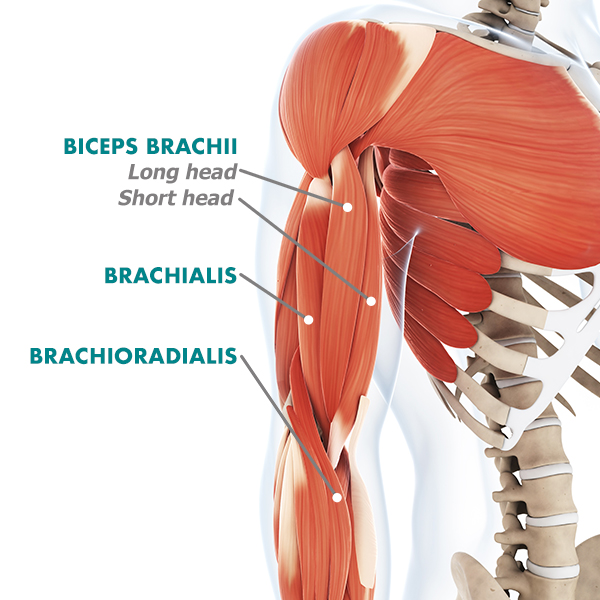
The muscular tissues on the fronts of the higher arm, liable for flexing (bending) the elbow.
Glutes (gluteals)
The “butt muscles” on the backs of the hip joints liable for extending the hips.
Lats (latissimus dorsi)
The thick muscular tissues on the edges of the torso liable for drawing the arms again and down, and serving to to increase the decrease again.
Pecs (pectorals)
The chest muscular tissues, liable for drawing your higher arms in the direction of, and previous, your heart line.
Quads (quadriceps)
The muscular tissues on the fronts of your thighs, liable for extending your knee joint.
Traps (trapezius)
The kite-shaped muscle in your higher again, liable for drawing your shoulder blades upwards, backwards, and downwards.
Triceps
The muscular tissues on the backs of your higher arms, liable for extending (straightening) your elbows.
Abduction
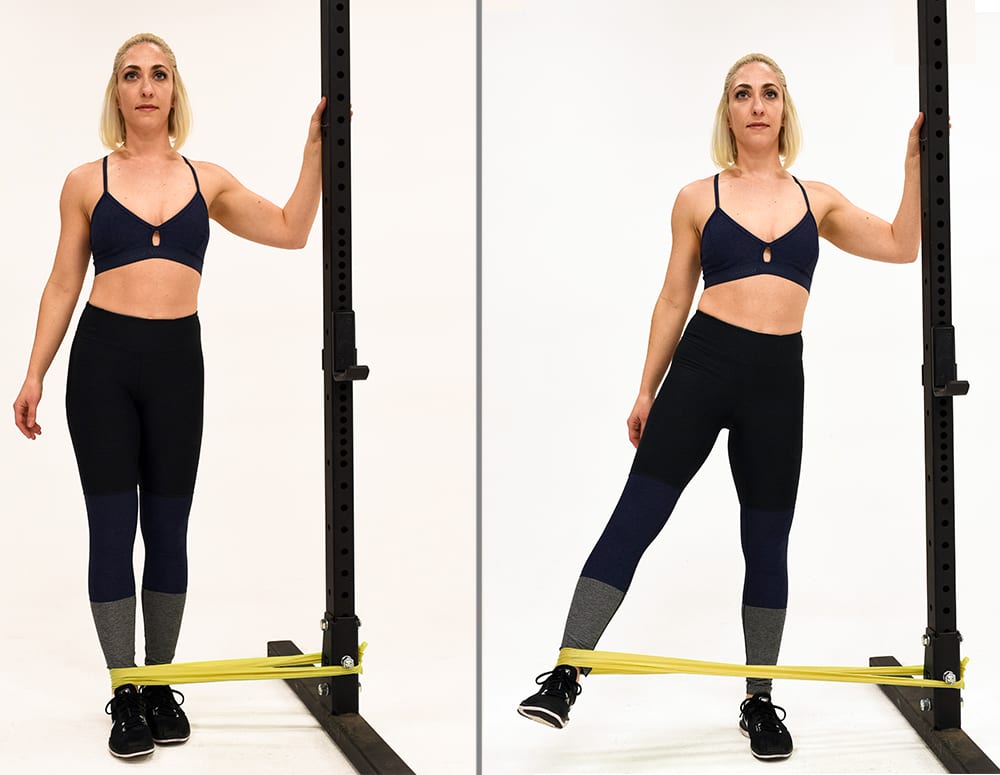

The act of transferring an arm or leg away from the middle line of the physique.
Adduction
The act of transferring an arm or leg towards the middle line of the physique.
Anabolism
All metabolic actions that contain progress, or the assembling of smaller organic elements into bigger ones. Muscle progress, which includes the development of latest muscle tissue from amino acids, is one instance.
Atrophy
Muscle loss or breakdown.
Body composition
A measurement or the proportion of physique fats in an individual relative to their total physique mass.
Muscle fiber sort
A means of categorizing the lengthy, parallel, hair-like fibers that comprise muscle tissue. (See additionally quick twitch and gradual twitch).
Recomposition
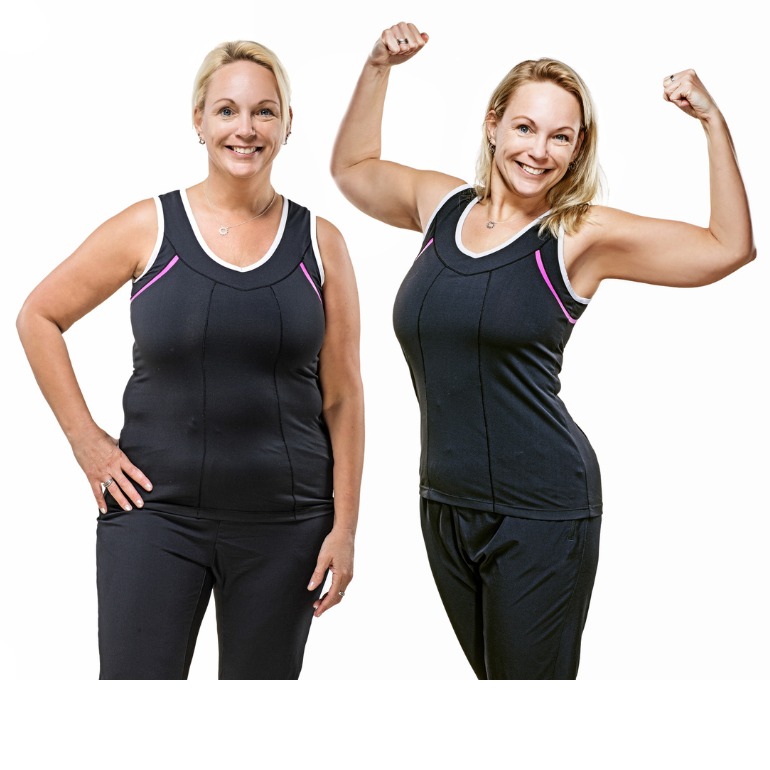

Changing the relative proportion of physique fats and muscle tissue within the physique, with minimal change in complete physique mass.
Catabolism
Metabolic actions that contain breakdown, or the breaking of bigger organic elements into smaller ones. Fat loss, which includes the breaking of fats tissue into triglyceride gasoline, is one instance.
DOMS (Delayed onset muscle soreness)
Soreness in muscular tissues felt many hours — or typically days — following a tough train session.
Fast twitch
A kind of muscle fiber, also called sort II, that’s massive and light-weight in shade, and liable for quick, high-effort, high-exertion actions like all-out sprints and heavy lifts.
These are distinguished from slow-twitch, or sort I, fibers, that are slimmer and darker, and liable for slower, decrease effort actions like jogging and lighter, quicker lifts.
Midline
An imaginary heart line that bisects the physique vertically.
Mind-muscle connection
The psychological consciousness of the motion of your muscular tissues as they lengthen and contract, proven to enhance the effectiveness of a strength-training program.
Muscle imbalance
A distinction within the relative power of muscular tissues on two sides of the physique or two sides of a joint, believed to play a job in posture and susceptibility to harm.
Range of movement

The route and diploma to which a joint or a collection of joints transfer — or are able to transferring — in a selected train or stretch.
Sarcopenia
Loss of muscle mass stemming from illness, getting older, or disuse.
[ad_2]
